
Concept explainers
Common baker’s yeast (
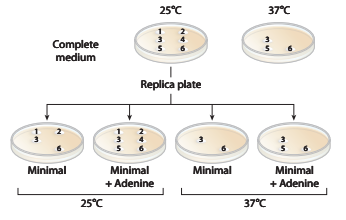
a. Which colonies are prototrophic and which are auxotrophic? What growth information is used to makethese determinations?
b. Classify the nature of the mutations in colonies
c. What can you say about colony
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- Baker's yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is a single-celled, diploid fungus (which is, of course, a eukaryote, that is capable of both meiosis and sexual reproduction). Wild type yeast can normally grow on solid or liquid minimal medium; you isolate three mutant strains which are no longer capable of growing on minimal medium alone, however, they can grow on medium supplemented with adenine. All three yeast strains are homozygous for the underlying alleles. When you cross mutant strain 1 and mutant strain 2, the offspring cannot grow on minimal medium alone and require adenine supplementation; when you cross mutant strain 1 and mutant strain 3, the offspring can grow on minimal medium alone and do not require adenine. After crossing the F1 generation of the cross between mutant strains 1 and 3, you count and determine the phenotypes of 1,000 colonies (here a colony is equivalent to an individual): 563 colonies that can grow on minimal medium alone; 437 colonies that require adenine…arrow_forwardBaker's yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is a single-celled, diploid fungus (which is, of course, a eukaryote, that is capable of both meiosis and sexual reproduction). Wild type yeast can normally grow on solid or liquid minimal medium; you isolate three mutant strains which are no longer capable of growing on minimal medium alone, however, they can grow on medium supplemented with adenine. All three yeast strains are homozygous for the underlying alleles. When you cross mutant strain 1 and mutant strain 2, the offspring cannot grow on minimal medium alone and require adenine supplementation; when you cross mutant strain 1 and mutant strain 3, the offspring can grow on minimal medium alone and do not require adenine. A. What conclusions can you make about the alleles of mutant strains 1, 2, and 3 and their relationships with each other? B. What phenomenon is occurring in the cross between mutant strains 1 and 3? After crossing the F1 generation of the cross between mutant strains 1…arrow_forwardBaker's yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is a single-celled, diploid fungus (which is, of course, a eukaryote, that is capable of both meiosis and sexual reproduction). Wild type yeast can normally grow on solid or liquid minimal medium; you isolate three mutant strains which are no longer capable of growing on minimal medium alone, however, they can grow on medium supplemented with adenine. All three yeast strains are homozygous for the underlying alleles. When you cross mutant strain 1 and mutant strain 2, the offspring cannot grow on minimal medium alone and require adenine supplementation; when you cross mutant strain 1 and mutant strain 3, the offspring can grow on minimal medium alone and do not require adenine. A. What conclusions can you make about the alleles of mutant strains 1, 2, and 3 and their relationships with each other? B. What phenomenon is occurring in the cross between mutant strains 1 and 3?arrow_forward
- After preparing cultures and completing a six-hour growth and viability trial, you notice that your lab partner had only used 5 mL of YPD media to prepare your low concentration experimental culture. Your medium and high concentration experimental cultures received 10 mL of YPD as required. What do you think happened to the growth and viability of your yeast during your trials? Why?arrow_forwardA pure culture of an unknown bacterium was streaked onto plates of a variety of media. You notice that the colony morphologyis strikingly different on plates of minimal media with glucose compared to that seen on trypticase soy agar plates. How can you explain these differences in colony morphology? Also, describe what happens when a nonsense mutation is introduced into the gene encoding transposase within a transposon and why is it more likely that insertions or deletions will be more detrimental to a cell than point mutations?arrow_forwardA high cell density culture of recombinant E. coli was carried out according to the following strategy:-Step 1: single batch with exponential growth until 98% conversion of the substrate, starting from V0= 4.0 L, S0=50 g/L/ X0= 1.0 g/LStep 2: batch fed with exponential flow (SF-800 g/L, μ= 0.1 h-1) until reaching X= 50.9 g/L;Step 3: batch fed with constant flow (F= 0.1 L/h) for 4 hours (induction phase with IPTG)Note: consider that the quasi-steady state is reached in both fed-batch stages.Extra data: YX/S = 0.4 gx/gs; μmax= 0.25 h-1; Ks== 1.0 g/L a) What was the cell concentration reached at the end of step 1?b) For step 3, considering that the substrate concentration in the feed was 1/4 of that used in step 2, what was the concentration of cells reached at the end of step 3?C) In terms of cell productivity, which of the three phases of cultivation was the most productive?arrow_forward
- A research group is studying a bacterium X that binds to mucosal cells in the lung and invades. Wildtype X has an LD50 value of 10 bacteria when administered to mice by inhalation. Using transposon mutagenesis, the researchers have isolated two mutants of X that they call Xmut1 and Xmut2, both of which have LD50 values of 105 when inhaled by mice. However, in tissue culture cells, Xmut1 can invade the cells just as well as wild-type X, while Xmut2 cannot. Provide a possible explanation for these results.arrow_forwardpZERO®-1 is a 2808 bp cloning vector from Invitrogen. This vector allows effective selection of positive recombinants via disruption of the lethal gene, ccdB. Besides the lethal gene, it has an additional Zeocin resistance gene for tighter screening control. The Zeocin resistance gene in this vector is certainly more advantageous over ampicillin resistance gene. Give its THREE (3) advantages.arrow_forwardThe following two strains of E. coli are crossed with each other: Hfr pan* thi* ala* and F¯pan¯ thi¯ ala¯ It was shown that the pan marker entered last in interrupted conjugation experiments. By spreading the bacteria from these experiments on different selection media, the following results (in number of colonies) were obtained: MM + Gluc IM + Gluc + ala MM + Gluc + thi MM + Gluc + thi + ala 280 281 286 339 Give the number of each phenotypic class and justify your answer. Determine the order of the genes. What are the genetic distances between the different loci? Abbreviations: Gluc: glucose; Ala: alanine; Thi: thiamine; Pan: pantothenic acid.arrow_forward
- You have conducted a transposon mutagenesis experiment using the same PRL27 system that was used during your lab exercise. After allowing for conjugation. you plate the conjugation mix on Luria agar and Luria + Kanamycin agar. After incubation, you count the following number of colonies on each type of plate: Media Dilution Number of Colonies Too Many to Luria 10-5 Count 10-6 173 10-7 28 Luria + Kanamycin 100 324 10-1 217 10-2 3 Determine the transformation efficiency. Note: You can enter you answer using long form (e.g. 1500000) or scientific notation using e notation (e.g. 1.5e6). Do not enter units.arrow_forwardOrder the steps of generating a yeast knockout.arrow_forwardGiven what we've discussed in class, what will be most likely outcome if you conjugate an streptomycin resistant ampicillin sensitive methionine auxotroph E. coli strain (engineered to be pir+) that is F- with a streptomycin sensitive non-HFR methionine prototroph strain that is F- and RP4+ but contains pUC18? Colonies on minimal media + ampicillin +streptomycin plates No colonies on minimal media +ampicillin +streptomycin platesarrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
