
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134015187
Author: John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 7, Problem 7.21UKC
Two curves are shown in the following energy diagram:
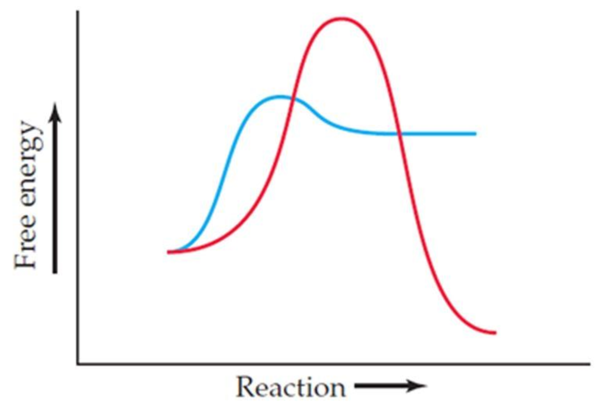
(a) Which curve represents the faster reaction, and which the slower?
(b) Which curve represents the spontaneous reaction, and which the nonspontaneous?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Show work. don't give Ai generated solution....give correct solution
Biochemistry
What is the process of "transamination" in either the muscles or the liver, that involves keto acid or glutamic acid?
Please explain how the steps work. Thank you!
Biochemistry
Please help. Thank you
What is the importance of glutamic acid in the metabolism of nitrogen from amino acids? (we know therole; it’s used to remove the nitrogen from amino acids so that the remaining carbon skeleton can bebroken down by the “usual” pathways, but what is the important, unique role that only glutamicacid/glutamate can do?)
Chapter 7 Solutions
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (8th Edition)
Ch. 7.1 - Classify each of the following as having potential...Ch. 7.2 - Based on bond energies, which atmospheric gas in...Ch. 7.3 - Prob. 7.1CIAPCh. 7.3 - How many Calories (i.e., kilocalories) are in a...Ch. 7.3 - Prob. 7.3PCh. 7.3 - Prob. 7.4PCh. 7.3 - Prob. 7.5PCh. 7.3 - Prob. 7.6PCh. 7.4 - Prob. 7.7PCh. 7.4 - Prob. 7.8KCP
Ch. 7.5 - The reaction between iron and oxygen to form rust...Ch. 7.6 - Prob. 7.10PCh. 7.8 - Prob. 7.11PCh. 7.8 - Prob. 7.12PCh. 7.8 - Prob. 7.13PCh. 7.8 - The following diagrams represent two similar...Ch. 7.9 - Prob. 7.3CIAPCh. 7.9 - Prob. 7.4CIAPCh. 7.9 - Is the yield of SO3 at equilibrium favored by a...Ch. 7.9 - Prob. 7.16PCh. 7.9 - Prob. 7.17PCh. 7 - What are the signs of H, S, and G for the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.19UKCCh. 7 - Prob. 7.20UKCCh. 7 - Two curves are shown in the following energy...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.22UKCCh. 7 - Prob. 7.23APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.24APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.25APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.26APCh. 7 - Acetylene (H C C H) is the fuel used in welding...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.28APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.29APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.30APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.31APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.32APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.33APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.34APCh. 7 - Why are most spontaneous reactions exothermic?Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.36APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.37APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.38APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.39APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.40APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.41APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.42APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.43APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.44APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.45APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.46APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.47APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.48APCh. 7 - What is meant by the term chemical equilibrium?...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.50APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.51APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.52APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.53APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.54APCh. 7 - Use your answer from Problem 7.53 to calculate the...Ch. 7 - Use your answer from Problem 7.54 to calculate the...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.57APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.58APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.59APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.60APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.61APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.62APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.63APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.64APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.65APCh. 7 - Prob. 7.66APCh. 7 - For the unbalanced combustion reaction shown, 1...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.68CPCh. 7 - Prob. 7.69CPCh. 7 - Prob. 7.70CPCh. 7 - Urea is a metabolic waste product that decomposes...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.72CPCh. 7 - Prob. 7.73CPCh. 7 - Methanol, CH3OH, is used as race car fuel. (a)...Ch. 7 - Prob. 7.75CPCh. 7 - Prob. 7.76CPCh. 7 - Prob. 7.77CPCh. 7 - Prob. 7.78GPCh. 7 - Prob. 7.79GPCh. 7 - Prob. 7.80GP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Biochemistry Please help. Thank you When carbamyl phosphate is joined to L-ornathine, where does the energy for the reaction come from?arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question Please help. Thank you What is the function of glutamate dehydrogenase?arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question Please help. Thank you How and why does a high protein diet affect the enzymes of the urea cycle?arrow_forward
- Biochemistry What is the importance of the glucose-alanine cycle?arrow_forwardBiochemistry Assuming 2.5 molecules of ATP per oxidation of NADH/(H+) and 1.5molecules of ATP per oxidation of FADH2, how many ATP are produced per molecule of pyruvate? Please help. Thank youarrow_forward1. How would you explain the term ‘good food’? 2. How would you define Nutrition? 3. Nutrients are generally categorised into two forms. Discuss.arrow_forward
- Biochemistry Question. Please help solve. Thank you! Based upon knowledge of oxidation of bioorganic compounds and howmuch energy is released during their oxidation, rank the following, from most to least, with respect to how much energy would be produced from each during their oxidation. Explain your placement for each one.arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question.For the metabolism of amino acids what is the first step for theirbreakdown? Why is it necessary for this breakdown product to be transported to the liver? For the catabolism of the carbon backbone of these amino acids, there are 7 entry points into the “standard” metabolic pathways. List these 7 entry points and which amino acids are metabolized to these entry points. Please help. Thank you!arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question. Please help. Thank you. You are studying pyruvate utilization in mammals for ATP production under aerobic conditions and have synthesized pyruvate with Carbon #1 labelled with radioactive C14. After only one complete cycle of the TCA cycle, which of the TCA cycle intermediates would be labeled with C14? Explain your answer. Interestingly, you find C14 being excreted in the urine. How does it get there?arrow_forward
- Biochemistry question. Please help with. Thanks in advance For each of the enzymes listed below, explain what the enzyme does including function, names (or structures) of the substrate and products and the pathway(s) (if applicable) it is/are found in. (a) ATP synthetase (b) succinate dehydrogenase (c) isocitrate lyase (d) acetyl CoA carboxylase (e) isocitrate dehydrogenase (f) malate dehydrogenasearrow_forwardDraw and name each alcohol and classify it as primary, secondary, or tertiary. Explain your answer thoroughly.arrow_forwardDraw the product of each reaction. If there are multiple products, draw only the major product. Explain your answer thoroughly.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...
Health & Nutrition
ISBN:9781337711067
Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna Balac
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Enzyme Kinetics; Author: MIT OpenCourseWare;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FXWZr3mscUo;License: Standard Youtube License