
Concept explainers
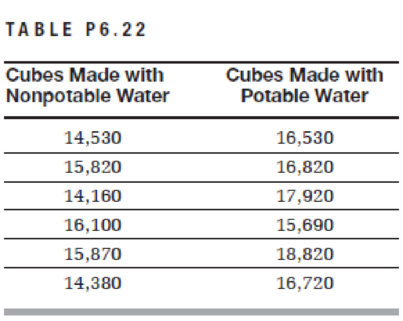
In order to evaluate the suitability of nonpotable water available at the job site for mixing concrete, six standard mortar cubes were made using that water and six others using potable water. The cubes were tested for compressive strength after 7 days of curing and produced the loads to failure (in pounds) shown in Table P6.22.
a. Based on these results only, would you accept that water for mixing concrete according to ASTM C94?
b. According to ASTM C94, are there other tests to be performed to evaluate the suitability of that water? Discuss briefly.
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 6 Solutions
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers (4th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
BASIC BIOMECHANICS
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
- Please solve the example, explaining the solution steps and writing by handarrow_forwardNote: (please show handwritten answers, and no AI usage !) Provide a clear, step-by-step handwritten solution (without any detailed explanations). Ensure the work is simplified and completed manually, adhering to expert-level accuracy. Refer to the provided image for clarity and ensure all calculations are double-checked for correctness before submission. Thank you!. Question 1: A cylindrical soil sample is connected to two water reservoirs: a) Determine the pressure, elevation, and total head at a point one meter above the bottom of the sample (point A). b) Calculate the pore pressure and effective stress at point A if the soil has a saturated unit weight of 18.7kN/m^3. c) Determine the water flow rate though the sample if the soil has a coefficient of permeability of 0.19 cm/s and the radius of the sample is 20 mm. d) Is it possible for the soil to reach the “quick condition”(zero effective stress) by raising the level of the water in the upper reservoir? Why or why not?. Question…arrow_forwardNote: Please provide a clear, step-by-step simplified handwritten working out (no explanations!), ensuring it is done without any AI involvement. I require an expert-level answer, and I will assess and rate based on the quality and accuracy of your work and refer to the provided image for more clarity. Make sure to double-check everything for correctness before submitting thanks!. Questions 1: A clay rich soil is totally saturated, has a bulk density of 2.12 g/cm3, and a void ratio of 0.33. a) Draw the full three phase diagram for this soil including all the volume and mass quantities. b) Determine the density of the soil solids. c) Determine the total density of the soil if the saturation was reduced to 50%. Question 2: A soil sample was tested yielding the following grain-size distribution chart: (refer to the image provided) The soil fines (inorganic) were also tested and had a liquid limit of 76 and a plastic limit of 49 Determine the coefficients of uniformity and curvature.…arrow_forward
- Note: Provide a clear, step-by-step handwritten solution (without any detailed explanations). Ensure the work is simplified and completed manually, adhering to expert-level accuracy. Refer to the provided image for clarity and ensure all calculations are double-checked for correctness before submission. Thank you!. Question 1: A cylindrical soil sample is connected to two water reservoirs: a) Determine the pressure, elevation, and total head at a point one meter above the bottom of the sample (point A). b) Calculate the pore pressure and effective stress at point A if the soil has a saturated unit weight of 18.7kN/m^3. c) Determine the water flow rate though the sample if the soil has a coefficient of permeability of 0.19 cm/s and the radius of the sample is 20 mm. d) Is it possible for the soil to reach the “quick condition”(zero effective stress) by raising the level of the water in the upper reservoir? Why or why not?. Question 2: A new structure is planned to be constructed in…arrow_forwardNote: Provide a clear, step-by-step, simplified handwritten solution (no explanations), ensuring it is completed without any AI involvement. The solution must demonstrate expert-level accuracy and will be evaluated for its quality and precision. Please refer to the provided image for additional clarity. Double-check all calculations for correctness before submission. Thank you!. Question 1: (refer to the image for visual understanding) For the soil element shown on the right: a) Draw the Mohr’s circle for this case b) Find the major and minor principal stresses c) Find the normal and shear stresses on plane AB. Question 2: (refer to the image) A soil sample in a triaxial test with a cell pressure of 100 kPa fails when the vertical stress reaches 400 kPa. The resulting failureplane is observed to dip 60 degrees from horizontal (see figure). Assume that the soil is drained during the test, i.e. there is no pore pressure. a) Determine the friction angle of the soil. Hint: draw the…arrow_forwardPlease solve all pointsarrow_forward
- 1: find out the optimal solution: 1- Reliability Function 2- Serial Configuration 3- M.T.T.F 4- Probability distribution function (P.D.F) 5- Failure rate function :calculate the reliability of the system for the following Figure 0.90 0.80 0.95 0.80 0.80 0.94) 0.80 : A system containing four connected compounds in series, each one has a distribution and its parameters as shown in the table below Component Scale parameter Shape parameter 1 100 1.20 2 150 0.87 3 510 - 1.80 4 720 1.00arrow_forwardTime: 1. Hrs During the last ten days: In one of the productive operations, the electronic control calculator equipped with No. of defects for a specific volume of samples as shown: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Day No. 6673 6976 7505 6991 7028 6960 7916 7010 6591 7350 Total No. 53 55 60 58 16 22 49 48 64 17 Defect No. DRAW THAT & CHOOSE THE BEST A-P chart. B-C chart 1. Key functions of quality control include: A) Control of design, materials received and products and conduct studies of operations B-Design and develop reasonable specifications C) The use of equipment that gives the required accuracy D) Provide appropriate screening equipment 2. The basic principles of critical pathways are: A-fragmentation of the system to the objectives of the secondary clear and specific B-Drawing the network diagram C-Finding the critical path D- All of the above 3- The production system is the following: A-An integral part of the plant's completion B-An effective system to integrate the efforts of various…arrow_forwardPlease solve all pointsarrow_forward
- Please solve all pointsarrow_forwardPlease solve the question by hand with a detailed explanation of the steps.arrow_forward) We started a new production process and its study gave the total deviations The standard value (for 25 samples of the product, sample size 4) is .105 .Calculate the capacity of this process The product specification limits are: 6.30 = LSL 6.50 = USL Standard deviation in a manufacturing system is 0.038 = We made improvements to the system and the deviation has become Standard 0.030 = σ What is required is to calculate the estimated coefficient before and after the operation Optimization. What is your conclusion? : A find out the optimal solution: 1-Average Outgoing Quality AOQ 2- operating Characteristics Curve 100% Inspection 3-Acceptable Quality level 4- Average outgoing Quality AOQ 5- Capability Index CPKarrow_forward
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage,
Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage, Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning





