
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781938168000
Author: Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 6CQ
A round pencil lying on its side as in Figure 9.13 is in neutral equilibrium relative to displacements perpendicular to its length. What is its stability displacements parallel to its length?
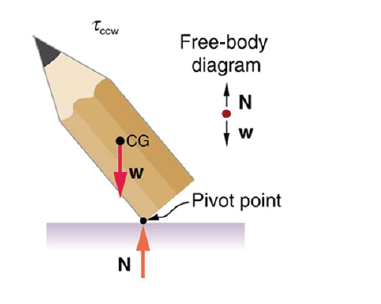
Figure 9.13 If the pencil is displaced too far, the torque caused by its weight changes direction to counterclockwise and causes the displacement to increase.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS
Question 01
A solid circular cylinder and a solid spherical ball of the same mass and radius are rolling
together down the same inclined. Calculate the ratio of their kinetic energy. Assume pure
rolling motion Question 02
A sphere and cylinder of the same mass and radius start from ret at the same point and more
down the same plane inclined at 30° to the horizontal
Which body gets the bottom first and what is its acceleration
b) What angle of inclination of the plane is needed to give the slower body the same
acceleration
Question 03
i)
Define the angular velocity of a rotating body and give its SI unit
A car wheel has its angular velocity changing from 2rads to 30 rads
seconds. If the radius of the wheel is 400mm. calculate
ii)
The angular acceleration
iii)
The tangential linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the wheel
Question 04
in 20
Question B3
Consider the following FLRW spacetime:
t2
ds² = -dt² +
(dx²
+ dy²+ dz²),
t2
where t is a constant.
a)
State whether this universe is spatially open, closed or flat.
[2 marks]
b) Determine the Hubble factor H(t), and represent it in a (roughly drawn) plot as a function
of time t, starting at t = 0.
[3 marks]
c) Taking galaxy A to be located at (x, y, z) = (0,0,0), determine the proper distance to galaxy
B located at (x, y, z) = (L, 0, 0). Determine the recessional velocity of galaxy B with respect
to galaxy A.
d) The Friedmann equations are
2
k
8πG
а
4πG
+
a²
(p+3p).
3
a
3
[5 marks]
Use these equations to determine the energy density p(t) and the pressure p(t) for the
FLRW spacetime specified at the top of the page.
[5 marks]
e) Given the result of question B3.d, state whether the FLRW universe in question is (i)
radiation-dominated, (ii) matter-dominated, (iii) cosmological-constant-dominated, or (iv)
none of the previous. Justify your answer.
f)
[5 marks]
A conformally…
SECTION B
Answer ONLY TWO questions in Section B
[Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-B sub question.]
Question B1
Consider the line element
where w is a constant.
ds²=-dt²+e2wt dx²,
a) Determine the components of the metric and of the inverse metric.
[2 marks]
b) Determine the Christoffel symbols. [See the Appendix of this document.]
[10 marks]
c)
Write down the geodesic equations.
[5 marks]
d) Show that e2wt it is a constant of geodesic motion.
[4 marks]
e)
Solve the geodesic equations for null geodesics.
[4 marks]
Chapter 9 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 9 - What can you say about the velocity of a moving...Ch. 9 - Under what conditions can a rotating body be in...Ch. 9 - What three factors affect the torque created by a...Ch. 9 - A wrecking ball is being used to knock down a...Ch. 9 - Mechanics put a length of Pipe over the handle of...Ch. 9 - A round pencil lying on its side as in Figure 9.13...Ch. 9 - Explain the need for tall towers on a suspension...Ch. 9 - When visiting some countries, you may see a person...Ch. 9 - Scissors are like a double-lever "Stem, Which of...Ch. 9 - Suppose you pull a nail at a constant rate using a...
Ch. 9 - Why are the forces exerted on the outside world by...Ch. 9 - Explain why the forces in our joints are several...Ch. 9 - Why are the forces exerted on the outside world by...Ch. 9 - Explain why the forces in our joints are several...Ch. 9 - Certain of dinosaurs were bipedal (walked on two...Ch. 9 - Swimmers and athletes during competition need to...Ch. 9 - If the maximum force the biceps muscle can exert...Ch. 9 - Suppose the biceps muscle was attached through...Ch. 9 - Explain one of the reasons why pregnant women...Ch. 9 - (a) When opening a door, you push on it...Ch. 9 - When tightening a bolt, you push perpendicularly...Ch. 9 - Two children push on opposite sides of a door...Ch. 9 - Use the second condition for equilibrium (net =0 )...Ch. 9 - Repeat the seesaw problem in Example 9.1 with the...Ch. 9 - Suppose a horse leans against a wall as in Figure...Ch. 9 - Two children of mass 20.0 kg and 30.0 kg sit...Ch. 9 - (a) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the...Ch. 9 - A person carries a plank of wood 2.00 m long with...Ch. 9 - A 17.0-m-high and 11.0-m-long wall under...Ch. 9 - (a) What force must be exerted by the wind to...Ch. 9 - Suppose the weight of the drawbridge in Figure...Ch. 9 - Suppose a 900-kg car is on the bridge in Figure...Ch. 9 - A sandwich board advertising sign is constructed...Ch. 9 - (a) What minimum coefficient of friction is needed...Ch. 9 - A gymnast is attempting to perform splits. From...Ch. 9 - To get up on the roof, a person (mass 70.0 kg)...Ch. 9 - In Figure 9.21, the cg of the pole held by the...Ch. 9 - What is the mechanical advantage of a nail puller...Ch. 9 - Suppose you needed to raise a 250-kg mower a...Ch. 9 - a) What is the mechanical advantage of a...Ch. 9 - A typical car has an axle with 1.10 cm radius...Ch. 9 - What force does the nail puller in Exercise 9.19...Ch. 9 - If you used an ideal pulley of the type shown in...Ch. 9 - Repeat Exercise 9.24 for the pulley shown in...Ch. 9 - Verity that the force in the elbow joint in...Ch. 9 - Two muscles in the back of the leg pull on the...Ch. 9 - The upper leg muscle (quadriceps) exerts a force...Ch. 9 - A device for exercising the upper leg muscle is...Ch. 9 - A person working at a drafting board may hold her...Ch. 9 - We analyzed the biceps muscle example with the...Ch. 9 - Even when the head is held erect, as in Figure...Ch. 9 - A 75-kg man stands on his toes by exerting an...Ch. 9 - A father lifts his child as shown in Figure 9.43....Ch. 9 - Unlike most of the other muscles in our bodies,...Ch. 9 - Integrated Concepts Suppose we replace the 4.0-kg...Ch. 9 - (a) What force should the woman in Figure 9.45...Ch. 9 - You have just planted a sturdy 2-m-tall palm tree...Ch. 9 - Unreasonable Results Suppose two children are...Ch. 9 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider a method for...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
8. Studies of DNA support which of the following?
a. Members of the group called australopiths were the first t...
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Body, Heal Thyself The precision of mitotic cell division is essential for repairing damaged tissues like those...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
CAUTION Why does the presence of extinct forms and transitional features in the fossil record support the patte...
Biological Science (6th Edition)
A geneticist from an alien planet that prohibits genetic research brought with him to Earth two pure-breeding l...
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Glycine has pK2 values of 2.34 and 9.60. At what pH does glycine exist in the forms shown?
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Why is it necessary to be in a pressurized cabin when flying at 30,000 feet?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Page 2 SECTION A Answer ALL questions in Section A [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-A sub question.] Question A1 SPA6308 (2024) Consider Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates th = (t, x, y, z), such that ds² = dt² + dx² + dy² + dz². (a) Consider the vector with components V" = (1,-1,0,0). Determine V and V. V. (b) Consider now the coordinate system x' (u, v, y, z) such that u =t-x, v=t+x. [2 marks] Write down the line element, the metric, the Christoffel symbols and the Riemann curvature tensor in the new coordinates. [See the Appendix of this document.] [5 marks] (c) Determine V", that is, write the object in question A1.a in the coordinate system x'. Verify explicitly that V. V is invariant under the coordinate transformation. Question A2 [5 marks] Suppose that A, is a covector field, and consider the object Fv=AAμ. (a) Show explicitly that F is a tensor, that is, show that it transforms appropriately under a coordinate transformation. [5 marks] (b)…arrow_forwardHow does boiling point of water decreases as the altitude increases?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 14 Z In figure, a closed surface with q=b= 0.4m/ C = 0.6m if the left edge of the closed surface at position X=a, if E is non-uniform and is given by € = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the (3+2x²) net electric flux leaving the closed surface.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardsuggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?arrow_forward
- Checkpoint 4 The figure shows four orientations of an electric di- pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta- tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di- pole, greatest first. (1) (2) E (4)arrow_forwardWhat is integrated science. What is fractional distillation What is simple distillationarrow_forward19:39 · C Chegg 1 69% ✓ The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take F=1700 lb. (Figure 1) Figure 800 lb ||-5- F 600 lb بتا D E C BO 10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft- Solved Part A The compound beam is fixed at E and... Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm Problem A-12 % Chia sẻ kip 800 lb Truy cập ) D Lưu of C 600 lb |-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft D E 5 ft- Trying Cheaa Những kết quả này có hữu ích không? There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!) Chegg Solved The compound b... Có Không ☑ ||| Chegg 10 וחarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What is Torque? | Physics | Extraclass.com; Author: Extraclass Official;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zXxrAJld9mo;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY