
Concept explainers
Write the products of the following sequences of reactions. Refer to your reaction road-map to see how the combined reactions allow you to “navigate” between the different
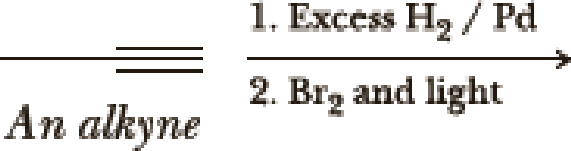
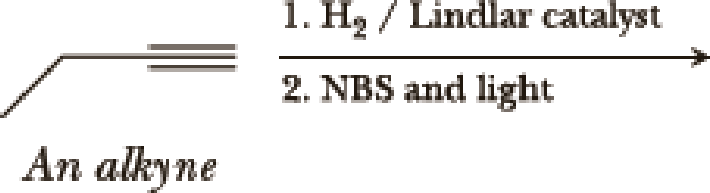
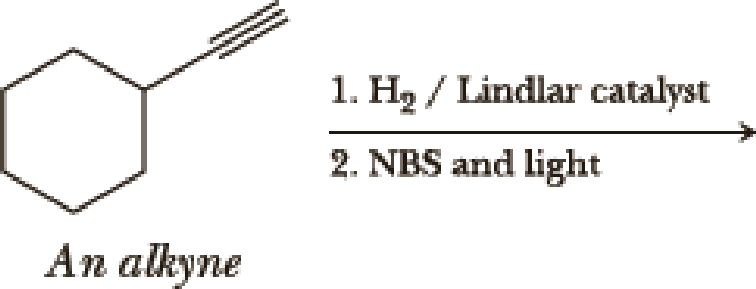
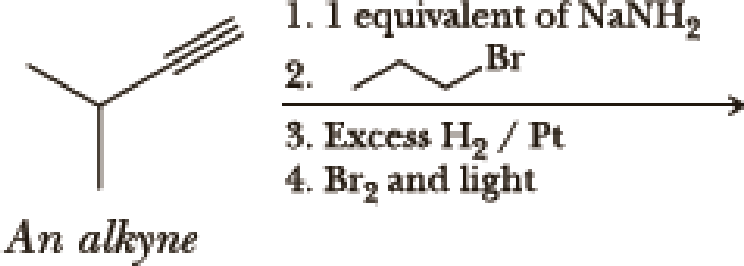
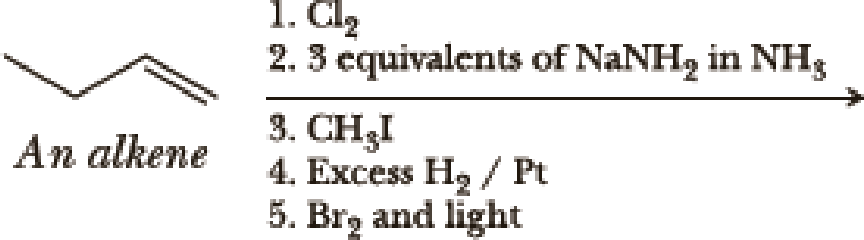
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction has to be determined.
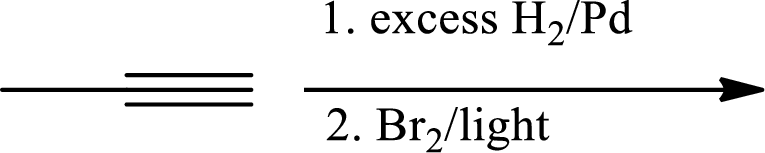
Concept Introduction:
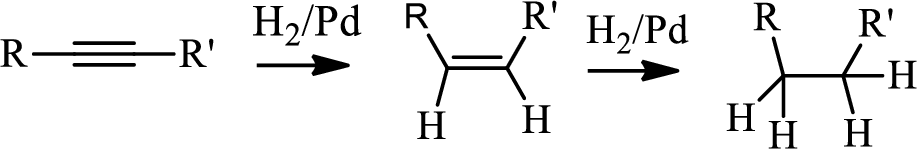
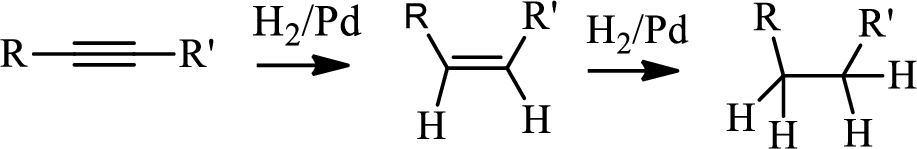
Hydrogenation of alkynes:
Treatment of an alkyne with
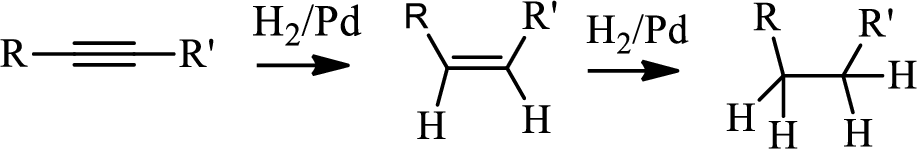
Bromination to alkanes:
Bromination to alkanes is addition of bromine in alkanes. This reaction proceeds via radical formation in the presence of light or high heat by chain mechanism. The reaction proceeds in three steps which are chain initiation, chain propagation and chain termination respectively. In first step of chain initiation bromine radical (

Explanation of Solution
The product is,

The first step is the hydrogenation to alkynes that gives alkane, here propane.
Second step is the bromination to alkane that gives stable
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction has to be determined.
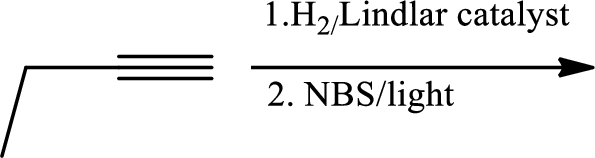
Concept Introduction:
Selective reduction of alkynes:
Hydrogenation of alkynes via the addition of
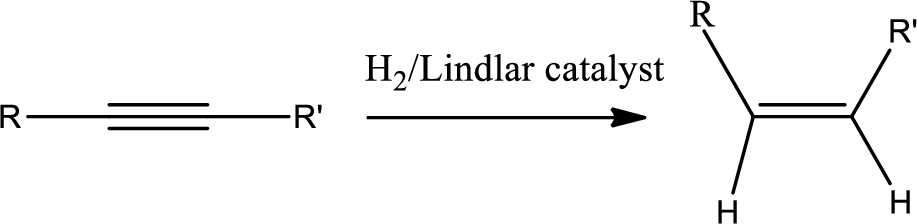
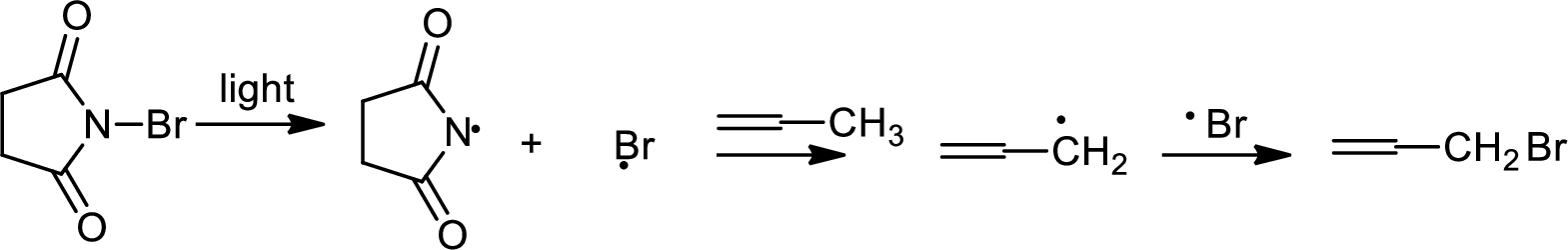
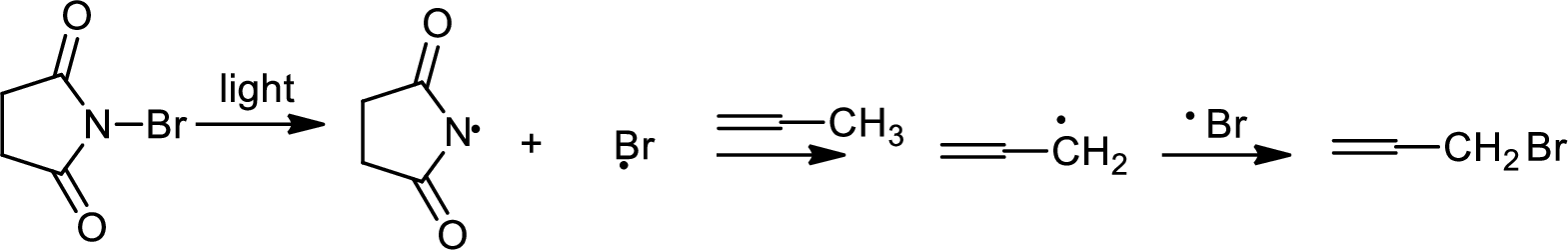
Allylic bromination:
Allylic bromination is the addition of bromine in allylic carbon atom. A very useful way of allylic bromination is done via NBS in dichloromethane at or slightly above room temperature. Reaction between NBS and alkene is most commonly initiated by light. This reaction involves a net double substitution that is bromine in NBS and hydrogen in alkene which exchange their places.
This reaction also proceeds via radical pathway. The reaction proceeds in three steps which are chain initiation, chain propagation and chain termination respectively. In first step of chain initiation bromine radical (
Explanation of Solution
The product is,
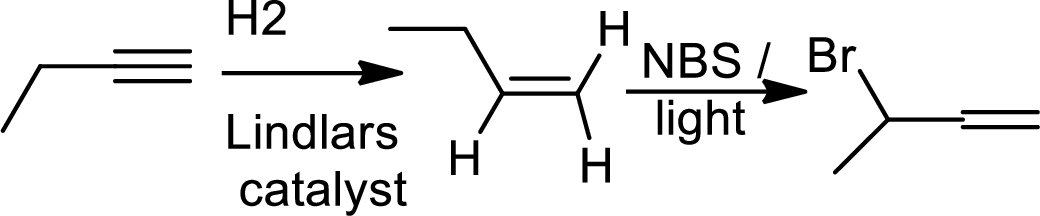
The 1st step is the selective reduction of alkyne that gives alkene.
The 2nd step gives allylic bromination which undergoes via formation of stable allylic radical.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction has to be determined.
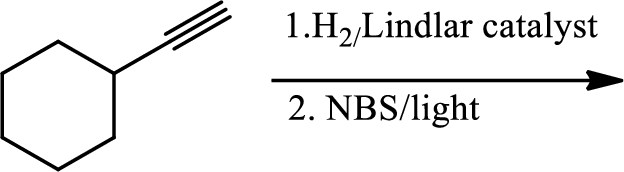
Concept Introduction:
Selective reduction of alkynes:
Hydrogenation of alkynes via the addition of
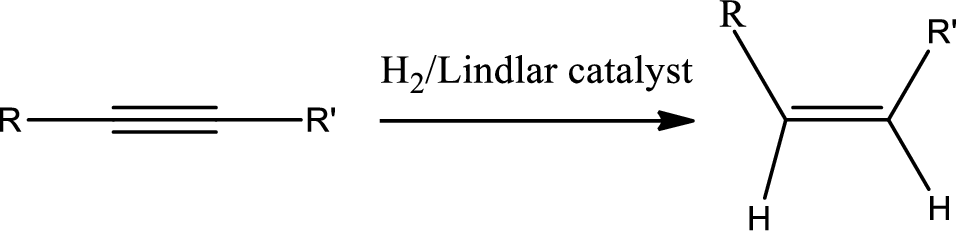
Allylic bromination:
Allylic bromination is the addition of bromine in allylic carbon atom. A very useful way of allylic bromination is done via NBS in dichloromethane at or slightly above room temperature. Reaction between NBS and alkene is most commonly initiated by light. This reaction involves a net double substitution that is bromine in NBS and hydrogen in alkene which exchange their places.
This reaction also proceeds via radical pathway. The reaction proceeds in three steps which are chain initiation, chain propagation and chain termination respectively. In first step of chain initiation bromine radical (
Explanation of Solution
The product is
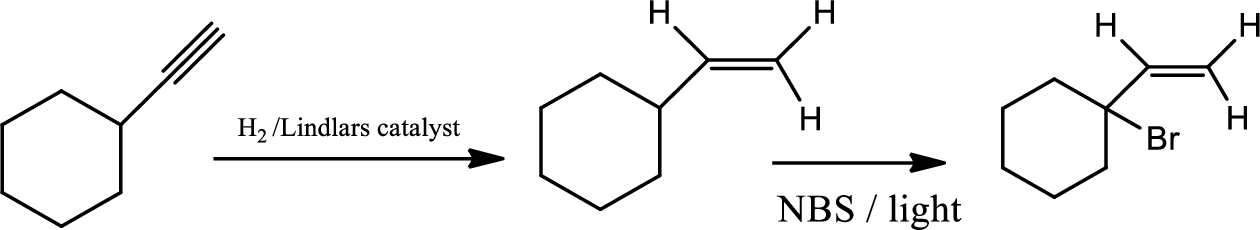
The 1st step is the selective reduction of alkyne that gives alkene.
The 2nd step gives allylic bromination which undergoes via formation of stable allylic radical. Here the allylic radical is much more stable due to presence of ring as much more conjugation will be there to stabilize the radical more.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction has to be determined.
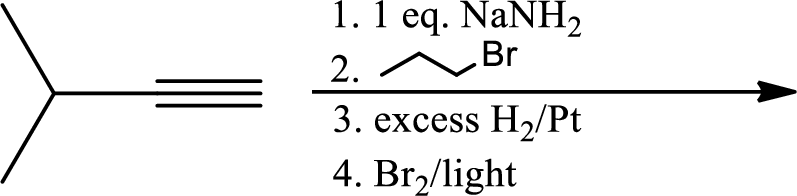
Concept Introduction:
Hydrogenation of alkynes:
Treatment of an alkyne with
Bromination to alkanes:
Bromination to alkanes is addition of bromine in alkanes. This reaction proceeds via radical formation in the presence of light or high heat by chain mechanism. The reaction proceeds in three steps which are chain initiation, chain propagation and chain termination respectively. In first step of chain initiation bromine radical (

Explanation of Solution
The product is,
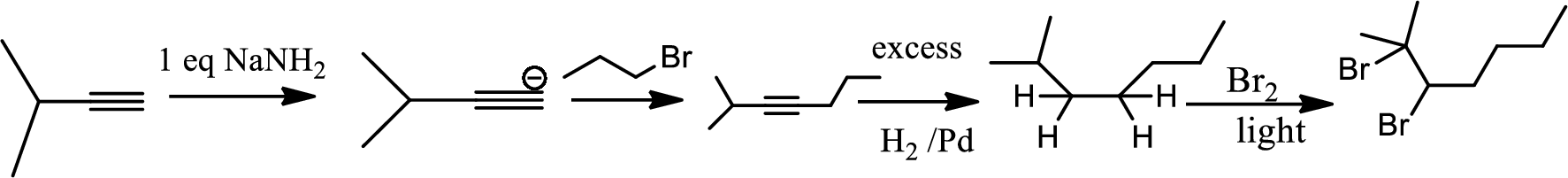
In the 1st step
In 2nd step simple substitution occurs as the bromine of alkene is taken up by the proton removed in 1st step and thus the carbanion formed in 1st step simply can attack the alkyl bromide and substitution product is formed.
The 3rd step is reduction of alkynes giving alkanes.
In 4th step bromination in alkane occurs. Here the attack by bromine radical will be more on left side on the tertiary carbon as then only
So this will be the major product.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product of the given reaction has to be determined.
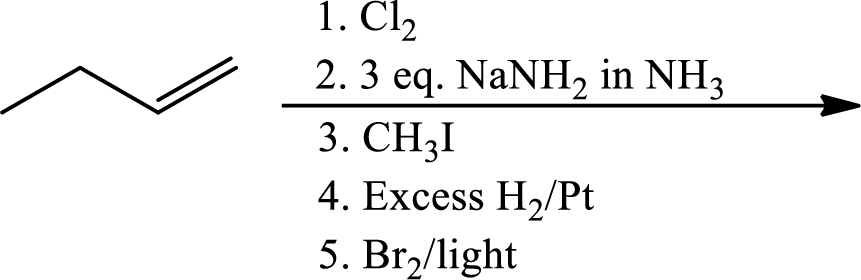
Concept Introduction:
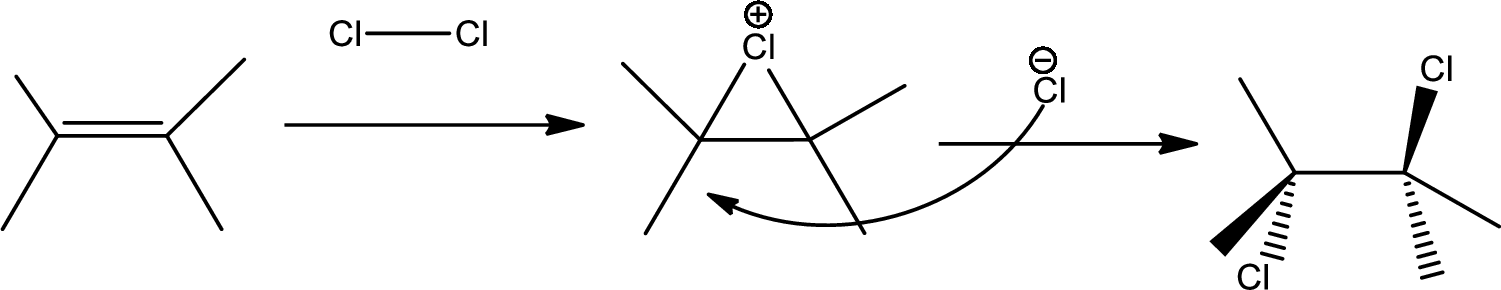
Chlorination to alkenes:
Chlorination of alkene forms dichloro alkane. In this reaction alkene acts as electrophile that attacks
Hydrogenation of alkynes:
Treatment of an alkyne with
Bromination to alkanes:
Bromination to alkanes is addition of bromine in alkanes. This reaction proceeds via radical formation in the presence of light or high heat by chain mechanism. The reaction proceeds in three steps which are chain initiation, chain propagation and chain termination respectively. In first step of chain initiation bromine radical (

Explanation of Solution
The product is,
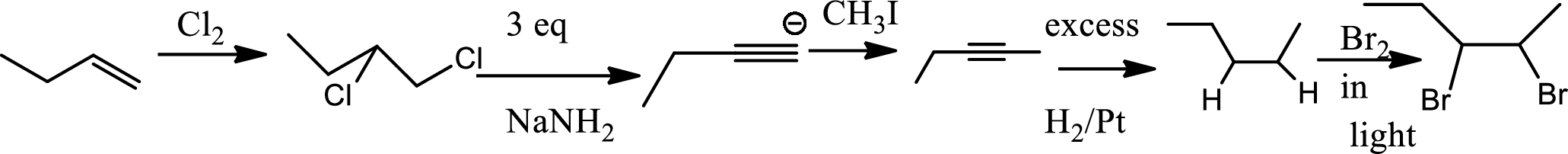
The 1st step is the chlorination to alkene that gives anti product.
In the 2nd step
In 3rd step normal substitution occurs and the carbanion formed in the 2nd step acts as nucleophile and attack alkyl halide.
In the 4th step hydrogenation of alkynes occur to give alkane.
In the last step bromine addition to alkanes occur. As the reaction proceeds via radical formation hence this product is the major product as both the radicals formed in this pathway are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 19.57 Using one of the reactions in this chapter, give the correct starting material (A-L) needed to produce each structure (a-f). Name the type of reaction used. (b) ہ مرد (d) HO (c) དང་ ་་ཡིན་ད་དང་ (f) HO Br B D of oli H J Br K C 人 ↑arrow_forwardInductive effect (+I and -I) in benzene derivatives.arrow_forward7. Helparrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole


