
Introductory Statistics (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780321989178
Author: Neil A. Weiss
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 15.1, Problem 12E
In Exercises 15.12–15.21, we repeat the data and provide the sample regression equations for Exercises 14.48–14.57.
- a. Determine the standard error of the estimate.
- b. Construct a residual plot.
- c. Construct a normal
probability plot of the residuals.
15.12
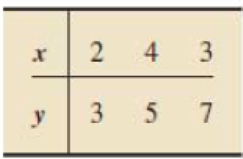
ŷ = 2 + x
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
?How do you find D? Asking about the end behavior of the data?
33)
Which command in R to make a plot of the data and then add the regression line of the two random variables x and y?
Chapter 15 Solutions
Introductory Statistics (10th Edition)
Ch. 15.1 - Suppose that x and y are predictor and response...Ch. 15.1 - Prob. 2ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 3ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 4ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 5ECh. 15.1 - In Exercises 15.315.6, assume that the variables...Ch. 15.1 - The difference between an observed value and a...Ch. 15.1 - Identify two graphs used in a residual analysis to...Ch. 15.1 - Which graph used in a residual analysis provides...Ch. 15.1 - Figure 15.8 shows three residual plots and a...
Ch. 15.1 - Figure 15.9 on the next page shows three residual...Ch. 15.1 - In Exercises 15.1215.21, we repeat the data and...Ch. 15.1 - In Exercises 15.1215.21, we repeat the data and...Ch. 15.1 - Prob. 14ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 15ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 16ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 17ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 18ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 19ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 20ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 21ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 22ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 23ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 24ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 25ECh. 15.1 - In Exercises 15.2215.27, we repeat the information...Ch. 15.1 - Prob. 27ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 28ECh. 15.1 - In Exercises 15.2815.33, a. compute the standard...Ch. 15.1 - Prob. 30ECh. 15.1 - In Exercises 15.2815.33, a. compute the standard...Ch. 15.1 - In Exercises 15.2815.33, a. compute the standard...Ch. 15.1 - In Exercises 15.2815.33, a. compute the standard...Ch. 15.1 - In Exercises 15.3415.43, use the technology of...Ch. 15.1 - In Exercises 15.3415.43, use the technology of...Ch. 15.1 - In Exercises 15.3415.43, use the technology of...Ch. 15.1 - In Exercises 15.3415.43, use the technology of...Ch. 15.1 - Prob. 38ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 39ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 40ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 41ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 42ECh. 15.1 - Prob. 43ECh. 15.2 - Explain why the predictor variable is useless as a...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 45ECh. 15.2 - Prob. 46ECh. 15.2 - In this section, we used the statistic b1 as a...Ch. 15.2 - In Exercises 15.4815.57, we repeat the information...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 49ECh. 15.2 - In Exercises 15.4815.57, we repeat the information...Ch. 15.2 - In Exercises 15.4815.57, we repeat the information...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 52ECh. 15.2 - Prob. 53ECh. 15.2 - Prob. 54ECh. 15.2 - In Exercises 15.4815.57, we repeat the information...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 56ECh. 15.2 - Prob. 57ECh. 15.2 - Prob. 58ECh. 15.2 - In Exercises 15.5815.63, we repeat the information...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 60ECh. 15.2 - In Exercises 15.5815.63, we repeat the information...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 62ECh. 15.2 - In Exercises 15.5815.63, we repeat the information...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 64ECh. 15.2 - In each of Exercises 15.6415.69, apply Procedure...Ch. 15.2 - In each of Exercises 15.6415.69, apply Procedure...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 67ECh. 15.2 - Prob. 68ECh. 15.2 - Prob. 69ECh. 15.2 - Prob. 70ECh. 15.2 - In Exercises 15.7015.80, use the technology of...Ch. 15.2 - In Exercises 15.7015.80, use the technology of...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 73ECh. 15.2 - Prob. 74ECh. 15.2 - Prob. 75ECh. 15.2 - In Exercises 15.7015.80, use the technology of...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 77ECh. 15.2 - Prob. 78ECh. 15.2 - In Exercises 15.7015.80, use the technology of...Ch. 15.2 - Prob. 80ECh. 15.3 - Without doing any calculations, fill in the blank....Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 82ECh. 15.3 - Prob. 83ECh. 15.3 - Prob. 84ECh. 15.3 - In Exercises 15.8215.91, we repeat the data from...Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 86ECh. 15.3 - Prob. 87ECh. 15.3 - In Exercises 15.8215.91, we repeat the data from...Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 89ECh. 15.3 - Prob. 90ECh. 15.3 - Prob. 91ECh. 15.3 - Prob. 92ECh. 15.3 - In Exercises 15.9215.97, presume that the...Ch. 15.3 - In Exercises 15.9215.97, presume that the...Ch. 15.3 - In Exercises 15.9215.9, presume that the...Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 96ECh. 15.3 - In Exercises 15.9215.97, presume that the...Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 98ECh. 15.3 - In Exercises 15.9815.108, use the technology of...Ch. 15.3 - In Exercises 15.9815.108, use the technology of...Ch. 15.3 - In Exercises 15.9815.108, use the technology of...Ch. 15.3 - In Exercises 15.9815.108, use the technology of...Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 103ECh. 15.3 - Prob. 104ECh. 15.3 - Prob. 105ECh. 15.3 - Prob. 106ECh. 15.3 - In Exercises 15.9815.108, use the technology of...Ch. 15.3 - Prob. 108ECh. 15.3 - Margin of Error in Regression. In Exercises 15.109...Ch. 15.3 - Refer to the confidence interval and prediction...Ch. 15.4 - Identify the statistic used to estimate the...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 112ECh. 15.4 - Suppose that, for a sample of pairs of...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 114ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 115ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 116ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 117ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 118ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 119ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 120ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 121ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 122ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 123ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 124ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 125ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 126ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 127ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 128ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 129ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 130ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 131ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 132ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 133ECh. 15.4 - In each of Exercises 15.13415.144, use the...Ch. 15.4 - In each of Exercises 15.13415.144, use the...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 136ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 137ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 138ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 139ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 140ECh. 15.4 - In each of Exercises 15.13415.144, use the...Ch. 15.4 - Prob. 142ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 143ECh. 15.4 - Prob. 144ECh. 15 - Prob. 1RPCh. 15 - Suppose that x and y are two variables of a...Ch. 15 - What two plots did we use in this chapter to...Ch. 15 - Regarding analysis of residuals, decide in each...Ch. 15 - Suppose that you perform a hypothesis test for the...Ch. 15 - Prob. 6RPCh. 15 - Prob. 7RPCh. 15 - Prob. 8RPCh. 15 - Prob. 9RPCh. 15 - Identify the relationship between two variables...Ch. 15 - Graduation Rates. Graduation ratethe percentage of...Ch. 15 - Prob. 12RPCh. 15 - Prob. 13RPCh. 15 - For Problems 1417, presume that the variables...Ch. 15 - For Problems 1417, presume that the variables...Ch. 15 - For Problems 1417, presume that the variables...Ch. 15 - Prob. 17RPCh. 15 - In Problems 1820, use the technology of your...Ch. 15 - In Problems 1820, use the technology of your...Ch. 15 - In Problems 1820, use the technology of your...Ch. 15 - Recall from Chapter 1 (see page 34) that the Focus...Ch. 15 - At the beginning of this chapter, we presented...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a. Draw a scatter diagram for the data. b. Draw a regression line of y on x. c. Determine the equation of the line of best fit.arrow_forwardQ.4. Use a test to discover whether given data are exponentially distributed or not. 0.09 0.29 0.35 0.38 0.52 0.63 1.33 1.41arrow_forwardRegression Practice Sheet The following scores were collected by a researcher: Participants Y 12 14 17 18 21 23 8. 7 3 4 5 3. 1 1. Calculate the appropriate statistics that describes the relationship between X and Y 2. Draw a scatterplot of the data 3. Compute the Linear regression equation 4. What is the expected value of a Y score when X= 12 5. What is the expected error associated with making such a prediction. 6. Calculate and plot the linear regression line for the above data. Activate Windowsarrow_forward
- Assume that the variables under consideration satisfy the assumptions for regression inferences. Fill in the blanks. What statistic is used to estimate a. the y-intercept of the population regression line? b. the slope of the population regression line? c. the common conditional standard deviation, σ, of the response variable?arrow_forwardX Y 5 10 3 6 6 7 4 3 2 4 a. Compute the Pearson correlation. b. Find the regression equation for predicting Y from X. c. Calculate SSresidualarrow_forwardA scientist claims that pneumonia causes weight loss in mice. The table shows the weights (in grams) of six mice before infection and two days after infection. At a= 0.05, is there enough evidence to support the scientist's claim? Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the population is normally distributed. Complete parts (a) through (e) below. Mouse 4. 6. Weight (before) Weight (after) 23.5 20.7 20.5 19.4 21.4 23.2 22.0 19.9 19.7 19.1 20.3 21.9 A. Pneumonia causes weight loss in mice. O B. Pneumonia causes weight gain in mice. OC. Weight loss causes pneumonia in mice. OD. Weight gain causes pneumonia in mice. Let p, be the hypothesized mean of the difference in the weights (before - after). What are H, and H,? O A H Ha sd O B. Ho Hd 70 Ha Pa0 OC. Ho Ha =0 Ha Ha 0 D. O E. H, Pa d OR Ho Ha20 . H, Pg S0 Ha Ha>0 Ha Ha O C. tarrow_forward
- The paired data below consists of heights and weights of 6 randomly selected adults. Find the linear correlation coefficient, the linear regression line, and predict the weight of a randomly selected person who is 1.69 meters tall. X Height (meters) 1.61 1.72 1.78 1.80 1.67 1.88 Y Weight (kg) 54 62 70 84 61 92arrow_forwardWhat is the correct answer? In a regression analysis the standard error is determined to be 4. In this situation the MSE - a. is 2 b. is 16 c. depends on the sample size d. depends on the degrees of freedomarrow_forwardListen 1. An electrical firm manufacturers light bulbs that have a length of life that is approximately Normally distributed, with a mean equal to 800 hours and a standard deviation of 40 hours. Let Y represent a random variable describing the length of life of a light bulb: Y = length of life of a light bulb; E(Y) = 800 hours; SD(Y) = 40 hours; Y~N(800 hours, 40 hours). Suppose a random sample of 16 light bulbs is selected. a. Find the expected value of the sample mean of 16 light bulbs. Express your answer as a whole number (e.g. 45). b. Find the standard deviation of the sample mean of 16 light bulbs. Express your answer as a whole number (e.g. 45). C. Find the probability that a random sample of 16 light bulbs will have an average life of less than 775 hours. Round your answer to three significant digits with a leading zero (e.g. 0.123).arrow_forward
- 1.1.6 Dwyane Wade of the Miami Heat hit 569 of his 1,093 field goal attempts in the 2012/2013 season for a shooting per- centage of 52.1%. Over the lifetime of Dwyane's career, can we say that Dwyane is more likely than not to make a field goal? a. Is the long-run proportion of Dwyane making a field goal a parameter or a statistic? b. Is 52.1% a parameter or a statistic? c. When simulating possible outcomes assuming the chance model, how many times would you flip a coin for one rep- etition of the 2012/2013 season? d. With each repetition, what would you keep track of? e. What would be a typical value from a repetition of 1093 coin flips? Justify your answer.arrow_forwardFind the regression equation using the following set of data with y as the response variable. y 66.8 5.8 54.3 73.3 70.1 18.5 64.1 54.9 70.6 2.8 81.9 -9 89 -50 51.7 58.3 39.9 95.1 46.4 76.7 61.4| 35.3 61.3 18.9 What is the correlation coefficient? use three decimal places. What is the regression line equation. Use each value to three decimal places. What is the predicted value of the response variable, when using a value of 50.4 as the explanatory variable. ? Write answer accurate to one decimal place. =arrow_forwardA scientist claims that pneumonia causes weight loss in mice. The table shows the weights (in grams) of six mice before infection and two days after infection. At a= 0.05, is there enough evidence to support the scientist's claim? Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the population is normally distributed. Complete parts (a) through (e) below. Mouse Weight (before) 19.4 19.8 21.5 20.7 21.6 23.7 Weight (after) 12 3 456e 9.2 19.8 21.4 20.8 21.5 23.6 (a) Identify the claim and state Ho and Ha. What is the claim? O A. Pneumonia causes weight gain in mice. O B. Weight loss causes pneumonia in mice. OC. Weight gain causes pneumonia in mice. OD. Pneumonia causes weight loss in mice. Let Ha be the hypothesized mean of the difference in the weights (before - after). What are Ho and H,? O A. Họ: He sa OB. Họ: He 2a OC. Hg: He =0 Hg: He 0 OD. Hg: Ha 20 OE. Ho: Ha s0 OF. Hg: He *0 Ha: Ha >0 Ha: He =0 d= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Calculate s. S = (Round to three decimal…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...
Algebra
ISBN:9781680331141
Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...
Algebra
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...
Algebra
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Correlation Vs Regression: Difference Between them with definition & Comparison Chart; Author: Key Differences;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ou2QGSJVd0U;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Correlation and Regression: Concepts with Illustrative examples; Author: LEARN & APPLY : Lean and Six Sigma;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xTpHD5WLuoA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY