
Concept explainers
Which of the DNA molecules shown are recombinant?
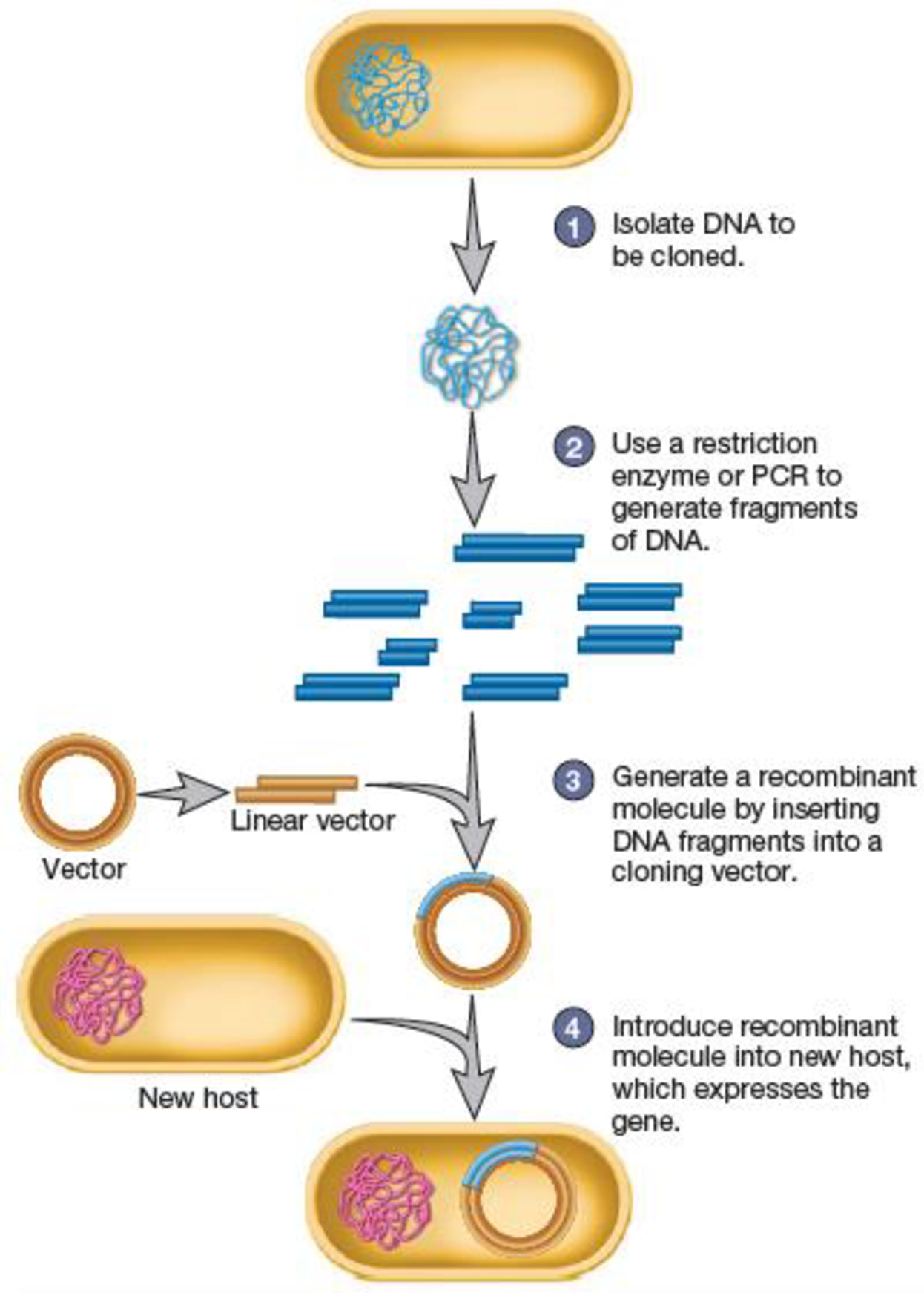
A recombinant DNA is a type of DNA having new nucleotide sequences. Such type of DNA is formed by linking the fragments obtained from two or more different sources. The first breakthrough of the recombinant DNA technology was the bacterial enzymes that cut the double-stranded DNA. These bacterial enzymes are referred to as restriction enzymes.
Explanation of Solution
The provided figure shows four steps that are involved in the cloning of a gene. These steps include:
- 1. Isolation of DNA which is to be cloned.
- 2. Generation of DNA fragments by means of restriction enzymes or PCR.
- 3. Insertion of DNA fragments into the cloning vector in order to generate a recombinant DNA molecule.
- 4. Introduction of recombinant DNA into the new host cell which expresses the gene.
The DNA molecule shown in step 3 in the given figure is the recombinant DNA molecule. This step shows the vector along with an insert referred to as a recombinant DNA molecule. The bacterium produced, shown in step 4, is the recombinant organism.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Prescott's Microbiology
- A DNA strand was sequenced using the Sanger method (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KTstRrDTmWI). The reaction tube contained the DNA strand, fluorescently labelled dideoxynucleotide triphosphates (ddATP – yellow, ddGTP – green, ddCTP – blue, ddTTP - red), deoxynucleotide triphosphates, DNA polymerase, or its Klenow fragment. Synthesis of DNA is allowed to proceed, and the results are shown on the right: 15 14 13 12 11 10 (a) What is the sequence of the copy and the template strands? (b) If the template strand were in the 5'-3' direction, what will be the sequence of the DNA copy? Nucleotide Lengtharrow_forwardIS the order of the base pairs exactly the same in the 2 new DNA strands?arrow_forwardAnswer the following questions: A) Why the extension cannot be 3´---5´ and why it has to be 5´------3´? B) What is a gene?arrow_forward
- A. In NOT more than 200 words, explain how the double-helical structure of DNA suggests a mechanism for DNA replication? B. In NOT more than 200 words, explain the special mechanism used to replicate chromosome ends?arrow_forwardIs the DNA soluble in the aqueous solution or alcohol?arrow_forwardWhat is the axial ratio (length:diameter) of a DNA molecule 20 μm long?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





