
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name for the given trivial name is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols consist of an alkyl group attached to a hydroxyl group,
In a tertiary alcohol, the
IUPAC name for the given structure is determined by first identifying the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest ring containing the
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name for the given trivial name is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols consist of an alkyl group attached to a hydroxyl group,
In a tertiary alcohol, the
iso is a trivial name for the alkyl group, and its structure is
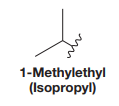
IUPAC name for the given structure is determined by first identifying the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest ring containing the functional group. The chain is then numbered so that to assign the lowest possible locator numbers to the carbon atoms that contain the functional group. The suffix is replaced by ol while writing the name.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name for the given trivial name is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols consist of an alkyl group attached to a hydroxyl group,
In a tertiary alcohol, the
IUPAC name for the given structure is determined by first identifying the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest ring containing the functional group. The chain is then numbered so as to assign the lowest possible locator numbers to the carbon atoms that contain the functional group. The suffix is replaced by ol while writing the name.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name for the given trivial name is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols consist of an alkyl group attached to a hydroxyl group,
In a tertiary alcohol, the
IUPAC name for the given structure is determined by first identifying the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest ring containing the functional group. The chain is then numbered so as to assign the lowest possible locator numbers to the carbon atoms that contain the functional group. The suffix is replaced by ol while writing the name.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter E Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Draw general formulas for an alcohol and phenol, showing the functional group.arrow_forwardWhat is the line structure and the functional groups present (if any)? a) cyclohexane b) cyclohexanol c) cyclohexanonearrow_forwardKindly answer everything that is written on the photo. If you can't please let other people do it.arrow_forward
- Which of the following is the IUPAC name of sec-butyl alcohol? a) 1-butanol b) 2-butanol c) 2-methyl-1-propanol d) 2-methyl-2-propanolarrow_forwardWhat is the condensed structural formula for: A) 2-methyl-2-heptanol B) 3-phenyl-1butanol C) 3-ethyl-2-pentanolarrow_forwardGive the structure and correct IUPAC name of each.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





