
Introduction to Heat Transfer
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780470501962
Author: Frank P. Incropera, David P. DeWitt, Theodore L. Bergman, Adrienne S. Lavine
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 2.11P
Consider steady-state conditions for one-dimensional conduction in a plane wall having a thermal conductivity
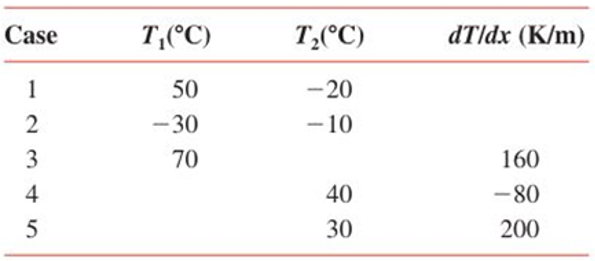
Determine the heat flux and the unknown quantity for each case and sketch the temperature distribution, indicating the direction of the heat flux.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
(A) Consider a plane wall of thickness L and thermal conductivity k. The two sides of the
wall are maintained at constant temperatures of T1 and T2 respectively. Show that the
temperature distribution through the wall is represented as
Т, - Т,
T =
- x +
x+T|
L
Assume one dimensional steady state heat conduction
Problems
within the wall is T(x) = a(L- ) +b where
a = 10°C/m2 and b 30°C, what is the thermal con-
ductivity of the wall? What is the value of the convec-
tion heat transfer coefficient, h?
2.11 Consider steady-state conditions for one-dimensional
conduction in a plane wall having a thermal conductiv-
ity k 50 W/m K and a thickness L = 0.25 m, with no
internal heat generation.
2.
T2
T1
L
Determine the heat flux and the unknown quantity for
each case and sketch the temperature distribution, indi-
cating the direction of the heat flux.
2
Case
TC)
dTldx (K/m)
T2(°C)
1
50
-20
2
-30
- 10
3
70
160
4
40
-80
5
30
200
Q1: Consider one-dimensional conduction in a plane composite wall (Im x Im) as shown in
the figure below. The outer surfaces are exposed to a fluid at 25°C and a convection heat transfer
coefficient of 1000 W/m K. The middle wall B experiences uniform heat generation dg, while
there is no generation in walls A and C. The temperatures at the interfaces are T=261°C and T;
-211°C. Assuming negligible contact resistance at the interfaces:
A) Determine the outside surface temperature of walls A and C?
B) Compute the value of dg?
(20 M)
A
B.
ーム
k= 25 Wim-K
A = 50 W/m-K
L = 30 mm
Le= 30 mm
L = 20 mm
%3D
Chapter 2 Solutions
Introduction to Heat Transfer
Ch. 2 - Assume steady-state, one-dimensional heat...Ch. 2 - Assume steady-state, one-dimensional conduction in...Ch. 2 - A hot water pipe with outside radius r1 has a...Ch. 2 - A spherical shell with inner radius r1 and outer...Ch. 2 - Assume steady-state, one-dimensional heat...Ch. 2 - A composite rod consists of two different...Ch. 2 - A solid, truncated cone serves as a support for a...Ch. 2 - To determine the effect of the temperature...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.9PCh. 2 - A one-dimensional plane wall of thickness 2L=100mm...
Ch. 2 - Consider steady-state conditions for...Ch. 2 - Consider a plane wall 100 mm thick and of thermal...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.13PCh. 2 - In the two-dimensional body illustrated, the...Ch. 2 - Consider the geometry of Problem 2.14 for the case...Ch. 2 - Steady-state, one-dimensional conduction occurs in...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.17PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.18PCh. 2 - Consider a 300mm300mm window in an aircraft. For a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.20PCh. 2 - Use IHT to perform the following tasks. Graph the...Ch. 2 - Calculate the thermal conductivity of air,...Ch. 2 - A method for determining the thermal conductivity...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.24PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.25PCh. 2 - At a given instant of time, the temperature...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.27PCh. 2 - Uniform internal heat generation at q.=5107W/m3 is...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.29PCh. 2 - The steady-state temperature distribution in a...Ch. 2 - The temperature distribution across a wall 0.3 m...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.32PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.33PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.34PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.35PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.36PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.37PCh. 2 - One-dimensional, steady-state conduction with no...Ch. 2 - One-dimensional, steady-state conduction with no...Ch. 2 - The steady-state temperature distribution in a...Ch. 2 - One-dimensional, steady-state conduction with no...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.42PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.43PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.44PCh. 2 - Beginning with a differential control volume in...Ch. 2 - A steam pipe is wrapped with insulation of inner...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.47PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.48PCh. 2 - Two-dimensional, steady-state conduction occurs in...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.50PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.51PCh. 2 - A chemically reacting mixture is stored in a...Ch. 2 - A thin electrical heater dissipating 4000W/m2 is...Ch. 2 - The one-dimensional system of mass M with constant...Ch. 2 - Consider a one-dimensional plane wall of thickness...Ch. 2 - A large plate of thickness 2L is at a uniform...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.57PCh. 2 - Prob. 2.58PCh. 2 - A plane wall has constant properties, no internal...Ch. 2 - A plane wall with constant properties is initially...Ch. 2 - Consider the conditions associated with Problem...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.62PCh. 2 - A spherical particle of radius r1 experiences...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.64PCh. 2 - A plane wall of thickness L=0.1m experiences...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.66PCh. 2 - A composite one-dimensional plane wall is of...Ch. 2 - Prob. 2.68PCh. 2 - The steady-state temperature distribution in a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1.10 A heat flux meter at the outer (cold) wall of a concrete building indicates that the heat loss through a wall of 10-cm thickness is . If a thermocouple at the inner surface of the wall indicates a temperature of 22°C while another at the outer surface shows 6°C, calculate the thermal conductivity of the concrete and compare your result with the value in Appendix 2, Table 11.arrow_forward2.29 In a cylindrical fuel rod of a nuclear reactor, heat is generated internally according to the equation where = local rate of heat generation per unit volume at r = outside radius = rate of heat generation per unit volume at the centerline Calculate the temperature drop from the centerline to the surface for a 2.5-cm-diameter rod having a thermal conductivity of if the rate of heat removal from its surface is 1.6 .arrow_forward1.37 Mild steel nails were driven through a solid wood wall consisting of two layers, each 2.5-cm thick, for reinforcement. If the total cross-sectional area of the nails is 0.5% of the wall area, determine the unit thermal conductance of the composite wall and the percent of the total heat flow that passes through the nails when the temperature difference across the wall is 25°C. Neglect contact resistance between the wood layers.arrow_forward
- A square silicon chip 7mm7mm in size and 0.5-mm thick is mounted on a plastic substrate as shown in the sketch below. The top surface of the chip is cooled by a synthetic liquid flowing over it. Electronic circuits on the bottom of the chip generate heat at a rate of 5 W that must be transferred through the chip. Estimate the steady-state temperature difference between the front and back surfaces of the chip. The thermal conductivity of silicon is 150 W/m K. Problem 1.6arrow_forward1.4 To measure thermal conductivity, two similar 1-cm-thick specimens are placed in the apparatus shown in the accompanying sketch. Electric current is supplied to the guard heater, and a wattmeter shows that the power dissipation is 10 W. Thermocouples attached to the warmer and to the cooler surfaces show temperatures of 322 and 300 K, respectively. Calculate the thermal conductivity of the material at the mean temperature in W/m K. Problem 1.4arrow_forward2.38 The addition of aluminum fins has been suggested to increase the rate of heat dissipation from one side of an electronic device 1 m wide and 1 m tall. The fins are to be rectangular in cross section, 2.5 cm long and 0.25 cm thick, as shown in the figure. There are to be 100 fins per meter. The convection heat transfer coefficient, both for the wall and the fins, is estimated to be K. With this information determine the percent increase in the rate of heat transfer of the finned wall compared to the bare wall.arrow_forward
- 2.30 An electrical heater capable of generating 10,000 W is to be designed. The heating element is to be a stainless steel wire having an electrical resistivity of ohm-centimeter. The operating temperature of the stainless steel is to be no more than 1260°C. The heat transfer coefficient at the outer surface is expected to be no less than in a medium whose maximum temperature is 93°C. A transformer capable of delivering current at 9 and 12 V is available. Determine a suitable size for the wire, the current required, and discuss what effect a reduction in the heat transfer coefficient would have. (Hint: Demonstrate first that the temperature drop between the center and the surface of the wire is independent of the wire diameter, and determine its value.)arrow_forwardOne end of a 0.3-m-long steel rod is connected to a wall at 204C. The other end is connected to a wall that is maintained at 93C. Air is blown across the rod so that a heat transfer coefficient of 17W/m2 K is maintained over the entire surface. If the diameter of the rod is 5 cm and the temperature of the air is 38C, what is the net rate of heat loss to the air?arrow_forwardEstimate the rate of heat loss per unit length from a 5-cm ID, 6-cm OD steel pipe covered with high-temperature insulation having a thermal conductivity of 0.11 W/(m K) and a thickness of 1.2 cm. Steam flows in the pipe. It has a quality of 99% and is at 150C. The unit thermal resistance at the inner wall is 0.0026(m2K)/W the heat transfer coefficient at the outer surface is 17W/(m2K) and the ambient temperature is 16C.arrow_forward
- 1250 W/m and a = 90 W/m2 and the ég An infinite wall that has a thickness of L = 0.22 m has a uniform heat generation of thermal conductivity of k = 20 W/m-°C. At x = 0 the heat flux going into the wall is temperature of the surface at x = L is T = 42 °C. Find an equation for the steady state temperature distribution in this wall as a function of the position x. Also find the value of the temperature at x = 0. ég k do x= 0 x = Larrow_forwardA plane wall of thickness 2L has an internal heat generation that varies according to q = q0 cos(ax), where q0 is the heat generated per unit volume at the center of the wall (x = 0) and a is aconstant. If both sides of the wall are maintained at a constant temperature of Tw , derive anexpression for the total heat loss from the wall per unit surface area.arrow_forwardBy writing the Fourier heat conduction equation, we can find the meaning of each term in the equation in units. Please explain.25mm in diameter, 30mm in length, the temperatures of both sides respectively T1 = 40.2oC, T2 = 38.9oC, a cylindrical size with a given thermal power amount of 22.4W Find the heat transfer coefficient of the material.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Conduction and the Heat Equation; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6jQsLAqrZGQ;License: Standard youtube license