
Concept explainers
(b)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure, polarity, bond angle and hybrid orbital of
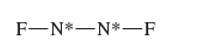
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The hybridization of bonded atoms can be calculated with the help of below formula:
A single covalent bond is formed by one sigma bond whereas a double bond consists of one sigma and one pi bond. <
(c)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure, molecular structure, polarity, bond angle and hybrid orbital of
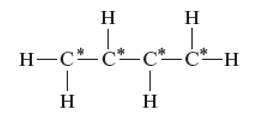
Concept Introduction:
Lewis dot structure is the representation which shows the bonding between atoms present in a molecule. It shows lone pairs and bond pairs that existing on each bonded atom. Lewis dot structure is also known as Lewis dot formula or electron dot structure. The hybridization of bonded atoms can be calculated with the help of below formula:
A single covalent bond is formed by one sigma bond whereas a double bond consists of one sigma and one pi bond. <
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 14 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- Consider the following compounds: CO2, SO2, KrF2, SO3, NF3, IF3, CF4, SF4, XeF4, PF5, TF5, and SCl6. These 12 compounds are all examples of different molecular structures. Draw the Lewis structures for each and predict the molecular structures. Predict the bond angles and the polarity of each. (A polar molecule has a net dipole moment, while a nonpolar molecule does not.) See Exercises 25 and 26 for the molecular structures based on the trigonal bipyramid and the octahedral geometries.arrow_forwardSuccessive substitution of F atoms for H atoms in the molecule NH3 produces the molecules NH2F, NHF2, and NF3. a. Draw Lewis structures for each of the four molecules. b. Using VSEPR theory, predict the geometry of each of the four molecules. c. Specify the polarity (polar or nonpolar) for each of the four molecules.arrow_forwardWhich of these molecules has a net dipole moment? For each of the polar molecules, indicate the direction of the dipole in the molecule. (a) nitrosyl fluoride, FNO (b) disulfur difluoride, S2F2arrow_forward
- Indicate whether each of the following hypothetical triatomic molecules is polar or nonpolar. Assume that A, X, and Y have different electronegativities. a. a linear XAX molecule b. a linear XXA molecule c. an angular AXY molecule d. an angular XAY moleculearrow_forwardDraw Lewis structures for the following species. (The skeleton is indicated by the way the molecule is written.) (a) Cl2CO (b) H3C—CN (c) H2C—CH2arrow_forwardIndicate which molecules are polar and which are nonpolar. (a) SeO2 (b) N2O (N is the central atom) (c) SCl4arrow_forward
- Successive substitution of F atoms for H atoms in the molecule CH4 produces the molecules CH3F, CH2F2, CHF3, and CF4. a. Draw Lewis structures for each of the five molecules. b. Using VSEPR theory, predict the geometry of each of the five molecules. c. Specify the polarity (polar or nonpolar) for each of the five molecules.arrow_forwardIn addition to CO, CO2, and C3O2, there is another molecular oxide of carbon, pentacarbon dioxide, C5O2, a yellow solid. (a) What is the approximate C-to-C-to-O bond angle in pentacarbon dioxide? (b) What is the approximate C-to-C-to-C bond angle in this compound?arrow_forwardTwo different molecules have the formula C2H6O. One of the molecules has the oxygen atom bonded to both carbon atoms. The other molecule has the oxygen atom bonded to only one carbon atom while both carbon atoms are bonded to each other. Write Lewis structures for both of these compounds.arrow_forward
- a Carbonyl fluoride, COF2, is an extremely poisonous gas used in organofluorine synthesis. Give the valence bond description of the carbonyl fluoride molecule. (Both fluorine atoms are attached to the carbon atom.) b Nitrogen, N2, makes up about 80% of the earths atmosphere. Give the valence bond description of this molecule.arrow_forwardDraw Lewis structures to illustrate the bonding in the following molecules. In each case, there will be at least one multiple bond present in a molecule. a. C3H4: A central carbon atom has two other carbon atoms bonded to it. Each of the noncentral carbon atoms also has two hydrogen atoms bonded to it. b. N2F2: The two nitrogen atoms are bonded to one another, and each nitrogen atom also has a fluorine atom bonded to it. c. C2H3N: The two carbon atoms are bonded to each other. One of the carbon atoms has a nitrogen atom bonded to it, and the other carbon atom has three hydrogen atoms bonded to it. d. C3H4: A central carbon atom has two other carbon atoms bonded to it. One of the noncentral carbon atoms also has one hydrogen atom bonded to it, and the other one has three hydrogen atoms bonded to it.arrow_forwardPredict the geometry of the following species: (a) SO2 (b) BeF2 (c) SeCl4 (d) Pcl5arrow_forward

 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





