
Concept explainers
Contrast Activity-Based Costing and Conventional Product Costing L04−
2, L04−3. L04−4
Puet World, Inc., Manufactures two models of television sets, the N 800 XL model and the N 500 model.
Data regarding the two products follow:
Additional information about the company follows:
a. Model N 800 XL requires $75 in direct materials per unit, and Model N 500 requires $25.
b. The direct labor wage rate is $18 per hour.
c. The company has always used direct labor-hours as the base for applying
d. Model N 800 XL is more complex to manufacture than Model N 500 and requires the use of special equipment. Consequently, the company is considering the use of activity-basedcosting to assign manufacturing overhead cost to products. Three activity cost pools havebeen identified as follows: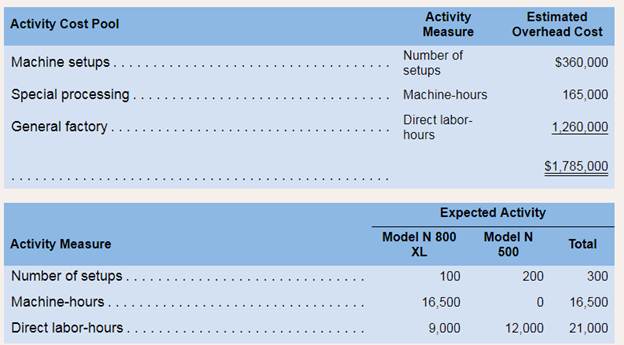
Required:
1. Assume that the company continues to use direct labor-hours as the base for applying overhead cost to products.
a. Compute the predetermined overhead rate.
b. Compute the unit product cost of each model.
2. Assume that the company decides to use activity-based costing to assign manufacturing overhead costto products.
a. Compute the activity rate for each activity cost pool and determine the amount of overhead costthat would be assigned to each model using the activity-based costing system.
b. Compute the unit product cost of each model.
3. Explain why manufacturing overhead cost shifts from Model N 500 to Model N 800 XL underactivity-based costing.
1
Predetermined overhead rate
It is a rate that a company determines to allocate its total manufacturing overhead cost to products manufactured. This rate uses estimated amount of cost and hours for its calculation.
Unit product cost
Unit product cost represents the total costincurred by a company to produce one unit. It can be calculated by the division of total cost and total number of units manufactured or by adding per unit direct material cost, per unit direct labor cost and per unit overhead cost.
To calculate: Predetermined overhead rate and unit product cost by using the predetermined overhead rate.
Answer to Problem 17P
Predetermined overhead rate is $85 per DLH.
Unit product cost for model N 800 XL is $384 and for model N 500 is $128.
Explanation of Solution
Part a
Predetermined overhead rate is calculated as:
Here, total manufacturing cost is given as $1,785,000 and total direct labor hours are 21,000. So, the predetermined rate will be calculated as:
Therefore, predetermined overhead rate is $85 per direct labor hour.
Part b
Unit product cost will be calculated by adding per unit cost of direct material, labor and overheads.
So, unit product cost will be calculated as follows:
| Particulars | Model N 800 XL (in $) | Model N 500 (in $) |
| Direct material (per unit) | 75 | 25 |
| Direct labor (per unit) | 54 (18*3) | 18 (18*1) |
| Manufacturing overheads (per unit) | 255 (85*3) | 85 (85*1) |
| Unit product cost | 384 | 128 |
Therefore, unit product cost for Model N 800 XL is $384 and unit product cost for Model N 500 is $128.
2
Activity rates
Activity rates are used in the ABC system, these rates help in allocating manufacturing cost to products and are calculated by dividing estimated manufacturing cost of each cost poolby total estimated activity.
Manufacturing overhead
It includes all the costs that are indirectly related to a product and does not include costs related to direct materials and direct labors.
To compute: Activity cost rates for the pools, manufacturing cost that will be assigned to each model and unit product cost for each model.
Answer to Problem 17P
Activity rates are:
| Machine setups | $1200 per setup |
| Special processing | $10 per MH |
| General factory | $60 per DLH |
Overhead cost that will be allocated to model N 800 XL is $825,000 and cost that will be assigned to model N 500 is $960,000.
Unit product of model N 800 XL is $404 and of model N 500 is 123.
Explanation of Solution
Part a
Activity rates will be calculated as follows:
| Cost pools | Activity measure | Estimated overhead cost (in $) (A) | Estimated activity (B) | Activity rates (A/B) (in $) |
| Machine setups | Number of setups | 360,000 | 300 | 1200 per setup |
| Special processing | Machine hours | 165,000 | 16,500 | 10 per MH |
| General factory | Direct labor hours | 1,260,000 | 21,000 | 60 per DLH |
So, activity rate for machine setups is $1200 per setup, for special processing is $10 per machine hour and for general factory is $60 per DLH.
In the ABC system, allocation of manufacturing overhead costs to all the products is done according to the ratio in which products use different activities. That ratio will be calculated as:
| Particulars | Model N 800 XL | Model N 500 | RatioN 800 XL: N 500 |
| Machine setups (setups) | 100 | 200 | 1:2 |
| Special processing (MHs) | 16:500 | 0 | 16,500:0 |
| General factory (DLHs) | 9,000 | 12,000 | 9:12 or 3:4 |
Now, allocation of overhead cost will be done as follows:
| Activity cost pool | Overhead expense(in $) | Ratio | Model N 800 XL (in $) | Model N 500 (in $) |
| Machine setups | 360,000 | 1:2 | 120,000 | 240,000 |
| Special processing | 165,000 | 16,500:0 | 165,000 | 0 |
| General factory | 1,260,000 | 3:4 | 540,000 | 720,000 |
| Total overhead cost | 825,000 | 960,000 | ||
So, total overhead cost that will be allocated to model N 800 XL is $825,000 and overhead cost that will be allocated to model N 500 is $960,000.
Part b
Unit product cost will be calculated by adding per unit cost of direct material, labor and overheads. Here, per unit cost of direct material and labor is given. Per unit cost of manufacturing overheads will be calculated as follows:
| Particulars | Model N 800 XL | Model N 500 |
| Total manufacturing overhead cost | 825,000 | 960,000 |
| Total units | 3,000 | 12,000 |
| Manufacturing cost per unit | $275 | $80 |
Now, Unit product cost will be calculated as follows:
| Particulars | Model N 800 XL (in $) | Model N 500 (in $) |
| Direct material (per unit) | 75 | 25 |
| Direct labor (per unit) | 54 (18*3) | 18 (18*1) |
| Manufacturing overheads | 275 | 80 |
| Unit product cost | 404 | 123 |
Unit product cost for model N 800 XL is $404 and model N 500 is $123.
4
Activity based costing
ABC system is used in cost accounting, this system identifies certain activities, build a relationship among product, activities and cost and assign manufacturing cost to all the products accordingly. Manufacturing cost are first assigned to activities and then to products.
To explain: Under ABC system, why manufacturing costs shift from model N 500 to model N 800 Xl.
Explanation of Solution
ABC system identifies certain activities, assign costs first to activities and then to products. In this system, manufacturing costs are assigned to products in the ratio in which each product consumes the activity. Machine setups are used by models N 800 Xl and Model N 500 in the ratio 1:2, therefore, total overhead cost is allocated in this ratio only. General factory activity is used in the ratio 3:4, therefore, total overhead cost is allocated in 3:4 ratio only and it is given that special processing activity is not used by model N 500 (used by model N 800 XL only), therefore, this cost is only allocated to model N 800 Xl and no amount is transferred to model N 500.
Manufacturing overhead cost is allocated based on consumption ratio and then per unit manufacturing overhead cost is calculated by dividing the total cost by the total number of units.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Introduction To Managerial Accounting
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning

