
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of aldehyde groups and ketone groups present in vanillin has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom.
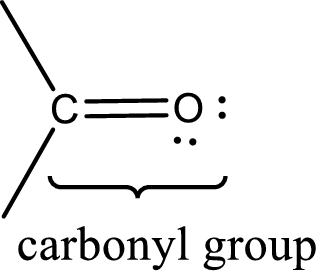
The groups that is attached to the carbonyl carbon atom can be either hydrogen or carbon atom. If the attached atoms are hydrogen and a carbon atom means then the compound is an aldehyde and if they are two carbon atoms means then the compound is a ketone.
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of aldehyde groups and ketone groups present in carvone has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. Aldehydes and ketones possess this carbonyl functional group in it. The structural representation of a carbonyl group can be given as shown below,
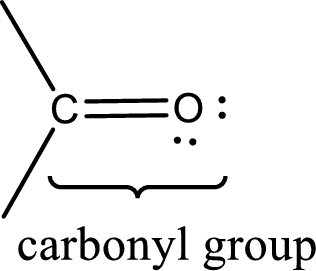
The groups that is attached to the carbonyl carbon atom can be either hydrogen or carbon atom. If the attached atoms are hydrogen and a carbon atom means then the compound is an aldehyde and if they are two carbon atoms means then the compound is a ketone.
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of aldehyde groups and ketone groups present in cortisone has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. Aldehydes and ketones possess this carbonyl functional group in it. The structural representation of a carbonyl group can be given as shown below,
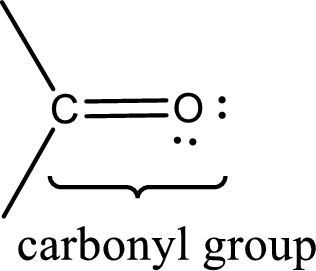
The groups that is attached to the carbonyl carbon atom can be either hydrogen or carbon atom. If the attached atoms are hydrogen and a carbon atom means then the compound is an aldehyde and if they are two carbon atoms means then the compound is a ketone.
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of aldehyde groups and ketone groups present in avobenzone has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
Carbonyl groups are the one which contain a double bond between carbon and oxygen atom. Aldehydes and ketones possess this carbonyl functional group in it. The structural representation of a carbonyl group can be given as shown below,
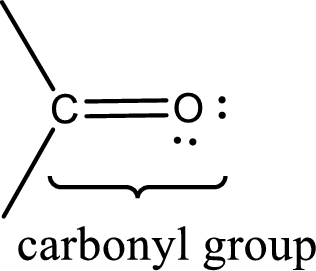
The groups that is attached to the carbonyl carbon atom can be either hydrogen or carbon atom. If the attached atoms are hydrogen and a carbon atom means then the compound is an aldehyde and if they are two carbon atoms means then the compound is a ketone.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 15 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- Q4: Rank the relative nucleophilicity of halide ions in water solution and DMF solution, respectively. F CI Br | Q5: Determine which of the substrates will and will not react with NaSCH3 in an SN2 reaction to have a reasonable yield of product. NH2 Br Br Br OH Brarrow_forwardQ7: Rank the following groups in order of basicity, nucleophilicity, and leaving group ability. a) H₂O, OH, CH3COOT b) NH3, H₂O, H₂Sarrow_forwardQ8: Rank the following compounds in order of increasing reactivity in a nucleophilic substitution reaction with CN as the nucleophile. Br A B NH2 LL F C D OH CI LLI E Q9: Complete the missing entities for following reactions (e.g., major product(s), reactants, and/or solvents) for the SN2 reactions to occur efficiently. Include curved-arrow mechanism for reactions a) to d). a) H "Cl D + -OCH 3 Page 3 of 5arrow_forward
- Q10: (a) Propose a synthesis of C from A. (b) Propose a synthesis of C from B. Br Br ...\SCH 3 A B Carrow_forward9: Complete the missing entities for following reactions (e.g., major product(s), reactants, and/or solvents) for the SN2 reactions to occur efficiently. Include curved-arrow mechanism for reactions a) to d).arrow_forwardComplete the missing entities for following reactions (e.g., major product(s), reactants, and/or solvents) for the SN2 reactions to occur efficiently. Include curved-arrow mechanism for reactions a) to d).arrow_forward
- QUESTION 3: Provide the synthetic steps that convert the starting material into the product (no mechanism required). HO OH NH CH3 multiple steps 요요 H3Carrow_forwardQ6: Predict the effect of the changes given on the rate of the reaction below. CH3OH CH3Cl + NaOCH3 → CH3OCH3 + NaCl a) Change the substrate from CH3CI to CH31: b) Change the nucleophile from NaOCH 3 to NaSCH3: c) Change the substrate from CH3CI to (CH3)2CHCI: d) Change the solvent from CH3OH to DMSO.arrow_forwardQ3: Arrange each group of compounds from fastest SN2 reaction rate to slowest SN2 reaction rate. a) CI Cl فيكم H3C-Cl A B C D Br Br b) A B C Br H3C-Br Darrow_forward
- Q2: Group these solvents into either protic solvents or aprotic solvents. Acetonitrile (CH3CN), H₂O, Acetic acid (CH3COOH), Acetone (CH3COCH3), CH3CH2OH, DMSO (CH3SOCH3), DMF (HCON(CH3)2), CH3OHarrow_forwardSuppose the rate of evaporation in a hot, dry region is 1.76 meters per year, and the seawater there has a salinity of 35 ‰. Assuming a 93% yield, how much salt (NaCl) can be harvested each year from 1 km2 of solar evaporation ponds that use this seawater as a source?arrow_forwardhelparrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning





