
(a)
The graph for the characteristic strength and Weibull modulus.
(a)
Answer to Problem 11.13P
The graph for the characteristic strength and Weibull modulus is shown in figure (1)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The following characteristic strengths are given as,
Formula Used:
Write the expression for the calculation of polymer specimen as:
Here,
Calculation:
The coordinates for the characteristic strength and Weibull modulus is calculated in table below.
| Rank | Stress | |||||
Table (1)
The graph between
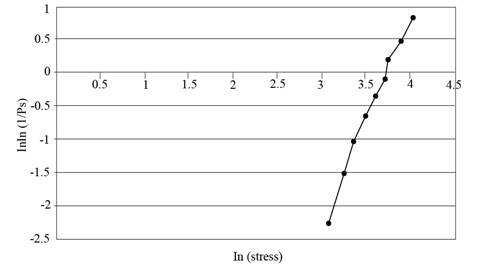
Figure (1)
From Figure (1) it is found that the natural log of characteristics strength on the horizontal axis is
Conclusion:
Thus, the graph for the characteristic strength and Weibull modulus is shown in figure (1)
(b)
The stress for the
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
At very low stresses, such as
From Table (1), it is found that the stress for 90% probability of survival is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the stress for 90% probability of survival is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Materials Science And Engineering Properties
- Q.1 The yield stresses (oy) have been measured using steel and aluminum specimens of various grain sizes, as follows: Material D (µm) σΥ (MPa) Steel 60.5 160 136 128 Aluminum 11.1 235 100 223 (a) Determine the coefficients o and kỵ in the Hall- Petch for these two materials. (b) Determine the yield stress in each material for a grain size of d=26 um.arrow_forwardA 5-mm-thick rectangular alloy bar is subjected to ajtensile load P by pins at A and B, as shown in the figure. The width of the bar is w = 33 mm. Strain gages bonded to the specimen measure the following strains in the longitudinal (x) and transverse (y) directions: €, =710 με and ε,--255 με (a) Determine Poisson's ratio for this specimen. (b) If the measured strains were produced by an axial load of P = 24 kN, what is the modulus of elasticity for this specimen? Answers: (a) v= (b) E= GPaarrow_forward3. Given the following fatigue data for a brass alloy: Cycles to Failure 2 x 105 1х 106 Stress Amplitude (MPa) 310 223 191 3х 106 168 1 x 107 153 3х 107 143 1х 108 134 3х 108 127 1х 109 a.) Plot the S-N curve for this alloy. b.) Does this material have an endurance limit? Explain. c.) Determine the fatigue strength at 5 x 105 cycles. d.) Determine the fatigue life for 200 MPa. e.) If the loading in part c is uniaxial, what is the minimum diameter of a circular rod required for this application if the maximum load is 500 kN?arrow_forward
- In a tensile test for an aluminum alloy, the sample is 2 inches long and 0.5 inches in diameter. The proportional portion of the tension stress-strain diagram for an aluminum alloy is shown below. It the diameter change of the sample was also monitored during the above test, and it was found that the lateral strain of the sample is 1/3 of its axial longitudinal strain, what is the Poisson' ratio of the material under test: ___. Calculate your answer to 2 decimal place.arrow_forwardA thin plate of a ceramic material with E = 225 GPa is loaded in tension, developing a stress of 450 MPa. Is the specimen likely to fail if the most severe flaw present is an internal crack oriented perpendicular to the load axis that has a total length 0.25 mm and a crack tip radius of curvature equal to 1 μm?arrow_forwardA Brinell hardness tester with a diameter of 10 mm and a load of 500 kg gives an impression with a diameter of 1.62 mm in a steel alloy. Calculate the Brinell hardness (HB) in the steel alloyarrow_forward
- For a bronze alloy, the stress at which plastic deformation begins is 275 MPa (40,000 psi), and the modulus of elasticity is 115 GPa (16.7 x106 psi). (a) What is the maximum load that may be applied to a specimen with a cross-sectional area of 325 mm2 (0.5 in.2) without plastic de- formation? (15pts)(b) If the original specimen length is 115 mm (4.5 in.), what is the maximum length to which it may be stretched without causing plastic deformation?(15pts)arrow_forwardThe (G-E) diagram obtained in the tensile test performed on a metal sample with a diameter of 16 mm is as follows. The loads at points A, B and C and the elongation measured on l. 16 cm gauge length were determined as follows: B A B C Load (kgf) 4800 8400 7200 Elongation (mm) 0.192 28.8 38.4 c) Calculate the fracture work and the maximum elastic energy the metal rod can store. d) Find the cross-sectional area of a 6 m long rod made of this metal such that it can carry 12 tons of load with 2 times the safety of yield strength. How long does the rod extend under this load?arrow_forwardFor a material when tested within the elastic limit, the value of Poisson's ratio is 0.35. When the same material is tested in plastic stage, its Poisson's ratio in the plastic stage will be (a) 0.42 (b) 0.37 (c) 0.40 (d) 0.53arrow_forward
- A specimen of metal of original length 80mm and original diameter 21mm was subjected to tensile a test. The load and extension at the limit of proportionality were found to be 105,000N and 0.082mm. The yield point was at a load of 112,00ON. The maximum load before the material failed was 199,000N. The final length at failure was 91mm. Calculate: i. the stress at the limit of proportionality i. the yield stress iii. the ultimate tensile stress iv. the value of Young's Modulus V. the strain at failurearrow_forwardConsider a cylindrical metal 6 mm in diameter and 50 mm long ispulled in tension. It is known that yield strength and elastic (Young’s) Modulus of thematerial are 200 MPa and 100 GPa, respectively, and its Poisson’s Ratio is 0.3.(a) Determine whether the deformation is elastic or plastic when 6000 N is applied.(b) Calculate specimen elongation (∆l) and reduction in diameter (∆d) when 5000 N isapplied? What are the values ∆l and ∆d when the load is released?(c) If necking occurs at a load of 8850 N, determine the UTS of the metal.(d) Calculate the ductility in terms of % E.L. if the length of the specimen at fracturepoint is 56.0 mm.arrow_forwardA cylindrical metal specimen 12.7 mm (0.5 in.) in diameter and 250 mm (10 in.) long is to be subjected to a tensile stress of 28 MPa (4000 psi); at this stress level, the resulting deformation will be totally elastic. (a) If the elongation must be less than 0.080 mm (3.2 x 10-3 in.), which of the metals in Table 6.1 are suitable candidates? O Steel O Nickel Brass O Magnesium O Aluminum O Copper O Titanium O Tungsten (b) If, in addition, the maximum permissible diameter decrease is 1.2 x 103 mm (4.7 × 105 in.) when the tensile stress of 28 MPa is applied, which of the metals that satisfy the criterion in part (a) are suitable candidates? O Aluminum O Magnesium O Steel O Tungsten O Copper O Brass O Titanium O Nickelarrow_forward
 Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
