
Concept explainers
Effects of Dietary Fats on Lipoprotein Levels
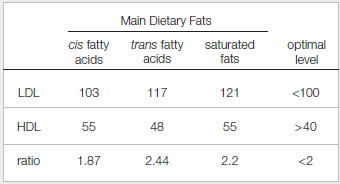
Cholesterol that is made by the liver or that enters the body from food cannot dissolve in blood, so it is carried through the bloodstream in clumps called lipoprotein particles. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles carry cholesterol to body tissues such as artery walls, where they can form deposits associated with cardiovascular disease. Thus, LDL is often called “bad” cholesterol. High-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles carry cholesterol away from tissues to the liver for disposal, so HDL is often called “good” cholesterol. In 1990, Ronald Mensink and Martijn Katan published a study that tested the effects of different dietary fats on blood lipoprotein levels. Their results are shown in FIGURE 3.2.
FIGURE 3.2 Effect of diet on lipoprotein levels. Researchers placed 59 men and women on a diet in which 10 percent of their daily energy intake consisted of cis fatty acids, trans fatty acids, or saturated fats.
The amounts of LDL and HDL in the blood were measured after three weeks on the diet; averaged results are shown in mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter of blood). All subjects were tested on each of the diets. The ratio of LDL to HDL is also shown.
In which group was the level of LDL (“bad” cholesterol) highest?
To explain: The group that had the highest level of LDL (“bad” cholesterol).
Concept introduction: Lipoproteins are carriers of hydrophobic molecules in the extracellular matrix and the blood. The lipoproteins are made of phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins. The proteins are made of amino acids. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports fat, essentially cholesterol molecules in aqueous medium. LDL can get oxidized with arterial walls and forms plaque. Saturated fatty acids have fatty acid chains lacking double bonds between their carbon atoms.
Explanation of Solution
In the experiment, the amount of LDL was checked in three groups of main dietary fats: cis fatty acids, trans fatty acids, and saturated fats. Their optimal levels were also checked. The optimal level of LDL is lesser than 100. The amount of LDL in cis fatty acids is 103, trans fatty acids is 117, and saturated fats is 121.
The saturated fats had the highest level of LDL also known as bad cholesterol among the three groups.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
HUMAN ANATOMY
Physical Science
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- Selection of Traits What adaptations do scavengers have for locating and feeding on prey? What adaptations do predators have for capturing and consuming prey?arrow_forwardCompetition Between Species What natural processes limit populations from growing too large? What are some resources organisms can compete over in their natural habitat?arrow_forwardSpecies Interactions Explain how predators, prey and scavengers interact. Explain whether predators and scavengers are necessary or beneficial for an ecosystem.arrow_forward
- magine that you are conducting research on fruit type and seed dispersal. You submitted a paper to a peer-reviewed journal that addresses the factors that impact fruit type and seed dispersal mechanisms in plants of Central America. The editor of the journal communicates that your paper may be published if you make ‘minor revisions’ to the document. Describe two characteristics that you would expect in seeds that are dispersed by the wind. Contrast this with what you would expect for seeds that are gathered, buried or eaten by animals, and explain why they are different. (Editor’s note: Providing this information in your discussion will help readers to consider the significance of the research).arrow_forwardWhat is the difference between Uniporters, Symporters and Antiporters? Which of these are examples of active transport?arrow_forwardWhat are coupled transporters?arrow_forward
- How do histamine and prostaglandins help in the mobilization of leukocytes to an injury site? What are chemotactic factors? How do they affect inflammation process?arrow_forwardCompare and contrast neutrophils and macrophages. Describe two ways they are different and two ways they are similar.arrow_forwardDescribe the effects of three cytokines (not involved in the initial inflammation response). What cells release them?arrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
