
Becker's World of the Cell (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780321934925
Author: Jeff Hardin, Gregory Paul Bertoni
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 14, Problem 14.2CC
CONCEPT CHECK 14.2
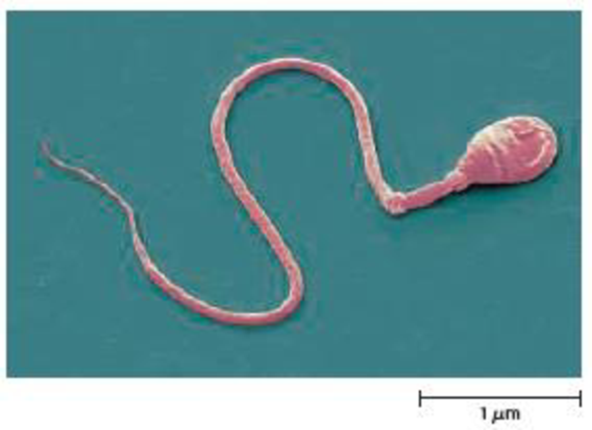
Human sperm swim using a flagellum. They also have mitochondria at the base of the flagellum (see Figure 4.13). What advantage do you think this structure provides, based on what you know about flagella?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Exercise 5
Membrane receptors are proteins that are incorporated in the cytoplasmic membrane of a cell, allowing the
detection of specific molecules such as (hormones, growth factor) and triggering a cascade of biochemical
Synthesis of protein
reactions.
The adjacent schema represents the steps of
the synthesis of these membrane receptors.
1. Label the structures from a to f.
In order to study the biosynthesis and
secretion of this protein (membrane
receptors), a solution containing radioactive
amino acid was injected in the blood of an
animal. Samples of certain cells were taken
at regular intervals of time. The intensity of
radioactivity was measured in different
cellular organelles.
2000
The table below represents the variations of the quantity of a membrane protein in different parts of the cell,
as function of time.
Time (min)
15
40
50
Structure X
26
12
2
1
Structure Z
0.
6.
10
6.
Structure Y
0.
10
24
2. Represent the obtained results in the form
3. 3.1. Analyze the obtained…
Molecular Biochemistry
Q. Why can’t Myosin V motor proteins “walk” towards the negative end of the actin molecule? Why do most myosins move toward the positive end? Why do most myosins move toward the positive end instead of the negative end? Explain
Participation Problem: Chapter 10, Problem 4: The lipid portion of a typical bilayer is about 30
Å thick.
(a) Calculate the minimum number of residues in an a-helix required to span this distance.
(b) Calculate the minimum number of residues in a ß-strand required to span this distance.
Skip part (c)
(d) The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) has a single transmembrane helix. Find it in
this partial sequence.
...RGPKIPSIATGMVGALLLLVVALGIGILFMRRRH...
Table for reference (for parts a-b):
TABLE 6.1 Parameters of some polypeptide
secondary structures
Structure Type
B Strand (antiparallel)
B Strand (parallel)
a helix
310 helix
Polypeptide II helix
Residues
per Turn
2.0
2.0
3.6
3.0
3.0
Rise (h) per
Residue
3.4 Å
3.2 Å
1.5 Å
2.0 Å
4.7 Å
Pitch (p)
6.8 Å
6.4 Å
5.4 Å
6.0 Å
9.4 Å
Chapter 14 Solutions
Becker's World of the Cell (9th Edition)
Ch. 14 - If myosin V moved more like an inchworm (meaning...Ch. 14 - Kinesins and dyneins are both microtubule-based...Ch. 14 - CONCEPT CHECK 14.2 Human sperm swim using a...Ch. 14 - A single myosin II motor domain can exert about 15...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.4CCCh. 14 - In addition to being found at the rear of...Ch. 14 - Ciliobrevins. Ciliobrevins were reported in 2012...Ch. 14 - Prob. 14.2PSCh. 14 - Prob. 14.3PSCh. 14 - Rigor Mortis and the Contraction Cycle. After...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- HELPING TAGS: Biology, developmental biology, plants, actin filaments Can non-motile cells, such as plants, benefit from actin filaments' motion-related functions? Explain your answer. Will UPVOTE, just pls help me answer the question. Thanks.arrow_forwardDescrive in 2-3 sentences an in vitro experiment that differentiates between the Arp2/3 complex’ ability to associate with both the side of the ‘mother’ actin filament and with the barbed end of the ‘mother’ actin filament. Your experiment should take advantage of capping protein (binds and blocks barbed ends), and direct visualization of actin filaments.arrow_forwardQ3 Calculate the actual, physiological AG for the reaction Phosphocreatine Creatine NH--PO3 HN=c NCH,-CO0 NH2 NH=c. HNCH2- COO ČH3 Creatine ADP phosphokinase АТР At 37 °C, as it occurs in the cytosol of neurons, with phosphocreatine at 4.7 mM, creatine at 1.0 mM, ADP at 0.73 mM and ATP at 2.6 mM. HINT: AG° = 30.5 kJ/mol AG° = -43.0 kJ/mol ADP + Pi -> ATP + H,0 Phosphocreatine + H2O -> creatine + Piarrow_forward
- Data Table: Comparison of Mammalian Species (Humans, Mice, Cats, and Baboons) Test 6 Number of Differences in DNA base sequence for DATP gene * 1 4 Mouse Cat Baboonarrow_forwardModule 5 Concept Check 10. Name the set of structures inside the dotted lines in the figure below. Next, identify the process that occurs in this location. THREE C D E F G H bio INCH I J B • Na EB Attached to G: +11. Name the structures in the image. Letter A B G 100 E 69 WWW € Calv Cafe F Name of Structure Action Potential 11-1 E Oarrow_forwardmultiple choice question : The structure of silk fibroin is dominated by (a) B-form duplex with occasional flipping into left-handed Z-form (b) antiparral strands in stacked beta pleated sheets (c) hydrophobic residues form a surface shell with hydrophillic residues in the molten core (d) self-complementary stems terminated by loops (e) random coils and domains anchored to the nuclear scaffoldarrow_forward
- Question:- Transport into the lumen of some organelle systems requires an unfolded protein structure, while for other import mechanisms, unfolding is not required, since proteins may be transported in the folded state across the membrane. How is it decided whether a freshly made protein will be imported into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)?arrow_forwardVISUAL SKILLS During intense exercise, can a musclecell use fat as a concentrated source of chemical energy?Explain. (Review Figures 9.18 and 9.19.)arrow_forwardConcept Check 3.1. Grey squirrels, Sciurus carolinensis, abound in upstate New York. Contrary to their common name, not all members of this species are grey in color. Some populations have a considerable number of melanistic individuals who appear quite dark, almost black. If a population north of Geneva has 30% melanistic individuals, find the following probabilities and expected values: (a) A random sample of 18 has 4 melanistic squirrels. (b) A random sample of 18 has 4 or less melanistic squirrels. (c) A random sample of 18 has more than 4 melanistic squirrels. (d) The expected mumber of melanistic squirrels in a random sample of 18 individuals. (e) The expected variance for samples of size 18.arrow_forward
- Question. What exactly is the significance of the branching points in the tree diagram above, and what exactly is this diagram supposed to show?arrow_forwardVISUALIZE Label the following diagram and explain what this diagram illustrates.arrow_forwardAnimals and plants both have diploid and haploid cells. How does the animal life cycle differ from the alternation of generations exhibited hy plants?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning
KINE 2310-Chapter 4: Philosophy of Physical Activity; Author: HBU Online Course Development;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8Ky6t3nvP_4;License: Standard youtube license