
Concept explainers
To analyze:
The steps of the biosynthetic pathway that are associated with each type of mutation from the given data.
Given:
Two mutant strains of Neurospora (Leu-1 and Leu-2), the wild-type and the fused-type were supplied with different nutrient media and their growth was recorded in Table 1. The presence of growth is indicated by the positive sign (+) and the absence of growth is indicated by the negative sign (−).
Table 1: The results of the growth of different strains of Neurospora in different media.
| Types of strains used in the experiment | The growth of different strains of Neurospora in different media | ||||
| Minimal medium | Minimal medium+2-isopropylmalate | Minimal medium+leucine | Minimal medium+3-isopropylmalate | Minimal medium+α-ketoisocaproate | |
| Wild-type (haploid) | + | + | + | + | + |
| Leu-1 (haploid) | − | − | + | − | + |
| Leu-2 (haploid) | − | − | + | + | + |
| Fused cells (diploid): Leu-1, Leu-2 | − | + | + | + | + |
The following reaction shows the steps involved in the synthesis of leucine in Neurospora (Figure 1).
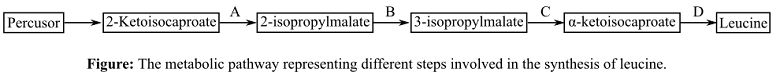
Figure 1:
Introduction:
The leucine is an essential amino acid that is basic in nature because of the presence of an amino group. Some organisms like Neurospora are able to catalyze the synthesis of leucine in their cells. The Neurospora is a haploid
Explanation of Solution
Neurospora is able to synthesize leucine in their cells and hence, are able to grow on a minimal medium (a medium that does not contain additional amino acids). The mutant strains of Neurospora lack the precursors that are required to perform the
From the given table and diagram, it is observed that Leu-1 strain contains a mutation in the protein that is required for the synthesis of α-ketoisocaproate. This is because this strain is unable to grow in the minimal medium supplied with 3-isopropylmalate and 2- isopropylmalate. Here the step C, i.e., the conversion of 3-isopropylmalate into α-ketoisocaproate, does not occur due to mutation, which prevents the further synthesis of leucine.
Leu-2 contains a mutant protein that is unable to synthesize the 3-isopropylmalate. This is because this strain is unable to grow on the minimal media, supplied with 2-isopropylmalate. The mutation in enzyme involved in step B that prevents the synthesis of 3-isopropylmalate from 2-isopropylmalate, thus, the final product leucine.
Thus, it can be concluded from the given data that the Leu-1 strain has a mutant protein that prevents the catalysis of step C and Leu-2 strain has a mutant protein that is unable to catalyze the step B of the given biosynthetic pathway.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 14 Solutions
Life: The Science of Biology
- In your own wordsarrow_forwardDiscuss the following statement: “from the nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone, the complete amino acid sequence of a protein can be deduced by applying the genetic code. thus, protein biochemistry has become superfluous because there is nothing more that can be learned by studying the protein.”arrow_forwardConsider a stretch of DNA (a hypothetical gene) that has the sequence 5’ ATG-CTA-TCA-TGG-TTC-TAA 3’ A) Transcribe and translate this gene using the genetic code table. Be sure to label the mRNA 3’ and 5’ ends. Write the amino acid sequence using 1 letter abbreviations. B) Now, our hypothetical gene has undergone a mutation. The mutant sequence is....3’ TAC-GAT-AGT-ACC-AAT-ATT 5’5’ ATG-CTA-TCA-TGG-TTA-TAA 3’ Transcribe and translate the mutant sequence. Be sure to label the mRNA 3’ and 5’ ends. Write the amino acid sequence using 1 letter abbreviations. C) Indicate the type of mutation (nonsense, missense, silent, or frame shift) present. D) How severe of a consequence will this mutation likely be in terms of protein function (none, mild, moderate or severe)? Why?arrow_forward
- DNA mutations can affect the reading frame for the genetic code. What is a human condition caused by these mutations? Identify how the reading frame is affected.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements are accurate descriptions of the genetic code? MARK ALL THAT APPLY Select one or more: a. The genetic code is made up of triplet nucleotides that specify an amino acid. b. The genetic code is unambiguous because codons only specific a single amino acid. C. The genetic code is read in an overlapping manner. d. The genetic code is redundant because a single codon can specify more than one amino acid. e. Some amino acids are encoded by more than one codon. f. All codons of the genetic code specify amino acids.arrow_forwardConsider the following segment of a template strand of DNA: Part A -ATA AGC TTC GAC- What is the mRNA produced for the segment? -UAU-UCG-AAG-CUC- Part B Complete previous part(s) • Part C What is the mRNA if a mutation changes AGC to AAC? Part D Complete previous part(s) Part E What is the MRNA produced if G is inserted at the beginning of the DNA segment?arrow_forward
- DNA RNA 000000O Proteinarrow_forwardGiven the following DNA sequence of the template strand for a given gene: 5' TTTCCGTCTCAGGGCTGAAAATGTTTGCTCATCGAACGC3' Part A ) Write the mRNA that will be transcribed from the DNA sequence above (be sure to label the 5' and 3' ends). Part B ) Use the genetic code to write the peptide sequence translated in a cell from the mRNA in part A. Please use the 3 letter abbreviation for each amino acid. Part C: How would the peptide synthesized in a cell be different if the mRNA was translated in vitro (i.e. not in the cell)?arrow_forwardHydrogen bonds are important in DNA replication and transcription. They are relatively weak chemical bonds. Why is this a desirable feature for DNA? Describe the effect (s) of changing (mutating) the promoter on the transcription of the DNA strand/gene the promoter controls. What happens to protein synthesis if a nonsense codon is inserted into the gene? Explain why a point mutation does not necessarily change the original amino acid sequence. (Explain silent mutations) Choose any pentapeptide composed of five different amino acids. List the amino acids. Present one messenger RNA codon for each amino acids and the sequence of nucleotides on the DNA that originally coded for your pentapeptide.arrow_forward
- Below is a polinucleotide sequence of the non-template strand of a coding DNA sequence. Use the info of this molecule as well as the attached addendum to demonstrate the flow of genetic information to protein sequence as described by the so-called “Central Dogma” . Clearly indicate the direction of your polynucleotide strands and peptide/protein. Example: (USE SPACES BETWEEN CODONS): ' XXX XXX XXX XXX ' Example: (USE SPACES BETWEEN AMINOACIDS): Polypeptide: direction-XXX-XXX-XXX-direction ATG GCA TGC AAT AGC TCA TGC b) What would happen to the amino acid sequence if the underlined nucleotide (C) would change to an A? (3arrow_forwardBriefly describe the function of the following in protein synthesis. a. rRNA b. tRNA c. mRNAarrow_forwardA segment of template DNA is known to contain the following base sequence: 3' GATACCTTTGTGTAGTCATCTT 5' a) Write the mRNA that would be transcribed from this DNA fragment. b) Highlight the starter and the stopper in your mRNA sequence. Write the sequence of amino acids which would be encoded in translation. asap pleasearrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
