
Concept explainers
Glycine has pK2 values of 2.34 and 9.60. At what pH does glycine exist in the forms shown?
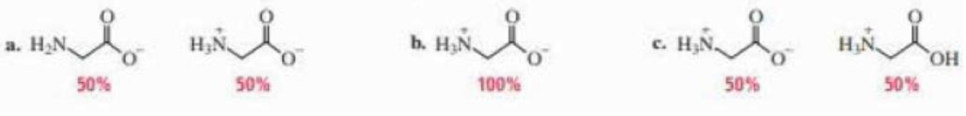
(a)
Interpretation:
The pH at which glycine exists at the given form has to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The isoelectric point
The value of
Protons are released when the
Answer to Problem 49P
The pH of the glycine for the given form is
Explanation of Solution
In the given form of glycine,
The
The
Therefore,
The pH of the glycine for the given form is
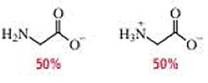
(b)
Interpretation:
The pH at which glycine exists at the given form has to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The isoelectric point
The value of
Protons are released when the
Explanation of Solution
In the given form of glycine,
The amount of positive charge and negative charge are equal or balanced for 100% system.
The isoelectric point (
Therefore,
The pH of the glycine for the given form is
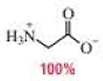
(c)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
The isoelectric point
The value of
Protons are released when the
Answer to Problem 49P
The pH of the glycine for the given form is
Explanation of Solution
In the glycine form of glycine,
The
The
Therefore,
The pH of the glycine for the given form is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
- Problem Set 4a Chem 1411. A latex balloon is filled with a total of carbon dioxide gas so that its volume reaches 1.352 L. The balloon whose weight was originally 0.753 g, now weighs 2.538 g. How many molecules of carbon dioxide have been added to the balloon?arrow_forwardQ18. 30 minutes left please help!!arrow_forwardQ35. Please help wth these drawings! I only have an hour left!!arrow_forward
- Briefly indicate and with examples the differences between metallic cluster and cage compound.arrow_forwardIndicate the correct answer.a) In boranes, the B-B bonds are the most reactive.b) The B-H-B bonds are the reactive centers in the B2H6 molecule.arrow_forwardIn boranes, the B-B bonds are the most reactive.arrow_forward
- The B-H-B bonds are the reactive centers in the B2H6 molecule. Correct?arrow_forwardPlease help me choose! {Apparently B is wrong}arrow_forward13) Which of the following configurations corresponds to the structure below? С соон SH Br 8H H CHBrCH3 a) (2S, 3S) (2S, 3R) c) (2R,3S) d) (2R, 3R)arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div



