
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of chlorination product obtained from radical chlorination of methylcyclohexane has to be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chlorination:
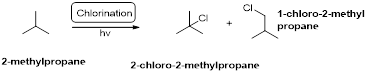
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination which yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product obtained in greater yield should be given and explained.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chlorination:
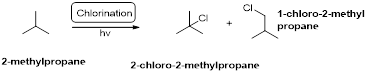
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination which yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of monochlorination products obtained by considering all stereoisomers should be given.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical.
Bond strength is depends on the formation of the radical, if the radical is involving in resonance which is weakest bond strength.
Chlorination:
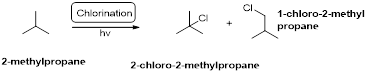
2-methylpropane undergoes radical chlorination which yields the 2-chloro-2-methylpropane and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
Chiral: Four different atoms attached to a carbon atom is called chiral molecule.
Stereoisomers: Stereoisomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula and they differ only in arrangement of atom in three-dimensional space.
Enantiomers: A compound which is non-superimposable mirror image is called enantiomers.
Diastereomers: A compound which is non-superimposable and non-mirror image is called enantiomers
Racemic mixture: A racemic mixture is simply a mixture containing an equal amount of each enantiomer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- How many moles of Bra are required to completely halogenate the alkene?A. One moleB. Two molesC. Three molesD. Four moles What is the expected arrangement of the bromine atoms relative to each other amongthe carbon involved in pi bonding?A. anti-conformationB. syn-conformationC. trans-configurationD. cis-configuration What happens to bromine when it is adjacent to an alkene during a chemical reaction?A. Bromine becomes stable. (? kasi before brown siya/acidic tas naging colorless? Jk ewan)B. Bromine becomes polarized.C. Bromine becomes hybridized.D. Bromine becomes acidic. The relative arrangement of bromine atoms in the product is primarily due to:A. ElectronegativityB. RepulsionC. Hydrogen bondingD. Atomic weightWhat is your observation after the reaction?A. A yellow flame is produced.B. Bromine water decolorizes.C. The alkene becomes denser.D. A brown precipitate forms.arrow_forward2-Methyl-2-butene reacts with HBr in the presence of peroxide to give a. a secondary alkyl bromide. b. a primary alkyl bromide. c. a tertiary alkyl bromide. d. a vicinal dibromide.arrow_forward* Explain the chemical foundation:a. The addition of water and alcohol to alkenes is only possible under. Acid catalysis.b. Electrophilic addition reactions are not stereospecific (except in the case of X2 addition).c. Regioselectivity in the X2 addition reactions, even though carbocations are not formed in this mechanism.arrow_forward
- 10. In free-radical substitution reaction of alkanes with halogens under uv light, A. the photolytic breaking of the halogen is the rate determining step. B. the abstraction of hydrogen from alkane by the halogen radical is the rate determining step C. the formation of alkylradical is the rate determining step. D. the formation of halogen radical is the rate determining step. 11. Which of the following processes could be the termination step in free radical substitution reaction? A. C₂H6 ---→ 2CH3- B. C₂H6 +H --⇒ H₂ + C₂H5 C. CH3 + CH3 --→ C₂H6 D. C₂H5 --→ C₂H4 + Harrow_forward10. In free-radical substitution reaction of alkanes with halogens under uv light, A. the photolytic breaking of the halogen is the rate determining step. B. the abstraction of hydrogen from alkane by the halogen radical is the rate determining step C. the formation of alkylradical is the rate determining step. D. the formation of halogen radical is the rate determining step. 11. Which of the following processes could be the termination step in free radical substitution reaction? A. C₂H6 ---→ 2CH3 B. C₂H6 +H. --→ H₂ + C₂H5 C. CH3 + CH3 --→ C₂H₂ D. C₂H5 --→ C₂H4 + H 12. Which of the following is the most stable carbonium ion intermediate? A. primary carbonium ion B. secondary carbonium ion C. tertiary carbonium ion D. allyl carbonium ionarrow_forward4. How many mono-chlorination products are possible for 3-methylpentane? Draw them out.arrow_forward
- Organic chemistry:What is Grignard reagent /synthesis used for ? And how can you tell if a a molecule is Grignard or NOT?arrow_forwardRadicals and carbocations are electrophiles. Define how and why ?arrow_forwardIn the addition reactions of alkynes, the reagents undergo transformation to form first. a. a nucleophile b. an electrophile c. a carbocation d. a radicalarrow_forward
- 1. Which among these can make a molecule nucleophilic? a.double bondsb.positive chargec. incomplete octet 2. Which among these can make a molecule electrophilic? a.Triple bondsb.positive chargec. radicalsarrow_forward5.) cyclopentane Why slightly soluble in water? Why insoluble in HCl? Why completely soluble in NaOH? Why insoluble in NaHCO?arrow_forwardShow how to convert propene to each of these compounds, using any inorganic reagents as necessary. a. Propane b.1,2-Propanediol c. 1-Propanol d. 2-Propanol e. Propanal f. Propanone g. Propanoic acid h. l-Bromo-2-propanol i. 3-Chloropropene j. 1,2,3-Trichloropropane k. 1-Chloropropane l. 2-Chloropropane m. 2-Propen-1-ol n. Propenalarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
