
Concept explainers
The voltage waveform in Fig. 6.46 is applied across a 55-μF capacitor. Draw the current waveform through it.
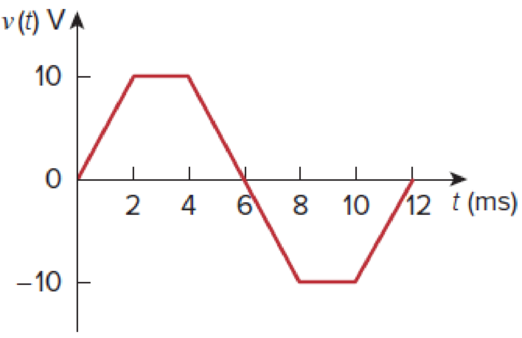
Figure 6.46
For Prob. 6.6.
Find the current waveform.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The value of the capacitor (C) is 55 μF.
Formula used:
Write the expression to calculate the straight line equation for two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2).
(y−y1)=y2−y1x2−x1(x−x1) (1)
Refer to Figure 6.46 in the textbook.
From the given graph, substitute t for x and v(t) for y in equation (1).
(v(t)−y1)=y2−y1x2−x1(t−x1) (2)
Write the expression to calculate the current through the inductor.
i(t)=Cdv(t)dt (3)
Here,
C is the value of the capacitor, and
dv(t)dt is the rate of change of voltage with time.
Calculation:
The given voltage waveform is redrawn as Figure 1.
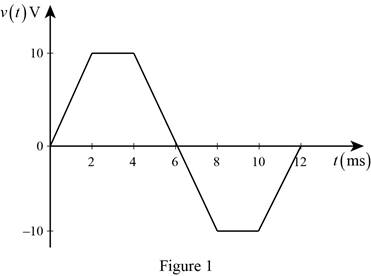
Refer to Figure 1, split up the time period as five divisions such as 0 ms<t<2 ms, 2 ms<t<4 ms, 4 ms<t<8 ms, 8 ms<t<10 ms and 10 ms<t<12 ms to find the respective voltage value.
Case (i): 0 ms<t<2 ms
The two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) are (0 ms,0 V) and (2 ms,10 V).
Substitute 0 ms for x1, 0 V for y1, 2 ms for x2 and 10 V for y2 in equation (2) to find v(t).
(v(t)−0 V)=10 V−0 V2 ms−0 ms(t−0 ms)
Simplify the equation to find v(t).
v(t)=10 V2 ms(t)=102×10−3t V{∵1 m=10−3}=(5000 t) V
Case (ii): 2 ms<t<4 ms
The two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) are (4 ms,10 V) and (2 ms,10 V).
Substitute 4 ms for x1, 10 V for y1, 2 ms for x2 and 10 V for y2 in equation (2) to find v(t).
v(t)−10 V=10 V−10 V2 ms−4 ms(t−4 ms)v(t)−10 V=0 V−2 ms(t−4 ms)v(t)−10 V=0
Simplify the equation to find v(t).
v(t)=10 V
Case (iii): 4 ms<t<8 ms
The two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) are (8 ms,−10 V) and (4 ms,10 V).
Substitute 8 ms for x1, −10 V for y1, 4 ms for x2 and 10 V for y2 in equation (2) to find v(t).
(v(t)−(−10 V))=10 V−(−10 V)4 ms−8 ms(t−8 ms)(v(t)+10 V)=10 V+10 V−4 ms(t−8 ms)(v(t)+10 V)=−20 V4 ms(t−8 ms)
Simplify the equation to find v(t).
v(t)= (−20 V4 ms(t−8 ms)−10 V)=(−(204×10−3)(t−(8×10−3))−10) V{∵1 m=10−3}=(−5000 t+40−10) V=(−5000 t+30) V
Case (iv): 8 ms<t<10 ms
The two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) are (8 ms,−10 V) and (10 ms,−10 V).
Substitute 8 ms for x1, −10 V for y1, 10 ms for x2 and −10 V for y2 in equation (2) to find v(t).
v(t)−(−10 V)=(−10 V)−(−10 V)10 ms−8 ms(t−8 ms)v(t)+10 V=−10 V+10 V2 ms(t−8 ms)v(t)+10 V=0 V2 ms(t−8 ms)v(t)+10 V=0
Simplify the equation to find v(t).
v(t)=−10 V
Case (v): 10 ms<t<12 ms
The two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) are (12 ms,0 V) and (10 ms,−10 V).
Substitute 12 ms for x1, 0 V for y1, 10 ms for x2 and −10 V for y2 in equation (2) to find v(t).
(v(t)−0 V)=−10 V−0 V10 ms−12 ms(t−12 ms)
Simplify the equation to find v(t).
v(t)=−10 V−2 ms(t−12 ms)=(102×10−3(t−(12×10−3))) V{∵1 m=10−3}=(5000 t−60) V
Therefore, the voltage function of the signal in Figure 1 is,
v(t)={(5000 t) V,0 ms<t<2 ms10 V,2 ms<t<4 ms(−5000 t+30) V,4 ms<t<8 ms−10 V,8 ms<t<10 ms(5000 t−60) V,10 ms<t<12 ms
For 0 ms<t<2 ms:
Substitute 55 μF for C and 5000 t V for v(t) in equation (3) to find i(t).
i(t)=(55 μF)ddt(5000 t V)=(55×10−6)(5000)ddt(t) V⋅F{∵1 μ=10−6}=(55×10−6)(5000)(1) V⋅Fs=0.275 A{∵1 A=1V⋅1F1s}
Simplify the equation to find i(t).
i(t)=0.275×103×10−3 A=275 mA{∵1 m=103}
For 2 ms<t<4 ms:
Substitute 55 μF for C and 10 V for v(t) in equation (3) to find i(t).
i(t)=(55 μF)ddt(10 V)=(55×10−6)ddt(10) V⋅F{∵1 μ=10−6}=(55×10−6)(0) V⋅Fs=0 A{∵1 A=1V⋅1F1s}
For 4 ms<t<8 ms:
Substitute 55 μF for C and (−5000 t+30) V for v(t) in equation (3) to find i(t).
i(t)=(55 μF)ddt(−5000 t+30) V=(55×10−6)ddt(−5000 t+30) V⋅F{∵1 μ=10−6}=(55×10−6)(−5000 (1)+0) V⋅Fs=−0.275 A{∵1 A=1V⋅1F1s}
Simplify the equation to find i(t).
i(t)=−0.275×103×10−3 A=−275 mA{∵1 m=103}
For 8 ms<t<10 ms:
Substitute 55 μF for C and −10 V for v(t) in equation (3) to find i(t).
i(t)=(55 μF)ddt(−10 V)=(55×10−6)ddt(−10) V⋅F{∵1 μ=10−6}=(55×10−6)(0) V⋅Fs=0 A{∵1 A=1V⋅1F1s}
For 10 ms<t<12 ms:
Substitute 55 μF for C and (5000 t−60) V for v(t) in equation (3) to find i(t).
i(t)=(55 μF)ddt(5000 t−60) V=(55×10−6)ddt(5000 t−60) V⋅F{∵1 μ=10−6}=(55×10−6)(5000 (1)−0) V⋅Fs=0.275 A{∵1 A=1V⋅1F1s}
Simplify the equation to find i(t).
i(t)=0.275×103×10−3 A=275 mA{∵1 m=103}
Therefore, the current function of the signal in Figure 1 is,
i(t)={275 mA,0 ms<t<2 ms0 A,2 ms<t<4 ms−275 mA,4 ms<t<8 ms0 A,8 ms<t<10 ms275 mA,10 ms<t<12 ms
From the current expression i(t), the current waveform is drawn in Figure 2.
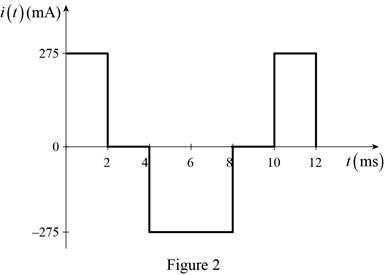
Conclusion:
Thus, the current equation is found and its respective waveform is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Modern Database Management
- Please do question 3 and 4 of this question, the first part is submitted as a separate question due to the limit. Thank you, I will give positive feedback. Please explain each step clearlyarrow_forwardIf the circuit shown in Fig. P12.38(a) is excited by thecurrent waveform is(t) shown in Fig. P12.38(b), determine i(t)for t ≥ 0, given that R1 = 10 W, R2 = 5 W, and C = 0.02 F.arrow_forwardPlease explain each step clearly and include a proper image of what the block diagram and plot must look like. thank youarrow_forward
- A three-phase, 480-V, 60-Hz, 6-pole, Y-connected induction motor has its speed controlled by slip power. The circuit parameters are given: Rs=0.06 ohms, Rr=0.05 ohms, Xs=0.2 ohms, Xr=0.3 ohms and Xm=6 ohms. The turn ratio of the rotor to stator winding is n=0.8. The no-load losses of the motor are equal to 150 W. The rotor and stator cupper losses are equal to 249.21 W. The slip power losses are estimated to 8000W. The load torque is 173.61 N.m. at 700 rpm. The efficiency is equal to: Select one: a. 71.5% b. None of these c. 81.5% d. 91.5%arrow_forwardQuestion 1: A 3 phase, 10 kW, 1700 rpm, Y- connected 460 V, 60 Hz, 4 poles, Y-connected induction motor has the following parameters: Rr = 0.2 ohms, Xs = 0.8 ohms, Xr = 0.8 ohms, Xm = 20 ohms. The no load losses are neglected. The rotor speed is assumed to be constant equal to 1700 rpm. The V/F control method is applied. The stator resistance is negligible. If the base synchronous speed is 188.5 rad/s and the voltage frequency ratio is 1.405, then the maximum torque Tm and the corresponding speed w at 30 Hz are equal to: Select one: a. 350 N.m and 70.69 rad/s b. None of these c. 350 N.m and 164.94 rad/s d. 700 N.m and 164.94 rad/s Question 2: A 3 phase, 10 kW, 1750 rpm, Y- connected 460 V, 60 Hz, 4 poles, Y-connected induction motor has the following parameters: Rs = 0.5 Ohms, Rr = 0.3 Ohms, Xs = 0.9 Ohms, Xr = 0.9 Ohms, Xm = 25 Ohms. The no load losses are neglected. In this type of control the developed torque is proportional to the square of the statoric voltage. In this part, the…arrow_forwardPlease explain each question vlearly and explain how to do it. Thank you, I will give pos feedbackarrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward12.43 For the circuit shown in Fig. P12.43, determine Vout (1) given that R₁ = 1 kQ, R₂ = 4k, and C = 1 μF, and (a) v(t)=2u(1) (V), (b) s(t)=2 cos(10001) (V), (c) vs(t) = 2e u(t) (V). R1 Us(1) + R2 Dout(1) Figure P12.43 Op-amp circuit for Problem 12.43.arrow_forward
- 12.41 The circuit shown in Fig. P12.41 was introduced in Problem 5.68. Then, a time-domain solution was sought for Dout, (1) and Dout₂ (1) for 10, given that v₁(1) = 10u(t) mV, Vcc 10 V for both op amps, and the two capacitors had no change prior to t = 0. Analyze the circuit and plot Dout, (t) and Dout (1) using the Laplace transform technique. 4μF 5 μF Οι 5 ΚΩ Dout 1 MQ Dout2 + Vcc = 10 V Vec = 10 V Figure P12.41 Circuit for Problems 12.41 and 12.42.arrow_forward12.38 If the circuit shown in Fig. P12.38(a) is excited by the current waveform is(t) shown in Fig. P12.38(b), determine i(t) for 1 > 0, given that R₁ = 102, R2 = 5 92, and C = 0.02 F. is(t) R₁ i(t) R₂ is(t) 1.5 A 1.5A | 1 A 0.5 A- M 0.5A- (a) Circuit www. (b) Waveform 0 = 4 rad/s t Figure P12.38 Circuit for Problems 12.38 to 12.40.arrow_forwardEXERCISE 1: Consider the waveguide of Example Calculate the phase constant, phase velocity and wave impedance for TE10 and TM11 modes at the operating frequency of 15 GHz. = 192.4 . For Answer: For TE10, B = 615.6 rad/m, u = 1.531 × 108 m/s, TE 529.4 rad/m, u = 1.78 x 10 m/s, TM = 158.8 Q. TM11, B Example 1: A rectangular waveguide with dimensions a = 2.5 cm, b = 1 cm is to operate below 15.1 GHz. How many TE and TM modes can the waveguide transmit? if the guide is filled with a medium characterized by σ = 0, &=4&o Hr = 1° Calculate the cutoff frequencies of the modes.arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





