
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The orbital energy level diagram and the number of unpaired electrons in
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The oxidation number of cobalt in
The orbital energy level diagram for
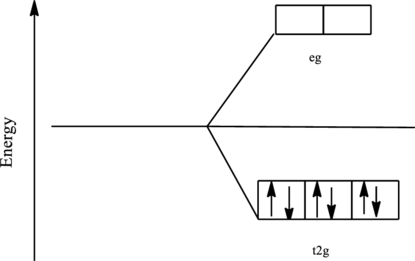
Since, ammonia acts as a strong ligand in
(b)
Interpretation:
The orbital energy level diagram and the number of unpaired electrons in
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The oxidation number of nickel in
The orbital energy level diagram for
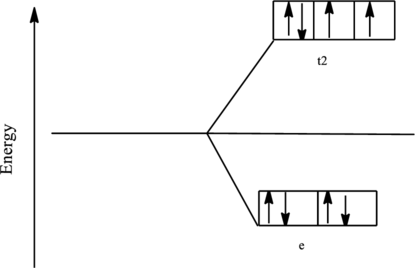
Since, chloride ion is a weak ligand the electrons are filled according to the Hund’s rule in the d-orbitals and the number of unpaired electron in nickel complex is two.
(c)
Interpretation:
The orbital energy level diagram and the number of unpaired electrons in
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The oxidation number of iron in
The orbital energy level diagram for
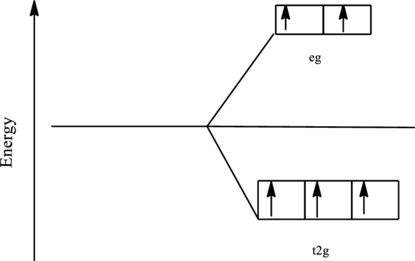
Since, water is a weak ligand the electrons are filled according to the Hund’s rule in the d-orbitals and the number of unpaired electron in iron complex is five.
(d)
Interpretation:
The orbital energy level diagram and the number of unpaired electrons in
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The oxidation number of iron in
The orbital energy level diagram for
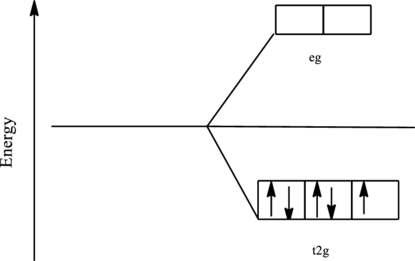
Since, cyanide acts as a strong ligand in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemical Principles: The Quest for Insight
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardQuizzes - Gen Organic & Biological Che... ☆ myd21.lcc.edu + O G screenshot on mac - Google Search savings hulu youtube google disney+ HBO zlib Homework Hel...s | bartleby cell bio book Yuzu Reader: Chemistry G periodic table - Google Search b Home | bartleby 0:33:26 remaining CHEM 120 Chapter 5_Quiz 3 Page 1: 1 > 2 > 3 > 6 ¦ 5 > 4 > 7 ¦ 1 1 10 8 ¦ 9 a ¦ -- Quiz Information silicon-27 A doctor gives a patient 0.01 mC i of beta radiation. How many beta particles would the patient receive in I minute? (1 Ci = 3.7 x 10 10 d/s) Question 5 (1 point) Saved Listen 2.22 x 107 222 x 108 3.7 x 108 2.22 x 108 none of the above Question 6 (1 point) Listen The recommended dosage of 1-131 for a test is 4.2 μCi per kg of body mass. How many millicuries should be given to a 55 kg patient? (1 mCi = 1000 μСi)? 230 mCiarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardQ3: Arrange each group of compounds from fastest SN2 reaction rate to slowest SN2 reaction rate. CI Cl H3C-Cl CI a) A B C D Br Br b) A B C Br H3C-Br Darrow_forwardQ4: Rank the relative nucleophilicity of halide ions in water solution and DMF solution, respectively. F CI Br | Q5: Determine which of the substrates will and will not react with NaSCH3 in an SN2 reaction to have a reasonable yield of product. NH2 Br Br Br .OH Brarrow_forward
- Classify each molecule as optically active or inactive. Determine the configuration at each H соон Chirality center OH 애 He OH H3C Ноос H H COOH A K B.arrow_forwardQ1: Rank the relative nucleophilicity of the following species in ethanol. CH3O¯, CH3OH, CH3COO, CH3COOH, CH3S Q2: Group these solvents into either protic solvents or aprotic solvents. Acetonitrile (CH3CN), H₂O, Acetic acid (CH3COOH), Acetone (CH3COCH3), CH3CH2OH, DMSO (CH3SOCH3), DMF (HCON(CH3)2), CH3OHarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- 10. The main product of the following reaction is [1.1:4',1"-terphenyl]-2'-yl(1h-pyrazol-4- yl)methanone Ph N-H Pharrow_forwardDraw the Fischer projection for a D-aldo-pentose. (aldehyde pentose). How many total stereoisomers are there? Name the sugar you drew. Draw the Fischer projection for a L-keto-hexose. (ketone pentose). How many total stereoisomers are there? Draw the enantiomer.arrow_forwardDraw a structure using wedges and dashes for the following compound: H- Et OH HO- H H- Me OHarrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





