
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780078028229
Author: Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 19P
Find the equivalent capacitance between terminals a and b in the circuit of Fig. 6.53. All capacitances are in μF.
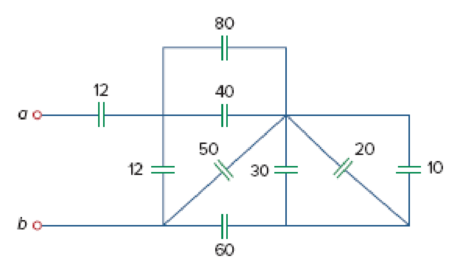
Figure 6.53
For Prob. 6.19.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
O Draw the four possible negative feedback
contigurations of an op-amp. Write the
input and output impedances of these
configurations in ideal cases.
5
E9.6 Determine the average power absorbed by the 4-2 and 3-2 resistors in Fig. E9.6.
302
j20
Figure E9.3
4Ω
ww
Figure E9.6
12/0° V
j30
-j2 N
13/10° A
(+60° V
(OEF
-160
For
the
P-channel
JFET
given in
the following figure,
the
IDSS = 2MA
a)
Determine
IDQ
and
VSDQ
b)
Determine
the
source-follower circuit
transistor parameters are:
Vp = +1,75 V, and λ=0.
Small-signal voltage gain, Av = So
VDD = 10V
R₁ = 90kr
Rs =5k
CC1
WW
R₂ = 110kn
50
C02
BL = 10 kr
GND
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Ch. 6.2 - What is the voltage across a 4.5-F capacitor if...Ch. 6.2 - If a 10-F capacitor is connected to a voltage...Ch. 6.2 - The current through a 100-F capacitor is i(t) = 50...Ch. 6.2 - Figure 6.11 For Practice Prob. 6.4. An initially...Ch. 6.2 - Under dc conditions, find the energy stored in the...Ch. 6.3 - Find the equivalent capacitance seen at the...Ch. 6.3 - Find the voltage across each of the capacitors in...Ch. 6.4 - If the current through a 1-mH inductor is i(t) =...Ch. 6.4 - The terminal voltage of a 2-H inductor is v = 10(1...Ch. 6.4 - Determine vC, iL, and the energy stored in the...
Ch. 6.5 - Calculate the equivalent inductance for the...Ch. 6.5 - In the circuit of Fig. 6.34, i1(t) = 3e2t A. If...Ch. 6.6 - The integrator in Fig. 6.35(b) has R = 100 k, C =...Ch. 6.6 - The differentiator in Fig. 6.37 has R = 100 k and...Ch. 6.6 - Design an analog computer circuit to solve the...Ch. 6 - What charge is on a 5-F capacitor when it is...Ch. 6 - Capacitance is measured in: (a)coulombs (b)joules...Ch. 6 - When the total charge in a capacitor is doubled,...Ch. 6 - Can the voltage waveform in Fig. 6.42 be...Ch. 6 - The total capacitance of two 40-mF...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6.43, if i = cos 4t and v = sin 4t, the...Ch. 6 - A 5-H inductor changes its current by 3 A in 0.2...Ch. 6 - If the current through a 10-mH inductor increases...Ch. 6 - Inductors in parallel can be combined just like...Ch. 6 - Prob. 10RQCh. 6 - If the voltage across a 7.5-F capacitor is 2te3t...Ch. 6 - A 50-F capacitor has energy w(t) = 10 cos2 377t J....Ch. 6 - Design a problem to help other students better...Ch. 6 - A voltage across a capacitor is equal to [2 2...Ch. 6 - The voltage across a 4-F capacitor is shown in...Ch. 6 - The voltage waveform in Fig. 6.46 is applied...Ch. 6 - At t = 0, the voltage across a 25-mF capacitor is...Ch. 6 - A 4-mF capacitor has the terminal voltage v=...Ch. 6 - The current through a 0.5-F capacitor is 6(1 et)...Ch. 6 - The voltage across a 5-mF capacitor is shown in...Ch. 6 - A 4-mF capacitor has the current waveform shown in...Ch. 6 - A voltage of 45e2000t V appears across a parallel...Ch. 6 - Find the voltage across the capacitors in the...Ch. 6 - Series-connected 20- and 60-pF capacitors are...Ch. 6 - Two capacitors (25 and 75 F) are connected to a...Ch. 6 - The equivalent capacitance at terminals a-b in the...Ch. 6 - Determine the equivalent capacitance for each of...Ch. 6 - Find Ceq in the circuit of Fig. 6.52 if all...Ch. 6 - Find the equivalent capacitance between terminals...Ch. 6 - Find the equivalent capacitance at terminals a-b...Ch. 6 - Determine the equivalent capacitance at terminals...Ch. 6 - Obtain the equivalent capacitance of the circuit...Ch. 6 - Using Fig. 6.57, design a problem that will help...Ch. 6 - In the circuit shown in Fig. 6.58 assume that the...Ch. 6 - (a)Show that the voltage-division rule for two...Ch. 6 - Three capacitors, C1 = 5 F, C2 = 10 F, and C3 = 20...Ch. 6 - Given that four 10-F capacitors can be connected...Ch. 6 - Obtain the equivalent capacitance of the network...Ch. 6 - Determine Ceq for each circuit in Fig. 6.61....Ch. 6 - Assuming that the capacitors are initially...Ch. 6 - If v(0) = 0, find v(t), i1(t), and i2(t) in the...Ch. 6 - In the circuit in Fig. 6.64, let is = 4.5e2t mA...Ch. 6 - Obtain the Thevenin equivalent at the terminals,...Ch. 6 - The current through a 25-mH inductor is 10et/2 A....Ch. 6 - An inductor has a linear change in current from...Ch. 6 - Design a problem to help other students better...Ch. 6 - The current through a 12-mH inductor is 4 sin 100t...Ch. 6 - The current through a 40-mH inductor is i(t)= 0,...Ch. 6 - The voltage across a 50-mH inductor is given by...Ch. 6 - The current through a 5-mH inductor is shown in...Ch. 6 - The voltage across a 2-H inductor is 20(1 e2t) V....Ch. 6 - If the voltage waveform in Fig. 6.67 is applied...Ch. 6 - The current in a 150-mH inductor increases from 0...Ch. 6 - A 100-mH inductor is connected in parallel with a...Ch. 6 - If the voltage waveform in Fig. 6.68 is applied to...Ch. 6 - Find vC, iL, and the energy stored in the...Ch. 6 - For the circuit in Fig. 6.70, calculate the value...Ch. 6 - Under steady-state dc conditions, find i and v in...Ch. 6 - Find the equivalent inductance of the circuit in...Ch. 6 - An energy-storage network consists of...Ch. 6 - Determine Leq at terminals a-b of the circuit in...Ch. 6 - Using Fig. 6.74, design a problem to help other...Ch. 6 - Find Leq at the terminals of the circuit in Fig....Ch. 6 - Find the equivalent inductance looking into the...Ch. 6 - Find Leq in each of the circuits in Fig. 6.77....Ch. 6 - Find Leq in the circuit of Fig. 6.78. Figure 6.78...Ch. 6 - Determine Leq that may be used to represent the...Ch. 6 - The current waveform in Fig. 6.80 flows through a...Ch. 6 - (a) For two inductors in series as in Fig....Ch. 6 - In the circuit of Fig. 6.82, io(0) = 2 A....Ch. 6 - Consider the circuit in Fig. 6.83. Find: (a) Leq,...Ch. 6 - Consider the circuit in Fig. 6.84. Given that v(t)...Ch. 6 - In the circuit of Fig. 6.85, sketch vo. Figure...Ch. 6 - The switch in Fig. 6.86 has been in position A for...Ch. 6 - The inductors in Fig. 6.87 are initially charged...Ch. 6 - The current i(t) through a 20-mH inductor is...Ch. 6 - An op amp integrator has R = 50 k and C = 0.04 F....Ch. 6 - A 6-V dc voltage is applied to an integrator with...Ch. 6 - An op amp integrator with R = 4 M and C = 1 F has...Ch. 6 - Using a single op amp, a capacitor, and resistors...Ch. 6 - Show how you would use a single op amp to generate...Ch. 6 - At t = 1.5 ms, calculate vo due to the cascaded...Ch. 6 - Show that the circuit in Fig. 6.90 is a...Ch. 6 - The triangular waveform in Fig. 6.91(a) is applied...Ch. 6 - An op amp differentiator has R = 250 k and C = 10...Ch. 6 - A voltage waveform has the following...Ch. 6 - The output vo of the op amp circuit in Fig....Ch. 6 - Prob. 78PCh. 6 - Figure 6.93 presents an analog computer designed...Ch. 6 - Design an analog computer to simulate the...Ch. 6 - Design an op amp circuit such that vo=10vs+2vsdt...Ch. 6 - Your laboratory has available a large number of...Ch. 6 - An 8-mH inductor is used in a fusion power...Ch. 6 - A square-wave generator produces the voltage...Ch. 6 - An electric motor can be modeled as a series...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Need a solarrow_forwardI need a drawing on how to connect the function generator, oscilliscope, and both multimeters. It is hard for me to follow text instructions. The function generator has a postive,common and negative. The oscilliscope has chanell A and B, both channels have a postive and a negative. I know you can provide text instruction but a little sketch would be very helpful thank you.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- Q1/ A three phase, 500 kVA, 6600 V, 50 Hz, 6 pole, star connected synchronous motor has synchronous impedance of J 70 ohm per phase at its normal rating, the motor is excited to give unity power factor at the input terminals. Find a) The rated current and power factor. b) The emf behind the synchronous impedance. c) The developed torque. d) The pull out torque. e) The increase in excitation which will just permit an increase of 30% of rated torque before pulling out of synchronism. (45 M.)arrow_forwardcan you fin Vds and Vgs of all transistors and specify te operating region off all transistors and prove it. 58V 5.8 V 1.8V M2 0.9V 22222 と A 4852 m 3 01 A Voy = 0.2 V V4)=0.SV λ=0.1 V-1arrow_forwardNeed a aolarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Capacitors Explained - The basics how capacitors work working principle; Author: The Engineering Mindset;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X4EUwTwZ110;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY