
(a)
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer
(b)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
(c)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of
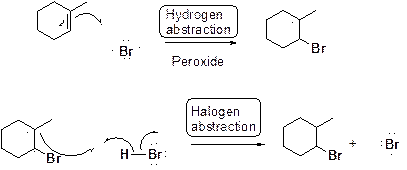
(d)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of alkene in presence of peroxide:
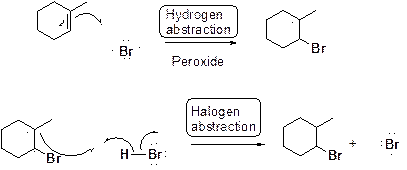
(e)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of alkene in presence of peroxide:
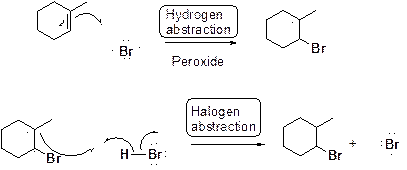
(f)
Interpretation:
The alkyl halide which will be obtained in greater yield from the given reaction has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-super imposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-super imposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer.
Bromination of alkene in presence of peroxide:
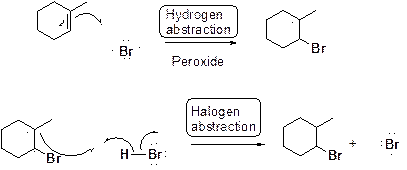
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Books a la Carte Edition (8th Edition)
- Which alkene product would you expect to be the major product under kinetic conditions? Under thermodynamic conditions? The given pictures are the reactions in which we have to determine which alkene product we expect would be the major product under kinetic and thermodynamic conditions.arrow_forwardDraw the alkene that would react with the reagent given to account for the product formed. ? + H₂O H₂SO4 CH3 CH3CCH3 OH You do not have to consider stereochemistry. You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. Sn [F ChemDoodleⓇarrow_forwardThe following reaction could produce an isomeric mixture of three alkenes. Please answer the following questions.arrow_forward
- 2. Explain the selectivity of the following reaction, which produces a single product despite both alkene carbons being equally substituted. H3C CF3 HBr CF3 H3C CF3 H3C Br- H3C only product -H CF3arrow_forwardSynthesize the products by drawing out reagents and intermediates along the way.arrow_forwardFrom which alkene can the following alkyl halides be obtained? a) 3-chloro-3-methylpentaneb) 1-bromo-1-ethylcyclopentanec) 1-chloro-3-methylcyclohexaned) 1-ethyl-1-iodocyclohexanec) 1-bromo-3-ethylpentanearrow_forward
- Alkyl halides undergo substitution reactions with nucleophiles. Explain this ?arrow_forwardDraw the alkene that would react with the reagent given to account for the product formed. ? + H₂O ● You do not have to consider stereochemistry. You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. 8 H₂SO4 // CH3 CH3CHCCH3 OH CH3 ? [F Previous Email Instructarrow_forwardProvide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. CH3 CI CH3 I (S)- (Z)- (R)-) ((E)-) 6- 3- 5-2-4-1- sec- iso cyclo di tert- tri chloro but carbo) pent] meth) (hex) ide ane yne yl ene Xarrow_forward
- 7. Draw a mechanism (use arrows) for the for the formation of products when 1-bromo-2-1 methylcyclohexane reacts with methanolarrow_forwardPredict the -elimination product(s) formed when each chloroalkane is treated with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. If two or more products might be formed, predict which is the major product.arrow_forwardcomplete the following synthesesarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

