
Concept explainers
A hereditary disease is inherited as an autosomalrecessive trait. The wild
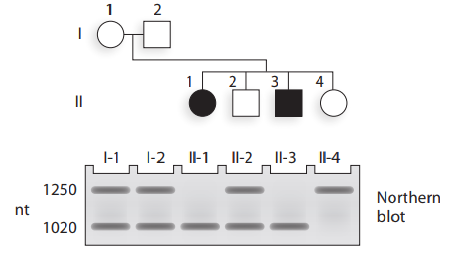
a. Identify the genotype of each family member, using the sizes of mRNAs to indicate each allele. (For example, a person who is homozygous wild type is indicated as
b. Based on your analysis, what is the most likely molecular abnormality causing the disease allele?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 13 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- A wildtype gene produces the polypeptide sequence: Wildtype: Met-Ser-Pro-Arg-Leu-Glu-Gly Each of the following polypeptide sequences is the result of a single mutation. Identify the most likely type of mutation causing each, be as specific as possible. M1:Met-Ser-Ser-Arg-Leu-Glu-Gly missense mutation M2:Met-Ser-Pro M3:Met-Ser-Pro-Asp-Trp-Arg-Asp-Lys M4:Met-Ser-Pro-Glu-Gly nonsense mutation frameshift insertion in frame deletion M5:Met-Ser-Pro-Arg-Leu-Glu-Gly in frame insertionarrow_forwardDuchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is an X-linked recessive genetic disease caused by mutations in the gene that encodes dystrophin, a large protein that plays an important role in the development of normal muscle fibers. The Dystrophin gene is immense, spanning 2.5 million base pairs, and includes 79 exons and 78 introns. Many of the mutations that cause DMD produce premature stop codons, which bring protein synthesis to a halt, resulting in a greatly shortened and nonfunctional form of dystrophin. Some geneticists have proposed treating DMD patients by introducing small RNA molecules that cause the spliceosome to skip the exon containing the stop codon (A. Goyenvalle et al., 2004. Science 306:1796–1799). The introduction of the small RNAs will produce a protein that is somewhat shortened because an exon is skipped and some amino acids are missing, but it may still result in a protein that has some function. The small RNAs, antisense RNAs, used for exon skipping are complementary to…arrow_forwardDuchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is an X-linked recessive genetic disease caused by mutations in the gene that encodes dystrophin, a large protein that plays an important role in the development of normal muscle fibers. The dystrophin gene is immense, spanning 2.5 million base pairs, and includes 79 exons and 78 introns. Many of the mutations that cause DMD produce premature stop codons, which bring protein synthesis to a halt, resulting in a greatly shortened and nonfunctionalform of dystrophin. Some geneticists have proposed treating DMD patients by causing the spliceosome to skip the exon containing the stop codon. Exon skipping would produce a protein that is somewhat shortened (because an exon is skipped and some amino acids are missing), but might still result in a protein that had some function (A. Goyenvalle et al. 2004. Science 306:1796–1799). Propose a possible mechanism to bring about exon skipping for the treatment of DMD.arrow_forward
- A polypeptide has the following amino acid sequence: Met-Ser-Pro-Arg-Leu-Glu-Gly The amino acid sequence of this polypeptide was determined in a series of mutants listed in parts a through e. For each mutant, indicate the type of mutation that occurred in the DNA (single-base substitution, insertion, deletion) and the phenotypic effect of the mutation (nonsense mutation, missense mutation, frameshift, etc.). a. Mutant 1: Met-Ser-Ser-Arg-Leu-Glu-Gly b. Mutant 2: Met-Ser-Pro c. Mutant 3: Met-Ser-Pro-Asp-Trp-Arg-Asp-Lys d. Mutant 4: Met-Ser-Pro-Glu-Gly e. Mutant 5: Met-Ser-Pro-Arg-Leu-Leu-Glu-Glyarrow_forwardHuman Chromosome 22 (48 × 106 nucleotide pairs in length) has about 700 protein-coding genes, which average 19,000 nucleotide pairs in length and contain an average of 5.4 exons, each of which averages 266 nucleotide pairs. What fraction of the average protein-coding gene is converted into mRNA? What fraction of the chromosome do these genes occupy?arrow_forwardA polypeptide has the following amino acid sequence: Met-Ser-Pro-Arg-Leu-Glu-Gly The amino acid sequence of this polypeptide was determined in a series of mutants listed in parts a through e. indicate the type of mutation that occurred in the DNA (single-base substitution, insertion, deletion) and the phenotypic effect of the mutation (nonsense mutation, missense mutation, frameshift, etc.). a. Mutant 5: Met-Ser-Pro-Arg-Leu-Leu-Glu-Glyarrow_forward
- A polypeptide has the following amino acid sequence: Met-Ser-Pro-Arg-Leu-Glu-Gly The amino acid sequence of this polypeptide was determined in a series of mutants listed in parts a through e. indicate the type of mutation that occurred in the DNA (single-base substitution, insertion, deletion) and the phenotypic effect of the mutation (nonsense mutation, missense mutation, frameshift, etc.). a. MMutant 4: Met-Ser-Pro-Glu-Glarrow_forwardBriefly discuss why mutant allele 1 fails to produce functional protein. Note that this mutation has no impact on the length of the mRNA transcribed from the gene.arrow_forwarda protein with a molar mass of 3800 g/mol is given. determine the number of nucleotides contained in the gene that encoded this protein, knowing that: 20% of it are introns, the mass of a nucleotide is 300 g/mol and the mass of an amino acid is 110 g/molarrow_forward
- The protein encoded by the cystic fibrosis gene is 1480amino acids long, yet the gene spans 250 kb. How is thisdifference possible?arrow_forwardA double mutant produced by uneven crossing-over contains two single nucleotide mutations that result in frame shifts and are separated by about 20 base pairs. The first is an insertion, while the second is a deletion. The amino acid sequences of the wildtype and mutant polypeptide in this region of the protein are as follows: Wildtype: Lys – Lys – Tyr – His – Gln – Trp – Thr – Cys – AsnDouble Mutant: Lys – Gln – Ile – Pro – Pro – Val – Asp – Met – Asn a) What are the original and double mutant mRNA sequences. You may find it useful to use the conventional symbols Y for pyrimidine, R for purine, N for any nucleotide, and H for A,C, or T. 2. b) Which nucleotide was inserted? 3. c) Which nucleotide was deleted?arrow_forwardMetabolic syndrome is a genetic disorder with symptoms of hypertension, elevated blood cholesterol concentrations, and lower-than-normal blood magnesium concentrations. This syndrome is caused by a mutation in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) in which a thymine nucleotide is replaced by a cytosine nucleotide. Which of the following identifies the mutated mtDNA and the corresponding mRNA and tRNA produced in a person with metabolic syndrome if the normal mtDNA triplet is TCG? Select one: a. Mutated mtDNA: CCG mRNA: GGC tRNA: GGC b. Mutated mtDNA: TCG mRNA: UGC tRNA: ACG c. Mutated mtDNA: CCG mRNA: GGC tRNA: CCG d. Mutated mtDNA: TTG mRNA: AAC tRNA: UUCarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





