
(a)
Interpretation: The electron sublevel starts to fill after the completion of 3s sublevel should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The rules for the allowed quantum numbers combinations are as follows:
- All the three quantum numbers ( n, l and m ) describes the orbital of an atom and they are integers.
- The principal quantum number, n value cannot be zero. Thus, the values allowed for the principal quantum number are 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.
- The value of angular quantum number, l can be between 0 to n-1. Thus, if value of n is equal to 3 the value of l can be 0, 1 or 2.
- The value of magnetic quantum number, m can be between − l to +l . Thus, if value of l is equal to 2, m can be wither -2, -1, 0, +1, or +2
For same number of principal quantum number, an orbital form a shell. The first character denotes the shell and the second identifies the sub-shell.
Here, for s orbital value of
The relative energy of orbitals is represented as follows:
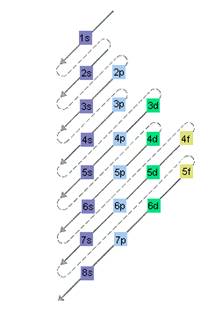
(b)
Interpretation: The electron sublevel starts to fill after the completion of 4p sublevel should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The rules for the allowed quantum numbers combinations are as follows:
- All the three quantum numbers ( n, l and m ) describes the orbital of an atom and they are integers.
- The principal quantum number, n value cannot be zero. Thus, the values allowed for the principal quantum number are 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.
- The value of angular quantum number, l can be between 0 to n-1. Thus, if value of n is equal to 3 the value of l can be 0, 1 or 2.
- The value of magnetic quantum number, m can be between − l to +l . Thus, if value of l is equal to 2, m can be wither -2, -1, 0, +1, or +2
lFor same number of principal quantum number, an orbital form a shell. The first character denotes the shell and the second identifies the sub-shell.
Here, for s orbital value of
The relative energy of orbitals is represented as follows:
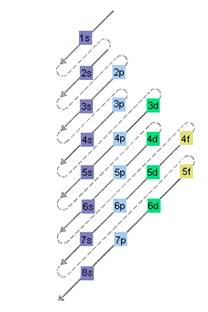
(c)
Interpretation: The electron sublevel starts to fill after the completion of 3d sublevel should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The rules for the allowed quantum numbers combinations are as follows:
- All the three quantum numbers ( n, l and m ) describes the orbital of an atom and they are integers.
- The principal quantum number, n value cannot be zero. Thus, the values allowed for the principal quantum number are 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.
- The value of angular quantum number, l can be between 0 to n-1. Thus, if value of n is equal to 3 the value of l can be 0, 1 or 2.
- The value of magnetic quantum number, m can be between − l to +l . Thus, if value of l is equal to 2, m can be wither -2, -1, 0, +1, or +2
lFor same number of principal quantum number, an orbital form a shell. The first character denotes the shell and the second identifies the sub-shell.
Here, for s orbital value of
The relative energy of orbitals is represented as follows:
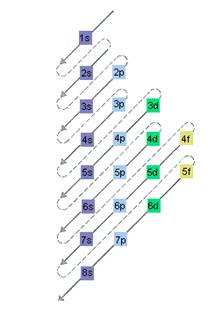
(d)
Interpretation: The electron sublevel starts to fill after the completion of 3p sublevel should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The rules for the allowed quantum numbers combinations are as follows:
- All the three quantum numbers ( n, l and m ) describes the orbital of an atom and they are integers.
- The principal quantum number, n value cannot be zero. Thus, the values allowed for the principal quantum number are 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.
- The value of angular quantum number, l can be between 0 to n-1. Thus, if value of n is equal to 3 the value of l can be 0, 1 or 2.
- The value of magnetic quantum number, m can be between − l to +l . Thus, if value of l is equal to 2, m can be wither -2, -1, 0, +1, or +2
For same number of principal quantum number, an orbital form a shell. The first character denotes the shell and the second identifies the sub-shell.
Here, for s orbital value of
The relative energy of orbitals is represented as follows:
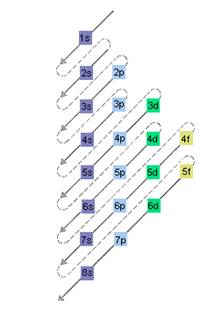
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Basic Chemistry
- 29. Calculate the maximum number of electrons in the energy levels with the following principal quantum numbers, n: (3.4) K (a) 1 (c) 3 (b) 2 (d) 4arrow_forwardnone of the above; there is no such particle QUESTION 5 Orbital shells of an atom: O contain electrons and are found in the nucleus O contain protons and are found in the nucleus O contain electrons and surround the nucleus O contain protons and surround the nucleus QUESTION 6 Suppose an oxygen atom has 8 protons and 9 neutrons. How many electrons does it have? 9. 17 Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save AL Answers to save all answers. archarrow_forward4.52 Identify the elements that have the following electron arrangements: Energy Level 4 a. 2 b. 8 6. C. 4 d. 8. 1. e. 8. 5.arrow_forward
- The effective nuclear charge of a nucleus is determined from a shielding factor. The shielding factor depends on the number of shielding electrons in the atoms' electronic structure. How many "shielding electrons" are present in the ground state of the element In (No. 49) Number of "shielding electrons": Answerarrow_forward1.1 What is the difference between the core electrons and valence electrons ? Why do we emphasize the valence electrons in an atom when discussing atomic properties? 1.2 Ranking the following in order of increasing atomic radius O, S and F? 1.3 Explain why sizes atoms change when proceeding across a period of the periodic table.arrow_forward6 of 11 I Review Constants Periodic Table Part C out ars. ying lue Consider the following equivalent expressions: 3 13 3 and 12 a 8 What are the values of a and b? Enter the value of a followed by the value of b, separated by a comma. - get the ons) ple, Submit Previous Answers Request Answer ") is X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remaining Part D Complete previous part(s)arrow_forward
- 1.1 The characteristic wavelengths of light absorbed by and emitted from an atom is known as the atom's:arrow_forward4.74 Which statements completed with a-d will be true and which will be false? An atom of Pb compared to an atom of C has a larger (greater) b. ionization energy d. metallic character a. number of neutrons c. atomic sizearrow_forward3.14 How many orbitals are found in the second shell? Write designations for the orbitals.arrow_forward
- Which of the subsequent sets gives the correct numbers of subatomic particles in an atom of an element with atomic number (Z) 48 and mass number (A) 120? a. 48 protons, 48 electrons, 72 neutrons b. 48 protons, 48 electrons, 120 neutrons c. 72 protons, 48 electrons, 48 neutrons d. 72 protons, 48 electrons, 72 neutrons What theory states that only a maximum of two electrons can occupy an orbital? a. Pauli's exclusion principle b. Principal quantum number c. Heisenberg's uncertainty principle d. Hund's rule If a particular isotope of Manganese has a number of neutrons (n) of 28, what is its mass number? a. 53 b. 52 c. 51 d. 50 If n=10, what are the possible values of ℓ? a. 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 b. 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 c. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 d. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9arrow_forwardThe maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in a sublevel for which I = 3 is: Select one: a. 14 b. 6 С. 8 d. 10 e. 2arrow_forwardComplete the followingequations: 32p with an atomic number of 15 splits into _______ and an electron and varrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning

