
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
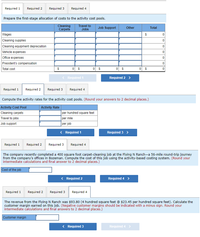
Transcribed Image Text:**Activity-Based Costing Exercise**
**Step 1: Allocation of Costs to Activity Cost Pools**
Prepare the first-stage allocation of costs to the activity cost pools:
| | Cleaning Carpets | Travel to Jobs | Job Support | Other | Total |
|---------------------|------------------|----------------|-------------|-------|-------|
| Wages | | | | | $0 |
| Cleaning supplies | | | | | 0 |
| Cleaning equipment depreciation | | | | | 0 |
| Vehicle expenses | | | | | 0 |
| Office expenses | | | | | 0 |
| President’s compensation | | | | | 0 |
| **Total Cost** | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
**Step 2: Computation of Activity Rates**
Compute the activity rates for the activity cost pools. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.)
| Activity Cost Pool | Activity Rate |
|----------------------|------------------------------|
| Cleaning carpets | _______ per hundred square feet |
| Travel to jobs | _______ per mile |
| Job support | _______ per job |
**Step 3: Job Cost Calculation**
The company recently completed a 400 square foot carpet-cleaning job at the Flying N Ranch—a 56-mile round-trip journey from the company’s offices in Bozeman. Compute the cost of this job using the activity-based costing system. (Round your intermediate calculations and final answer to 2 decimal places.)
| **Cost of the Job** | ____________________________ |
**Step 4: Customer Margin Calculation**
The revenue from the Flying N Ranch was $93.80 (4 hundred square feet @ $23.45 per hundred square feet). Calculate the customer margin earned on this job. (Negative customer margins should be indicated with a minus sign. Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.)
| **Customer Margin** | ______________________________ |
---
This exercise guides students through the process of activity-based costing by focusing on assigning costs to specific activities, determining activity rates, computing job costs, and assessing customer margins.

Transcribed Image Text:Gallatin Carpet Cleaning is a small, family-owned business based in Bozeman, Montana. The company traditionally charges a fee of $23.45 per hundred square feet of carpet cleaned. Some questions have arisen about the profitability of certain jobs, especially those on remote ranches that require extensive travel. The owner's daughter, using activity-based costing, designed a system comprising four activity cost pools with corresponding measures:
### Activity Cost Pools and Measures
| Activity Cost Pool | Activity Measure | Activity for the Year |
|----------------------------------|-------------------------------|-----------------------|
| Cleaning carpets | Square feet cleaned (00s) | 10,500 hundred square feet |
| Travel to jobs | Miles driven | 389,000 miles |
| Job support | Number of jobs | 2,000 jobs |
| Other (Organization-sustaining costs and idle capacity costs) | None | Not applicable |
### Total Operating Costs for the Year:
The annual cost of operating the company is $364,000, broken down as follows:
- Wages: $149,000
- Cleaning supplies: $30,000
- Cleaning equipment depreciation: $6,000
- Vehicle expenses: $78,000
- Office expenses: $68,000
- President's compensation: $33,000
- **Total cost**: $364,000
### Distribution of Resource Consumption Across Activities:
The table below displays how resources are distributed across different activities:
| | Cleaning Carpets | Travel to Jobs | Job Support | Other | Total |
|----------------------------------|----------------|----------------|------------|------|------|
| **Wages** | 75% | 5% | 11% | 9% | 100% |
| **Cleaning supplies** | 100% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 100% |
| **Cleaning equipment depreciation** | 100% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 100% |
| **Vehicle expenses** | 0% | 75% | 25% | 0% | 100% |
| **Office expenses** | 6% | 0% | 50% | 44% | 100% |
| **President's compensation** | 0% |
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- University Printers has two service departments (Maintenance and Personnel) and two operating departments (Printing and Developing). Management has decided to allocate maintenance costs on the basis of machine-hours in each department and personnel costs on the basis of labor-hours worked by the employees in each. The following data appear in the company records for the current period: Maintenance Personnel Printing Developing 3,000 2,000 $29,500 Machine-hours 1,000 1,000 Labor-hours 500 500 Department direct costs $14,000 $38,500 $43,500 University Printers estimates that the variable costs in the Personnel Department total $17,750 and in the Maintenance Department variable costs total $8,100. Avoidable fixed costs in the Personnel Department are $5,600. Required: If University Printers outsources the Personnel Department functions, what is the maximum it can pay an outside vendor without increasing total costs? (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Maximum Amountarrow_forwardA company computed the following activity rates using activity-based costing. Activity Setup Materials handling Inspection Activity Setup The company's deluxe model used the following activities to produce 2,000 units. Compute the overhead cost per unit for the deluxe model using activity-based costing. Materials handling Inspection /* 3 E Multiple Choice D C $ $6.00 $8.50. 4 101 R F V % 5 $2,000 per setup $100 per materials requisition $4 per unit inspected T 6 setups 50 materials requisitions 2,000 units inspected G Activity Rate ^ Activity Rate 40 6 Y H & Q Search 4- O ► 11 ) O fn P 112 + C = ins A prt sc ] delete backspacearrow_forwardYour Companey has two service departments – Personnel and Maintenance. The Maintenance Department's costs of $160,000 are allocated on the basis of standard hours used. The Personnel Department's costs of $40,000 are allocated based on the number of employees. The costs of the operating Departments A and B are $80,000 and $120,000, respectively. Data on standard service hours and number of employees are as follows: Standard Service Maintenance Dept. Personnel Dept. Production Depts. A B Hours used - 400 480 320 Number of Employees 20 - 80 240 What is the cost of the Maintenance Department allocated to Department B using the direct method? What is the cost of the…arrow_forward
- Hazelnut Corporation manufactures lawn ornaments. It currently has two product lines, the basic and the luxury. Hazelnut has a total of $143,484 in overhead. The company has identified the following information about its overhead activity pools and the two product lines: Quantity or Amount Consumed by Basic Activity Pools Materials handling Quality control Machine maintenance Cost Driver Number of moves Number of inspections Number of machine hours Required 1 Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Basic Model Luxury Model Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Required: 1. Suppose Hazelnut used a traditional costing system with machine hours as the cost driver. Determine the amount of overhead assigned to each product line. 2. Calculate the activity rates for each activity pool in Hazelnut's ABC system. 3. Calculate the amount of overhead that Hazelnut will assign to the basic line if it uses an ABC system. 4. Determine the amount of overhead Hazelnut will assign…arrow_forwardMack Precision Tool and Die has two production departments, Fabricating and Finishing, and two service departments, Repair and Quality Control. Direct costs for each department and the proportion of service costs used by the various departments for the month of March follow: Department Fabricating Finishing Repair Quality Control Required A Required B Direct Costs Repair $ 136,600 102, 200 43,800 81,800 Required: Use the step method to allocate the service costs, using the following: From: a. The order of allocation starts with Repair. b. The allocations are made in the reverse order (starting with Quality Control). Service department costs Repair Quality control Total costs allocated Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. $ $ Repair Proportion of Services Used by Quality Control 0 0.8 Use the step method to allocate the service costs, using the following: The order of allocation starts with Repair. Note: Amounts to be deducted should be indicated by a minus…arrow_forwardI am having trouble figuring out how to set this up. Rand Company computed the following activity rates using activity-based costing. Activity Activity Rate Setup $ 1,000 per setup Materials handling $ 50 per materials requisition Inspection $ 2 per unit inspected The company’s deluxe model used the following activities to produce 1,000 units. Activity Actual Activity Usage Setup 3 setups Materials handling 25 materials requisitions Inspection 1,000 units inspected Compute the overhead cost per unit for the deluxe model using activity-based costing.arrow_forward
- Fisher Fixtures manufactures three types of lighting fixtures, with model names of Silver, Gold, and Platinum. It applies all indirect costs according to an annual predetermined rate based on direct labor-hours. The plant controller has recommended that the company switch to an activity-based costing system. The controller's staff prepared the following cost estimates for next year (year 2) for the recommended cost drivers. Activity Recommended Cost Driver Estimated Cost Estimated Cost Driver Activity Purchasing material Number of purchase orders $ 130,800 240 purchase orders Receiving material Direct materials cost 238,400 $ 2,980,000 Setting up equipment Number of production runs 231,840 120 runs Machine depreciation and maintenance Machine-hours 80,260 16,052 hours Ensuring regulatory compliance Number of inspections 459,000 54 inspections Shipping Number of units shipped 1,087,200 604,000 units Total estimated cost $ 2,227,500 In addition, management…arrow_forwardDhapaarrow_forwardRex Industries has identified three different activities as cost drivers: machine setups, machine hours, and inspections. The overhead and estimated usage are: Compute the overhead rate for each activity. Round your answers to two decimal places. Overhead Overhead Annual Rate per Activity per Activity Usage Activity Machine Setups $157,850 4,100 $ Machine Hours 324,622 14,114 2$ Inspections 119,000 3,400arrow_forward
- Wheeler's Bike Company manufactures custom racing bicycles. The company uses a job order cost system to determine the cost of each bike. Estimated costs and expenses for the coming year follow: Bike parts Factory machinery depreciation Factory supervisor salaries Factory direct labor Factory supplies Factory property tax Advertising cost Administrative salaries Administrative-related depreciation Total expected costs Required: 1. Calculate the predetermined overhead rate per direct labor hour if the average direct labor rate is $11.91 per hour. 2. Determine the amount of applied overhead if 18,600 actual hours are worked in the upcoming year. Required 1 Required 2 Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. $ 341,800 61,500 140,000 211,998 Predetermined Overhead Rate 39,400 33,750 22,500 55,000 19, 200 $925,148 Calculate the predetermined overhead rate per direct labor hour if the average direct labor rate is $11.91 per hour. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal…arrow_forwardHensel Manufacturing separates its manufacturing overhead costs into 2 broad categories: (1) maintenance costs and (2) utility costs. Maintenance costs average $100,000 per month, whereas utility costs average $8,000 per month. Maintenance costs are allocated to 2 activity cost pools: (1) the repair cost pool and (2) the set-up cost pool. Utility costs also are allocated to 2 activity cost pools: (1) the heating and air conditioning cost pool (HVAC) and (2) the machinery cost pool. Maintenance costs are allocated to their unique activity cost pools on the basis of the number of employees associated with each pool. Utility costs are allocated to their unique activity cost pools on the basis of kilowatt-hour (kWh) consumption. Of the company's maintenance employees, 70% engage primarily in repair activities, whereas 30% engage primarily in set-up activities. Approximately 75% of the company's kWh consumption can be traced to HVAC use, whereas 25% of its kWh consumption can be traced to…arrow_forwardMultiple Choice $6.49 $5.63 $3.92 $5.20arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education