
Concept explainers
Update UML class diagram from the program below to include from the following program.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Fraction
{
private int n, d;
public Fraction()
{
this.n = this.d = 0;
}
public Fraction(int n, int d)
{
this.n = n;
this.d = d;
}
public int getNum()
{
return n;
}
public int getDen()
{
return d;
}
public boolean isZero()
{
return(getNum() == 0 && getDen() != 0);
}
public boolean isequals(Object c)
{
Fraction f = (Fraction) c;
return(Integer.compare(n,f.n))==0 && (Integer.compare(d,f.d)==0);
}
public String getSimplifiedFraction()
{
String result = "";
if(getNum() == 0 && getDen() == 0)
result = "0";
else if(isZero())
result = "0";
else if(getNum() != 0 && getDen() == 0)
result = "Undefined";
else
{
if(getNum() % getDen() == 0)
result = (getNum() / getDen()) + "";
else if(getNum() < 0 && getDen() < 0)
result = (getNum() * -1) + "/" + (getDen() * -1);
else if(getNum() < 0 || getDen() < 0)
{
if(getNum() < 0)
result = "-" + (getNum() * -1) + "/" + getDen(); // appending a sign.
else
result = "-" + getNum() + "/" + (getDen() * -1); // appending a sign.
}
else
result = (getNum() + "/" + getDen());
}
return result;
}
public void display()
{
System.out.println(getSimplifiedFraction());
}
public Fraction add(Fraction rhs) {
Fraction sum = new Fraction();
sum.d = d * rhs.d;
sum.n = n * rhs.d + d * rhs.n;
sum.simplify();
return sum;
}
private void simplify()
{
int a,b;
if(Math.abs(n) > Math.abs(d))
{
a = Math.abs(n);
b = Math.abs(d);
}
else
{
a = Math.abs(d);
b = Math.abs(n);
}
int r = a%b;
while(r != 0)
{
a = b;
b = r;
r = a%b;
}
n /= b;
d /= b;
}
}
class TestFraction
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String res;
int num, den, num1, den1;
ArrayList<Fraction> fractions = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
do
{
System.out.print("Enter the num: ");
num = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine().trim());
if(num < 0)
break;
System.out.print("Enter the den: ");
den = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine().trim());
Fraction fraction = new Fraction(num, den);
System.out.print("Enter the num to compare: ");
num1 = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine().trim());
if(num1 < 0)
break;
System.out.print("Enter the den to compare: ");
den1 = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine().trim());
Fraction fraction1 = new Fraction(num1, den1);
if(fraction1.isequals(fraction))
{
System.out.println("\nTrue-> Second fraction is equal to First Fraction");
}
else
System.out.println("\nFalse-> Second fraction is not equal to First Fraction");
fractions.add(fraction);
res = fraction.getSimplifiedFraction();
System.out.println("Fraction added to list as: " + res + "\n"); //result is stored in ‘res’ variable
}while(res != "0");
System.out.println("\nDISPLAYING ALL FRACTIONS:\n" + "-------------------------");
for(Fraction fr : fractions)
fr.display();
System.out.println();
sc.close();
Fraction f = new Fraction(4, 8);
System.out.println("1st fraction: ");
f.display();
Fraction fc = new Fraction(8, 24);
System.out.println("2nd fraction: ");
fc.display();
Fraction res1 = f.add(fc);
System.out.println("Sum: ");
res1.display();
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
class TestMain {
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args)
{
do
{
Fraction fraction = takeFractionValues();
if (!fraction.isZero())
{
System.out.println("\nEnter Second Fraction Details: ");
Fraction fraction1 = takeFractionValues();
System.out.println(fraction + " AND " + fraction1);
if (fraction1.isEquals(fraction)) {
System.out.println("\nTrue-> Both Fractions are Equal");
} else
System.out.println("\nFalse-> Both Fractions are not Equal");
Fraction result = fraction.add(fraction1);
result.simplify();
System.out.println("Result of Both Fraction Addition: " + result);
} else
break;
System.out.println("\nEnter First fraction as Zero Fraction to end the Loop");
}
while (true);
System.out.println("\n\nFinished Working with Fractions...");
}
public static Fraction takeFractionValues() {
int num, denom;
System.out.print("Enter the num: ");
num = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine().trim());
while (true) {
String append = "";
System.out.print("Enter the den "+append+": ");
denom = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine().trim());
if (denom == 0) {
System.out.println("Denominator can't be zero");
append = "again";
} else
break;
}
return new Fraction(num, denom);
}
}
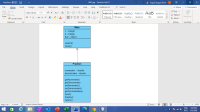
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

- I need help with fixing this java program as described in the image below: import java.util.Scanner; public class LabProgram { /* TODO: Write recursive drawTriangle() method here. */ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scnr = new Scanner(System.in); int baseLength; baseLength = scnr.nextInt(); drawTriangle(baseLength); } }arrow_forwardCreate the UML Diagram for this java code import java.util.Scanner; interface Positive{ void Number();} class Square implements Positive{ public void Number() { Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter a number: "); int a = in.nextInt(); if(a>0) { System.out.println("Positive number"); } else { System.out.println("Negative number"); } System.out.println("\nThe square of " + a +" is " + a*a); System.out.println("\nThe cubic of "+ a + " is "+ a*a*a); }} class Sum implements Positive{ public void Number() { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("\nEnter the value for a: "); int a = in.nextInt(); System.out.println("Enter the value for b" ); int b= in.nextInt(); System.out.printf("The Difference of two numbers: %d\n", a-b); System.out.printf("The…arrow_forwardimport java.util.Scanner; public class AverageWithSentinel{ public static final int END_OF_INPUT = -500; public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); // Step 2: Declare an int variable with an initial value // as the count of input integers // Step 3: Declare a double variable with an initial value // as the total of all input integers // Step 4: Display an input prompt // "Enter an integer, -500 to stop: " // Step 5: Read an integer and store it in an int variable // Step 6: Use a while loop to update count and total as long as // the input value is not -500. // Then display the same prompt and read the next integer // Step 7: If count is zero // Display the following message // "No integers were…arrow_forward
- import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Random; public class Board { /** * Construct a puzzle board by beginning with a solved board and then * making a number of random moves. That some of the possible moves * don't actually change what the board looks like. * * @param moves the number of moves to make when generating the board. */ public Board(int moves) { throw new RuntimeException("Not implemented"); } The board is 5 X 5. You can add classes and imports like rand.arrow_forwardimport java.util.*; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { Main m = new Main(); m.go(); } private void go() { List<Stadium> parks = new ArrayList<Stadium>(); parks.add(new Stadium("PNC Park", "Pittsburgh", 38362, true)); parks.add(new Stadium("Dodgers Stadium", "Los Angeles", 56000, true)); parks.add(new Stadium("Citizens Bank Park", "Philadelphia", 43035, false)); parks.add(new Stadium("Coors Field", "Denver", 50398, true)); parks.add(new Stadium("Yankee Stadium", "New York", 54251, false)); parks.add(new Stadium("AT&T Park", "San Francisco", 41915, true)); parks.add(new Stadium("Citi Field", "New York", 41922, false)); parks.add(new Stadium("Angels Stadium", "Los Angeles", 45050, true)); Collections.sort(parks, Stadium.ByKidZoneCityName.getInstance()); for (Stadium s : parks) System.out.println(s); }}…arrow_forwardC++arrow_forward
- Using Java.arrow_forwardStringFun.java import java.util.Scanner; // Needed for the Scanner class 2 3 /** Add a class comment and @tags 4 5 */ 6 7 public class StringFun { /** * @param args not used 8 9 10 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Please enter your first name: "); 13 14 15 16 17 18 System.out.print("Please enter your last name: "); 19 20 21 //Output the welcome message with name 22 23 24 //Output the length of the name 25 26 27 //Output the username 28 29 30 //Output the initials 31 32 33 //Find and output the first name with switched characters 34 //All Done! } } 35 36 37arrow_forwardCorrect my codes in java // Arraysimport java.util.Scanner;public class Assignment1 {public static void main (String args[]){Scanner sc=new Scanner (System.in);System.out.println("Enter mark of student");int n=sc.nextInt();int a[]=new int [n];int i;for(i=0;i<n;i++){System.out.println("Total marks of student in smster");a[i]=sc.nextInt();}int sum=0;for(i=0;i<n;i++){sum=sum+a[i];}System.out.println("Total marks is :");for (i=0;i<n;i++);{System.out.println(a[i]);}System.out.println();}}arrow_forward
- PRACTICE CODE import java.util.TimerTask;import org.firmata4j.ssd1306.MonochromeCanvas;import org.firmata4j.ssd1306.SSD1306;public class CountTask extends TimerTask {private int countValue = 10;private final SSD1306 theOledObject;public CountTask(SSD1306 aDisplayObject) {theOledObject = aDisplayObject;}@Overridepublic void run() {for (int j = 0; j <= 3; j++) {theOledObject.getCanvas().clear();theOledObject.getCanvas().setTextsize(1);theOledObject.getCanvas().drawString(0, 0, "Hello");theOledObject.display();try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}theOledObject.clear();theOledObject.getCanvas().setTextsize(1);theOledObject.getCanvas().drawString(0, 0, "My name is ");theOledObject.display();try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}while (true) {for (int i = 10; i >= 0; i--)…arrow_forwardWrite in Java What is this program's exact outputarrow_forwardI need help with this Java problem to output as it's explained in this image below: import java.util.Scanner;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;public class LabProgram { static public int recursions = 0; static public int comparisons = 0; private static ArrayList<Integer> readNums(Scanner scnr) { int size = scnr.nextInt(); ArrayList<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { nums.add(scnr.nextInt()); } return nums; } static public int binarySearch(int target, ArrayList<Integer> integers, int lower, int upper) { recursions+=1; int index = (lower+upper)/2; comparisons+=1; if(target == integers.get(index)){ return index; } if(lower == upper){ comparisons+=1; if(target == integers.get(lower)){ return lower; } else{…arrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





