
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an amine and hydrochloric acid is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.26E
The complete reaction between an amine and hydrochloric acid is given below.
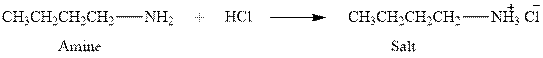
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an amine and hydrochloric acid gives salt of amine. This happens by the abstraction of proton by lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in amine from the hydrochloric acid. The intermediate then rearranges to give salt of amine.
The complete reaction between an amine and hydrochloric acid is given in Figure 1.
Figure 1
The complete reaction between an amine and hydrochloric acid is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an amine and water is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.26E
The complete reaction between an amine and water is given below.

Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an amine and water gives ammonium ion and hydroxide ion. This happens by the abstraction of proton by lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in amine from the water. The intermediate then rearranges to give ammonium ion and hydroxide ion.
The complete reaction between an amine and water is given in Figure 2.

Figure 2
The complete reaction between an amine and water is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an amine and
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.26E
The complete reaction between an amine and carboxylic acid is given below.
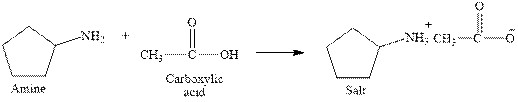
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an amine and carboxylic acid gives ammonium salt of carboxylic acid. This happens by the abstraction of proton by lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in amine from the carboxylic acid. The intermediate then rearranges to give ammonium salt of carboxylic acid.
The complete reaction between an amine and carboxylic acid is given in Figure 3.

Figure 3
The complete reaction between an amine and carboxylic acid is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.26E
The complete reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide is given below.
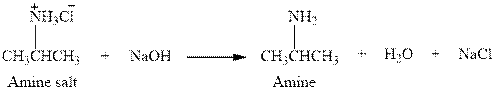
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide gives amine, water and sodium chloride. This happens by the abstraction of proton by lone pair of electrons of oxygen in sodium hydroxide from the amine salt. The intermediate then rearranges to give amine, water and sodium chloride.
The complete reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide is given in Figure 4.
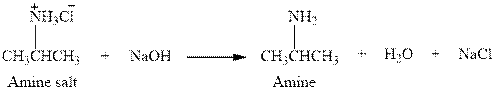
Figure 4
The complete reaction between an amine salt and sodium hydroxide is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an acid chloride and primary amine is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.26E
The complete reaction between an acid chloride and primary amine is given below.
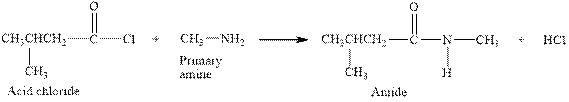
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an acid chloride and primary amine gives amide and hydrochloric acid. This happens by the attack of lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in amine on the carbonyl carbon of acid chloride. The intermediate then rearranges to give amide and hydrochloric acid.
The complete reaction between an acid chloride and primary amine is given in Figure 5.

Figure 5
The complete reaction between an acid chloride and primary amine is shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation:
The complete equation for the reaction between an acid anhydride and ammonia is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Amines are nitrogen-containing organic compounds. The general formula of amines is
In secondary amines, two of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
In tertiary amines, all hydrogen atoms of ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl group.
Answer to Problem 16.26E
The complete reaction between an acid anhydride and ammonia is given below.
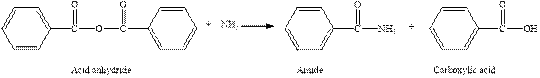
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between an acid anhydride and ammonia gives amide and carboxylic acid. This happens by the attack of lone pair of electrons of nitrogen in ammonia on the carbonyl carbon of acid anhydride. The intermediate then rearranges to give amide and carboxylic acid.
The complete reaction between an acid anhydride and ammonia is given in figure 6.
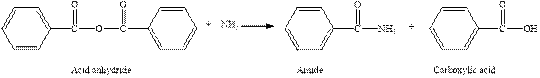
Figure 6
The complete reaction between an acid anhydride and ammonia is shown in figure 6.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 16 Solutions
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry
- Pleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forwardThe Ksp for lead iodide ( Pbl₂) is 1.4 × 10-8. Calculate the solubility of lead iodide in each of the following. a. water Solubility = mol/L b. 0.17 M Pb(NO3)2 Solubility = c. 0.017 M NaI mol/L Solubility = mol/Larrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning





