
a.
To calculate: The equation
a.
Answer to Problem 4E
The solution of the equation
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The equation
Formula used:
To the help of middle term factorisation method.
Steps to use this method to solve a quadratic polynomial
Step 1. Multiply the coefficient of
Step 2. Now to get the coefficient of
Step 3. Now we have 4 terms now, take common from 1st two terms and take common from another two common and from there two factors were come.
Step 3. Take either one bracket is equal to zero or another is equal to zero.
Step 4. Now the value of
Calculation:
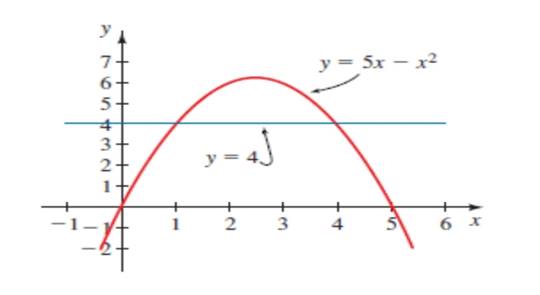
The graph of the equation
So find the roots of the equation
Rewrite the equation:
Rearrange the equation in a polynomial form and take ‘-’ common from the equation:
Further simplify the equation:
Now to take common:
Either
Simplify further as:
The solution of the equation
b.
To calculate: The solution of the equations
b.
Answer to Problem 4E
The solution of the inequality
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The inequality
Formula used:
To the help of middle term factorisation method.
Steps to use this method to solve a quadratic polynomial
Step 1. Multiply the coefficient of
Step 2. Now to get the coefficient of
Step 3. Now we have 4 terms now, take common from 1st two terms and take common from another two common and from there two factors were come.
Step 3. Take either one bracket is equal to zero or another is equal to zero.
Step 4. Now the value of
Calculation:
The inequality
So find the roots of the inequality
Rewrite the inequality:
Rearrange the equation in a polynomial form and take ‘-’ common from the equation:
Further simplify the equation:
Now to take common:
Either
Simplify further as:
Thus, the solution of the inequality
Chapter 1 Solutions
Precalculus - A Custom Text for UNLV
- Hyperbolic function - Home work show that: (sechu) = -sechu.tanu. Ju ax dx Prof that: (sechu) = du -(05451) u√T-u dx 1시기 x-( - X711 Show that: coth's the /x+ Proof that: cosh'x= /n/ x + √x=1/.. show thật, sinh CA+B) sinh A. Cash Becosh A. sinh B Find Jy, SO if y= ** ex. Solve; dx Solve: + exxex :S√coshx-1.dx Solve: da Sinho cosho Solve dx 4-x2 dx + Solve √ex+1 If y= (x+1). sech(lmx), fund dy. dx If y = /R/cschx + cothxl, Ind dyarrow_forward10:10 %01 目 YI HE1.PNG →> 1 + 3(8 - X) *w* =?? Example 7: Find Wn if M₁= -25 kN.m/m, M= -35 kN.m/m and Mc=+15 kN.m/m. We = 3X *W*+3(8-X) *w 1 1 1 Wi 25 3- +35*3* X + 15*3* 8-x + =?? 8-X We-Wi m ??=?? → W =?? dw =??= 0 - X =?? m dx ..Wn=?? kN/m² -L-8m Ꮎ Ꮎ x +8-x- 3marrow_forwardNote: The second option also should be analyzed and the lower load should be taken into consideration. Hint: X=0.535L not ok. XL H.W. L Larrow_forward
- By using Laplace transforms, solve the following differential equation subjectto the given initial conditions. y" + 4y' + 5y = 2^(e−2t) cost, y' = 0, y" = 3. *see image for clarificationarrow_forwardExample: Solve y" + 2xy' + 2y = 0 around x0 = 0.arrow_forwardSolve the given differential equations by using the principle of superposition (D2 − 1)y = sinh xarrow_forward
- Example: Solve (x − 1)y" + 2y′ = 0 around x0 = 0. -arrow_forward|| 8 Example: If ƒ (x + 2π) = f(x), obtain Fourier series expansion for the function given by 2x 1+ f(x): πT = 2x 1 ' 0 ≤ x ≤ n Π Hence or otherwise prove that 1 12 + 5² 13 + 12arrow_forward5. Submit answer Compute the surface area of the solid of revolution formed by rotating the bounded region formed from formed from y=4x+3, y= 0, x = 0, and x = 3 about the x-axis. S= Submit answer Answers Attempt 3 of 3 ETCH OUIT AND DCI A Y L T The Weather Channel DELL P UP % 5 6 7 8 9arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





