
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780134605173
Author: Mark F. Sanders, John L. Bowman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 13, Problem 22P
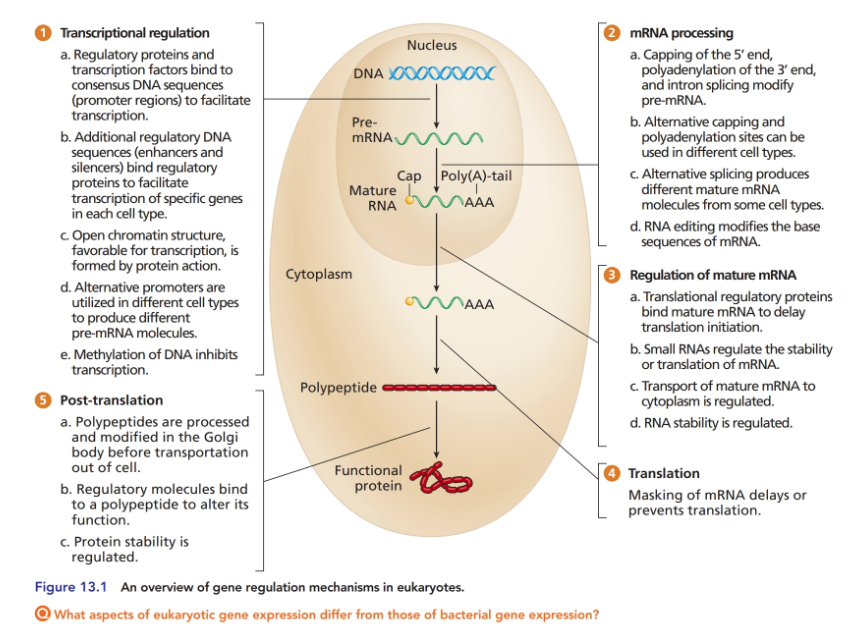
The majority of this chapter focused on gene regulation at the transcriptional level, but the quantity of functional protein product in a cell can be regulated in many other ways as well (see Figure
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
You are teaching a class on the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression. In order to demonstrate this complex process, you decide to draw for the class a typical eukaryotic gene/transcription unit with its major regions, such as the promoter regions, where the RNA polymerase II and transcription factors would bind
From the list given - choose all components that you think are part of a typical eukaryotic gene
From the list given - choose all the regulatory sequences that you think would control the expression of this eukaryotic gene
From the list given - choose all of the regulatory proteins that would bind the eukaryotic gene to control its expression
Identify which eukaryotic level of gene regulation is most applicable in the given examples. (Pre-transcriptional control, Transcriptional control, Translational control, Post-translational control)
The mouse REST gene is under the control of a promoter region which contains alternative promoters.
Functional insulin required the association of two polypeptides known as the A and B chains.
In Drosophila, differential mRNA decay rate is crucial during neural development.
The glycolytic enzyme pyruvate kinase is activated by dephosphorylation and inactivated by phosphorylation.
In the fruit fly, genes for rRNA can be replicated more or less often compared to the rest of the chromatin depending on the needs of the cell.
In the human beta-globin, two introns are spliced out in order to produce the mature mRNA.
DNA methylation can change the degree of condensation of the chromatin.
What are the functions of transcriptional activator proteins and repressor proteins? Explain how they work at the molecular level.
Chapter 13 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Ch. 13 - 13.1 Devoting a few sentences to each, describes...Ch. 13 - 13.2 Describe and give an example (real or...Ch. 13 - What is meant by the term chromatin remodeling?...Ch. 13 - 13.4 What general role does acetylation of histone...Ch. 13 - 13.5 Describe the roles of writers, readers, and...Ch. 13 - Outline the roles of RNA in eukaryotic gene...Ch. 13 - 13.7 What are the roles of the Polycomb and...Ch. 13 - Most biologists argue that the regulation of gene...Ch. 13 - Compare and contrast the transcriptional...Ch. 13 - The term heterochromatin refers to heavily...
Ch. 13 - 13.11 Compare and contrast promoters and enhancers...Ch. 13 - 13.12 What are the different chromatin...Ch. 13 - 13.13 Define epigenetics, and provide examples...Ch. 13 - What is one proposed role for lncRNAs?Ch. 13 - 13.15 What are the sources of dsRNA? Diagram the...Ch. 13 - How does dsRNA lead to posttranscriptional gene...Ch. 13 - 13.17 A hereditary disease is inherited as an...Ch. 13 - Prob. 18PCh. 13 - Prob. 19PCh. 13 - 13.20 A muscle enzyme called ME is produced by...Ch. 13 - Using the components in the accompanying diagram,...Ch. 13 - 13.22 The majority of this chapter focused on gene...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Help me pleasearrow_forwarda. How do bacteria increase the efficiency of gene expression? Is this possible in eukaryotes? b. A mutation in the promoter of Gene K disrupts an enzyme binding site and results in the loss of Gene K expression. Is this change in gene expression likely happening at the transcriptional or the translational level? Explain. c. Propose three different mutations to prevent initiation, elongation, and termination of bacterial transcription, respectively. Explain how/why each mutation would prevent its respective step. (Hint: mutations can be in genes that encode proteins or regulatory DNA sequences)arrow_forwardCompare the control of gene regulation in eukaryotes and bacteria at the level of initiation of transcription. How do the regulatory mechanisms work? What are the similarities and differences in these two types of organisms in terms of the specific components of the regulatory mechanisms?arrow_forward
- Debes et al recently described how aging in humans, mice, nematodes, and other eukaryotes is associated with an increase in the average speed of transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II. Overexpression of some proteins that decreased PolII elongation speed extended lifespan in the fly Drosophila. For each of the following proteins, predict whether overexpression of that protein (assuming all other cellular components are normal) would likely reduce transcriptional speed, and briefly justify your answer. a) Mediator proteinsb) Histone proteinsc) Insulator binding proteinsarrow_forwardIn response to potentially toxic substances (e.g., high levels of iron), eukaryotic cells often use translational or posttranslational regulatory mechanisms to prevent cell death, rather than using transcriptional regulatory mechanisms. Explain why.arrow_forwardEukaryotes have a multitude of ways of regulating gene expression. Why are all these regulatory mechanisms necessary to the functioning of a eukaryotic organism?arrow_forward
- "Upstream" "Downstream" Exons Start of transcription Termination codon 5 3' Promoter initiator codon Introns Polyadenylation signal (intervening sequences) 5' untranslated region 3' untranslated region Direction of transcription Please study the diagram above on eukaryotic gene expression. In order to provide instructions for gene expression, a eukaryotic gene should have the following sequences except for O A. Promoter B. Start codon also known as initiator codon C. Splicing signals (dinucleotide sequence in the intron) O D. 5' CAP sequencearrow_forwardGive the result(s) of the experiment in "MicroRNAs Control De Novo DNA Methylation Through Regulation of Transcriptional Repressors in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell" and how the figure clearly demonstrates that outcome. Also, note the positive and/or negative controls for the experiment.arrow_forwardYou are teaching a class on the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression. In order to demonstrate this complex process, you decide to draw for the class a typical eukaryotic gene/transcription unit with its major regions, such as the promoter regions, where the RNA polymerase II and transcription factors would bind etc…. I need the correct answer please From the list given - choose all components that you think are part of a typical eukaryotic genearrow_forward
- There are similarities and differences during regulation of gene expression in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Promoters, transcription factors and RNA polymerase are essential elements in transcription but their properties and function may differ.a) Predict the outcome or consequences of mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II in eukaryote without the presence of transcription factors (TF).arrow_forwardExplain using leucine zipper motifs as an example, how protein-protein interactions between transcription factors containing such motifs can generate diversity in transcriptional activation. Refer to the recognition of DNA elements in gene promoters to justify your answer. Assume transcription factor A binds to DNA element A’, transcription factor B binds to DNA element B’, and so forth.arrow_forwardGenes can be transcribed into mRNA, in the case of protein coding genes, or into RNA, in the case of genes such as those that encode ribosomal or transfer RNAs. Define a gene. For the following characteristics, state whether they apply to (a) continuous, (b) simple, or (c) complex transcription units.i. Found in eukaryotesii. Contain intronsiii. Capable of making only a single protein from a given genearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning
QCE Biology: Introduction to Gene Expression; Author: Atomi;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a7hydUtCIJk;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY