
(a)
Interpretation:
The given compound has to be classified as an ether, an alcohol, or neither an ether or alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
Ether is an organic compound. In ether, an oxygen atom is bonded to two carbon atoms by a single bond. The groups that are attached to the carbon atom by a single bond may be alkyl, aryl, or cycloalkyl groups. The
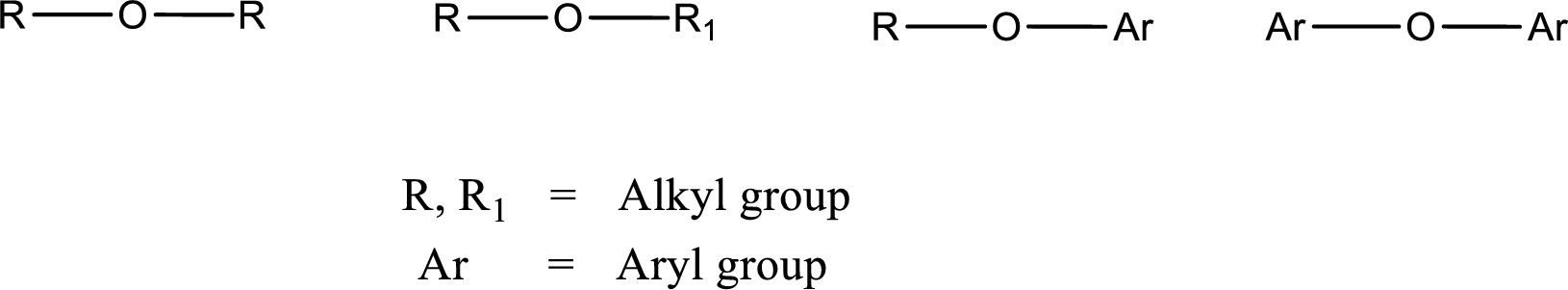
Alcohol is a compound in which a hydrocarbon group is bonded to a hydroxyl group. The generalized formula for alcohol can be given as,
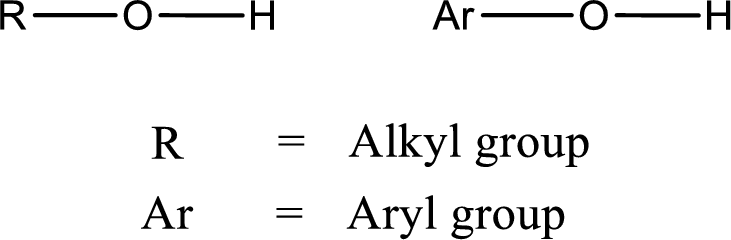
(b)
Interpretation:
The given compound has to be classified as an ether, an alcohol, or neither an ether or alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
Ether is an organic compound. In ether, an oxygen atom is bonded to two carbon atoms by a single bond. The groups that are attached to the carbon atom by a single bond may be alkyl, aryl, or cycloalkyl groups. The functional group of ether is
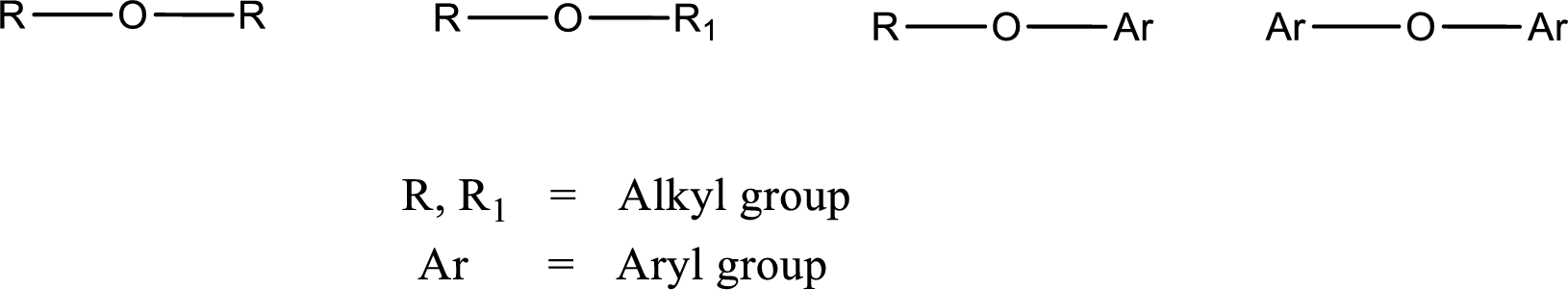
Alcohol is a compound in which a hydrocarbon group is bonded to a hydroxyl group. The generalized formula for alcohol can be given as,
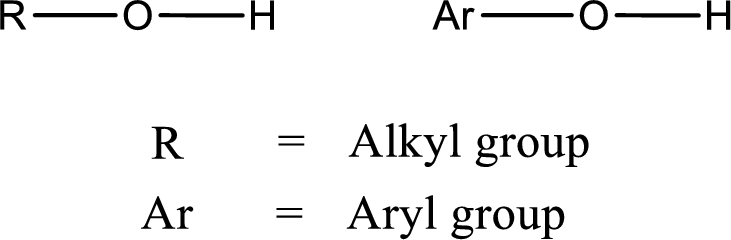
(c)
Interpretation:
The given compound has to be classified as an ether, an alcohol, or neither an ether or alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
Ether is an organic compound. In ether, an oxygen atom is bonded to two carbon atoms by a single bond. The groups that are attached to the carbon atom by a single bond may be alkyl, aryl, or cycloalkyl groups. The functional group of ether is
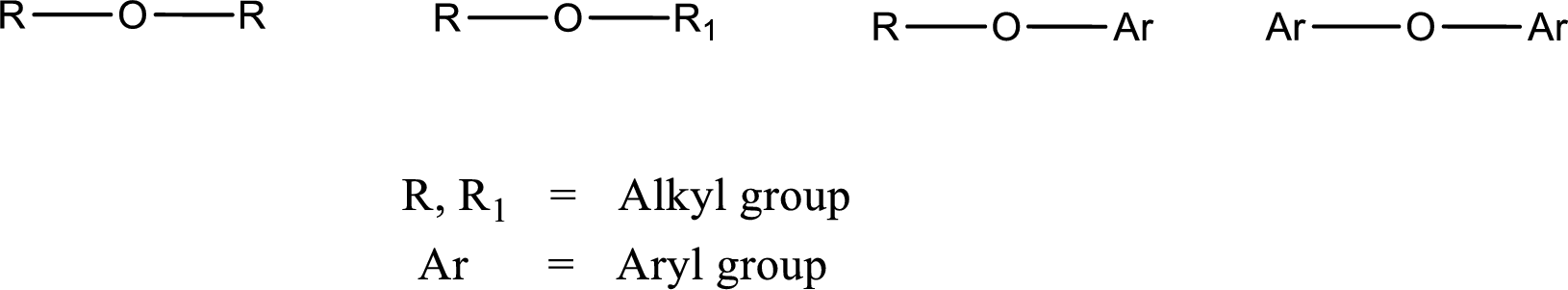
Alcohol is a compound in which a hydrocarbon group is bonded to a hydroxyl group. The generalized formula for alcohol can be given as,
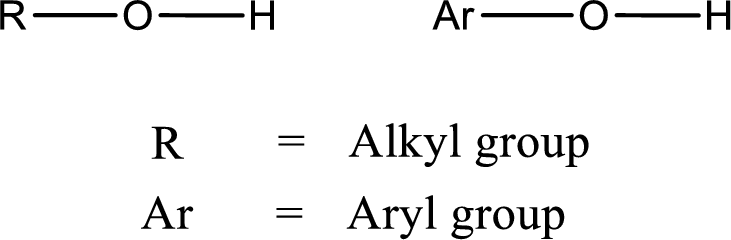
(d)
Interpretation:
The given compound has to be classified as an ether, an alcohol, or neither an ether or alcohol.
Concept Introduction:
Ether is an organic compound. In ether, an oxygen atom is bonded to two carbon atoms by a single bond. The groups that are attached to the carbon atom by a single bond may be alkyl, aryl, or cycloalkyl groups. The functional group of ether is
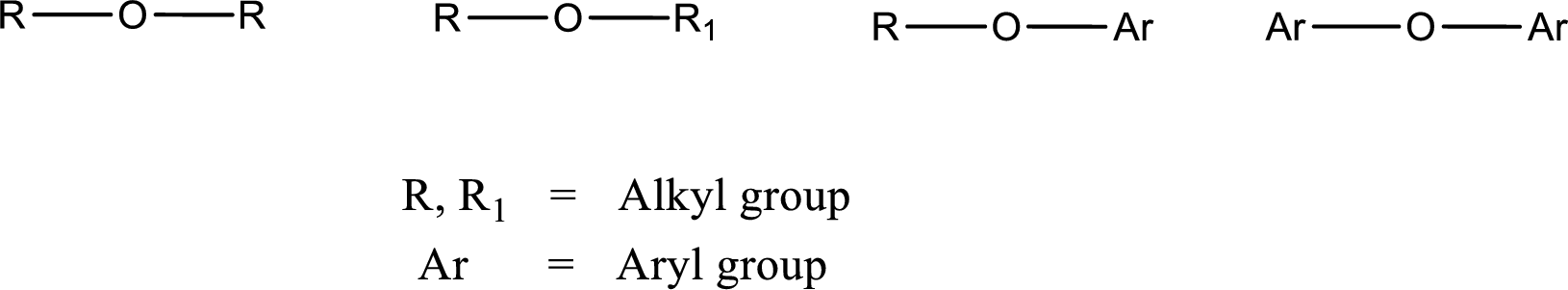
Alcohol is a compound in which a hydrocarbon group is bonded to a hydroxyl group. The generalized formula for alcohol can be given as,
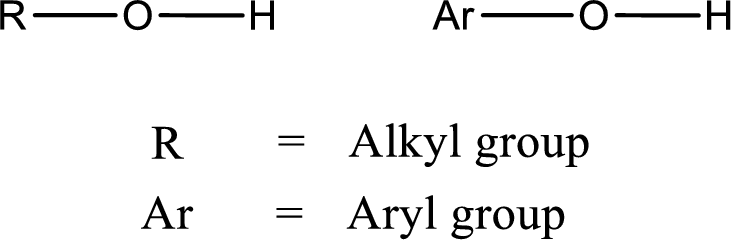
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 14 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
- Most ceramic materials have low thermal conductivities because:(a) Electron mobility is strongly restricted due to their strong ionic-covalent bonding.(b) False, in general they are excellent thermal conductors (they are used in ovens).(c) Electron mobility is dependent on T and therefore they are poor conductors at high temperatures.(d) Electron mobility is very restricted by secondary bonds.arrow_forwardResistivity and electrical conductivity.(a) In metals, resistivity decreases.(b) In metals, resistivity decreases and conductivity in semiconductors also decreases with increasing temperature.(c) With increasing temperature, resistivity in metals and conductivity in semiconductors also increases.(d) None of the above.arrow_forwardState the difference between concrete and Portland cement.(a) There are no differences, in concrete the chemical composition is silicates and in cement aluminates.(b) The chemical composition of concrete is based on silicates and in cement aluminates.(c) Concrete is composed of aggregates bound by cement and cement "only" contains different minerals.(d) Cement is aggregates bound by concrete.arrow_forward
- Amorphous polymers are usually transparent and semi-crystalline polymers are usually opaque. Correct?(a) No. They are all made up of polymer chains. True if they were monomers.(b) Yes. The arrangement of the chains determines the passage of light.(c) No. It is the other way around.(d) Crystallinity or amorphousness does not affect the transparency or opacity of the material.arrow_forwardThe name ferrites refers to a family of(a) ceramic materials that exhibit ferrimagnetic behavior due to their ionic composition.(b) polymeric materials that exhibit ferrimagnetic behavior due to their ionic composition.(c) concrete-based materials that exhibit ferrimagnetic behavior due to their ionic composition.(d) superconducting materials that exhibit ferrimagnetic behavior due to their ionic composition.arrow_forwardState the two main factors affecting ion packing in the solid state.(a) Number of covalent bonds and their unsaturation.(b) Mechanical properties and degradation temperature.(c) Number of crystalline phases present and grain size.(d) Electroneutrality and ion size.arrow_forward
- The ceramic materials alumina (Al2O3) and chromium oxide (Cr2O3) form an isomorphic phase diagram. The solubility will be(a) unlimited of one ceramic in the other.(b) very limited depending on the weight % of Al2O3(c) very limited depending on the weight % of Cr2O3(d) partial of one ceramic in the other.arrow_forwardAmong the main characteristics of optical fibers, indicate which of the following is not included:(a) Opacity and Rigidity(b) Flexibility(c) Transparency(d) Low thicknessarrow_forwardMost ceramic materials have low thermal conductivities because(a) Electron mobility is strongly restricted due to their strong ionic-covalent bonding.(b) False, in general they are excellent thermal conductors (they are used in ovens).(c) Electron mobility is dependent on T and therefore they are poor conductors at high temperatures.(d) Electron mobility is highly restricted by secondary bonds.arrow_forward
- Si increases its conductivity when doped with Ga and P.(a) True, because the conduction mechanism is due to electrons and holes generated by Ga and P as the case may be.(b) True, because a completely different compound is generated.(c) False, because when impurities are introduced, the opposite occurs.(d) False, because the conductivity of Si is only determined by the increase in temperature, which must be controlled.arrow_forwardIndicate whether a configuration and a microstate are the same:a) Yesb) No, a microstate encompasses several configurationsc) No, a configuration is the same as a macrostated) No, a configuration encompasses several microstatesarrow_forwardThe representation of a one-dimensional velocity distribution function for a gas, with increasing temperature the maximum occurs for vi = 0 m/s. Correct?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





