
Interpretation:
The principle of micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography and its difference from capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) needs to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Micellar electro kinetic capillary chromatography or MEKC is modified capillary electrophoresis wherein the samples are separated by partitioning the micelles and buffer solution. In this surfactant is added to buffer to get micelles. Micelle consists of conglomeration of 40 and above surfactant molecules in which the hydrocarbon tail which is positive points inward while the negative charged head point outwards.
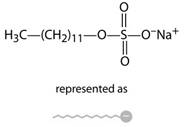
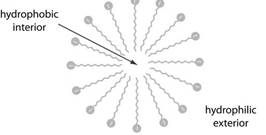
The capillary zone electrophoresis involves buffer solution and sample loaded is placedin additional buffer solution. The capillary tube containing the sample is anode and solute migrates towards cathode at velocity.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
- Part A Give the IUPAC name and a common name for the following ether: CH3-CH2-O-CH2-CH2-CH3 Spell out the full names of the compound in the indicated order separated by a comma. Submit My Answers Give Up Part B Give the IUPAC name and a common name for the following ether: Spell out the full names of the compound in the indicated order separated by a comma. Submit My Answers Give Uparrow_forwardFrenkel and Schottky are intrinsic or extrinsic defects, point or linear defects.arrow_forwardSelect the correct option:a) Frenkel and Schottky defects are linear crystal defects.b) Schottky defects involve atomic motions in a crystal lattice.c) Frenkel defects are vacancies in a crystal lattice.d) None of the above is correct.arrow_forward
 Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


