
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
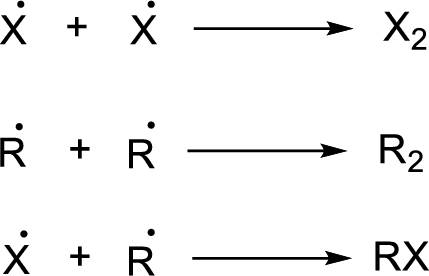
A second chain propagation step in the given reaction has to be proposed.
Concept introduction:
Halogenation of
Radical chain reaction:
Initiation reaction: 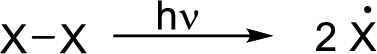
Chain propagation: 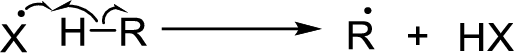
Chain termination:
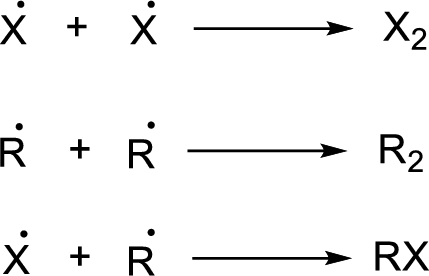
(b)
Interpretation:
Heat of the reaction,
Concept introduction:
Halogenation of alkanes: The replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by halogen. When alkanes is heated or irradiated with the light of specific wavelength, the alkyl halide are formed by radical chain reaction.
Radical chain reaction:
Initiation reaction: 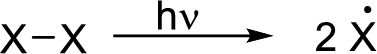
Chain propagation: 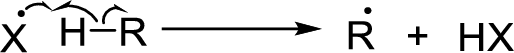
Chain termination:
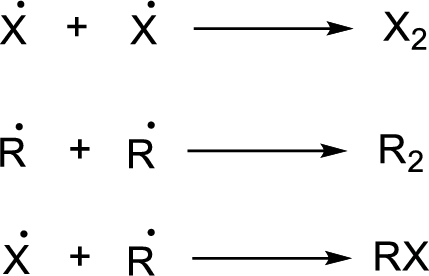
It is a change in enthalpy of a homolysis reaction at absolute zero where a molecule is broken down into two free radicals.
(c)
Interpretation:
The energies and relative rates of the set chain propagation steps in section 8.5B with given reaction has to be compared.
Concept introduction:
Halogenation of alkanes: The replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by halogen. When alkanes is heated or irradiated with the light of specific wavelength, the alkyl halide are formed by radical chain reaction.
Radical chain reaction:
Initiation reaction: 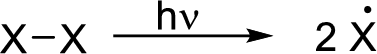
Chain propagation: 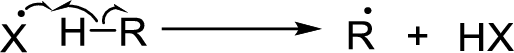
Chain termination:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- 4. Nitrogen gas is commonly sold in 49.0 L steal cylinders at a pressure of 150 atm. (a) How many moles of nitrogen are in the container if the temperature of the cylinder is 21°C. (b) How many moles of nitrogen will there be if the container above is heated to 100°C? (careful here) (c) What is the mass of nitrogen gas in the cylinder in part (a)? (d) What volume would the nitrogen occupy at 21°C, if the pressure was reduced to 1.02 atm? (e) What would be the pressure of the nitrogen gas in the cylinder when the temperature is raised to 39°C?arrow_forward6. A 0.4550 g sample of an unknown organic compound with the empirical formula CH2O was placed into a 150.0 ml vessel and was vaporized into a gas. At 175.0°C, the pressure of the vaporized compound was measured at 941.1 torr. (a) Determine the molar mass of the compound (b) Determine the molecular formula of the compound.arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- 3. A particular reaction calls for 2.40 g of chloride ion. The only source of chloride ion available is a 0.00300 M stock solution of strontium chloride. How much (in L) of this solution is needed for this reaction?arrow_forwardAbsorption Spectrum of NaphthaleneTitle: Understanding the Absorption Spectrum of NaphthaleneGraph: Show a graph with labeled peaks indicating the absorption spectrum of naphthalene in a suitable solventarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Show work..don't give Ai generated and copy the answer anywhere.arrow_forwardthis is an inorganic chemistry question please answer accordindly!! its just one question with parts till (n) JUST ONE QUESTION with its parts spread out in the form of different images attached 2 IMAGES ATTACHED PLEASE SEE BOTH, please answer EACH part till the end and dont just provide wordy explanations wherever asked for structures, graphs or diagrams, please DRAW DRAW them on a paper and post clearly!! answer the full question with all details as needed EACH PART CLEARLY please or let another expert handle it thanks!! im reposting this please solve all parts and drawit not just word explanations!!arrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


