
Interpretation:
The meaning of electroosmotic flow and the reason for itsoccurrence needs to be explained.
Concept introduction:
When electric field is applied in a liquid, the ions present in the liquid moves under the influence of potential gradient. This flow of liquid is termed as electroosmotic flow. It is most obvious is those having small channels. It occurs in buffered solutions and natural water.
Answer to Problem 30.1QAP
Electroosmotic flow of liquid is caused by gradient in potential across the capillary tube on the flowing liquid that has dissolved ions. This is caused when the capillary walls get electrically charged.
Explanation of Solution
When a capillary tube is filled with fluid having dissolved ions, and electrical field is applied, the buffer ions move to respond to the electrical charges. As the solvent which is water is neutral, it remains stationary and the fluid ions move towards its electrodes with respect to the charges applied. Below is depiction of movement of electrons:
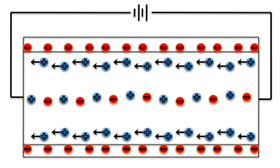
There is coulombic force induced by charges of ions in the solution wherein its net mobile charge causes electroosmotic flow. During this process of maintaining
Electroosmotic flow of liquid is caused due to a potential gradient across the capillary tube on the flowing liquid containing dissolved ions. This is caused when the capillary walls get electrically charged due to the application of electric field from outside.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Please helparrow_forward(a) 21.8 Name the following compounds. & (b) Br (e) O₂N. (h) H (c) Br (d) NH2 ☑N Br H ہیں Ph (g) OMe бл .0-0.e 21.9 Draw a structural formula for each compound. (a) 2,3-Dinitrotoluene (c) Diphenylmethanol (e) p-Nitroaniline (b) 3-Propylanisole (d) m-Propylphenol (f) Pentabromobenzenearrow_forwardIs this the major product of this reaction?arrow_forward
- Help me solve this problem.arrow_forwardDraw a mechanism for the following synthetic transformation including reagents and any isolable intermediates throughout the process. Please clearly indicate bond cleavage/formation using curly arrows. MeO2Carrow_forwardCHEM 310 Quiz 8 Organic Chemistry II Due: Tuesday, April 25th, at 11:59 pm. This quiz is open textbook / open notes - but you must work alone. You cannot use the internet or the solutions manual for the book. Scan in your work and record an explanation of your mechanism. You may record this any way that you like. One way would be to start an individual Zoom meeting, start recording, "share your screen" and then talk through the problem. This will be converted to an .mp4 file that you can upload into Canvas using the "record/upload media" feature. Pyridine, benzoic acid and benzene are dissolved in ethyl acetate. Design and provide a plan / flow chart for separating and isolating each of these components. Pyridine and benzene are liquids at room temperature. Benzoic acid is a solid. You have ethyl acetate, 2M NaOH, 2M HCI and anhydrous MgSO4 available, as well as all the glassware and equipment that you used in the organic lab this year. Provide accurate acid/base reactions for any…arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

