
Concept explainers
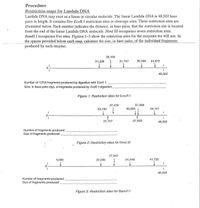
The horizontal line represents the whole genome of Lambda DNA (a virus that infects a bacterial cell). The genome is 48,502 base pairs long. You are going to estimate the number and length in base pairs the fragments that result from cutting the lambda genome with three different enzymes (Eco R1, Hind III and Bam H1)
Keep in mind that you are working with a linearized lambda DNA (has ends) because the DNA has been heated to 65oC and therefore, the cos site is not intact (not annealed)
The restriction enzyme is the restriction endonuclease which recognises and cut at the specific sequence in either a staggered or blunt manner.
The given genome is of Lambda phage whose cos site is not intact. The cos sites help in the circularization of phage DNA when present. Due to the loss of cos site, the genome of lambda phage will remain linear and will not circularize.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

- Choose the correct gel electrophoretic pattern that would be seen in dideoxy sequence analysis of the DNADNA molecule shown below. pGGCGACCGATTAGTCCCATCGATGGG−OHarrow_forwardGiven the DNA sequence of the restriction enzyme: gi|6329444|dbj|AB034757.1| Hynobius retardatus mRNA for larval beta-globin, complete cds GCAGAATCTGACTCAAGAAATCCCTCCTCACCCAACACCACCAGCAGCCATGGTTCACTGGACAGCAGAGGAGAAGGCAGCCATCAGCTCTGTGTGGAAGCAGGTGAACGTGGAGAGCGATGGACAGGAGGCCCTGGCCAGGTTGCTGATCGTCTACCCCTGGACCCAGAGATACTTCAGCTCTTTTGGGGACCTGTCGAGCCCAGCTGCCATTTGTGCCAACGCCAAGGTCCGTGCCCATGGCAAGAAGGTCCTGTCCGCCCTGGGAGCCGGCGCCAACCACCTGGATGACATCAAAGGCAACTTTGCTGATCTGAGCAAGCTTCACGCAGACACACTCCATGTGGACCCCAATAACTTCCTGCTCCTGGCAAACTGCCTGGTGATCGTCTTGGCCCGCAAGCTGGGAGCCGCCTTCAACCCTCAAGTCCATGCGGCCTGGGAGAAGTTCCTGGCCGTCTCCACCGCGGCTCTGTCCAGAAACTACCACTAGAGACTGGTCTTTGGGTTTAATTCTGTGAACGTCCCTGAGACAAATGATCTTTCAATGTGTAAACCTGTCATTACATCAATAAAGAGACATCTAACAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA Identify two blunt-end cutters Identify two sticky-end cutters. For each, Provide the sequence of the Restriction enzyme, Highlight using a specific color where the DNA sequence where the restriction enzyme will cut the DNA Indicate the…arrow_forwardBy average, how many Sau3A (5’GATC3’) sites are there in a 10 kd DNA molecule? (1/4)^6 * 10,000 = 2.44140625 => 2.4 For the above 10 kb DNA, if you use Sau3A to do a complete digestion, you will only get a lot of small fragments ( 200~500 base pairs). What should I do if I want to get larger digested fragments (say 3 to 5 kb) Please answer asap and type your answer and do not copy from anywhere pleasearrow_forward
- How much 340bp insert DNA should be added to a ligation in which 50ng of 4.3kb vector will be used? The desired vector: insert molar ratio needs to be 1:3.arrow_forwardCan you please help with 1c please picture with 1 graph is for question 1a) picture with 4 graphs is for question 1b) 1a) E. coli DNA and binturong DNA are both 50% G-C. If you randomly shear E. coli DNA into 1000 bp fragments and put it through density gradient equilibrium centrifugation, you will find that all the DNA bands at the same place in the gradient, and if you graph the distribution of DNA fragments in the gradient you will get a single peak (see below). If you perform the same experiment with binturong DNA, you will find that a small fraction of the DNA fragments band separately in the gradient (at a different density) and give rise to a small "satellite" peak on a graph of the distribution of DNA fragments in the gradient (see below). Why do these two DNA samples give different results, when they're both 50% G-C? 1b) If you denatured the random 1000 bp fragments of binturong DNA that you produced in question 1a by heating them to 95ºC, and then cooled them down to 60ºC…arrow_forwardEven though the eukaryotic genome is thousands of times larger than the prokaryotic genome, DNA replication times are relatively similar. Explain how this is possible.arrow_forward
- 1) Prepare the following enzymatic reaction, present it in tabulated form. In a final volume of 30 ul, where buffer 4 (10 ml). How much volume of each reagent would be used and how much of water? Is there any problem? 2) The DNA pol 1 enzyme comes at a concentration of 50,000 U/ml. You have to prepare a 50 ug PCR reaction where you must use 0.05 U/ml reaction. You add 10 ul of PCR buffer, 2 ng of tempered DNA that is at a concentration of 0.5 ng/ul, primers (which are at 200 mM) so that each one remains at a concentration of 200 uM, Mg+2 that is 5 mM (10 X), enzyme and water. Present the table of all the reagents included in the reaction, the volumes of each one in ul. Present where the initial and final concentration of each reagent applies. Assume you have micropipettes for all values.arrow_forwardBelow is an EMSA showing four different reactions, A-D. In each tube there is some combination of labelled DNA probe, Protein X (the protein you are studying), and an antibody for Protein X. Identify which combination of components are found in each of the four reactions and explain how you determined that based on the molecular interactions being studied and your knowledge of gel electrophoresis. It is possible that multiple lanes have the same component(s). A B C D EMSAarrow_forwardHow would I calculate sanger sequencing fragments that will produce greenarrow_forward
- All ingredients required for the synthesis of DNA were placed in a test tube. The primer has the sequence 5’-TCGATCA-3’. First determine where the primer will bind to the DNA template given below (Do this by writing the sequence of the primer on top of the template – make sure you find a location that is complementary in sequence and that the primer is antiparallel with respect to the template) and then indicate the nucleotides that DNA polymerase would attach onto the primer as it synthesizes DNA (hint: in which direction does DNA polymerase attach nucleotides onto a primer?) See figure 13.16 in book. 5’-GACGTAGTCTGATGCTAGCATGCTGATCGAAAGAG-3’arrow_forwarda. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a molecule composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix carrying genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses. Select from the drop down menus to complete the complimentary strand for the following DNA molecule: A [ Select ] [ Select ] G [ Select ] [ Select ] [ Select ] A [ Select ] [ Select ] [ Select ] [ Select ] > > > > > >arrow_forwardYou digest 4 uL of plasmid DNA that is 50 ng/uL concetration in a total volume of 20 uL. You run 10 uL of the digest on teh gel. You then do a DNA purification protocol with a Zippy prep on the remaining digested DNA. You elute the DNA in a 25 uL. A 2 uL ssample has the concentration of 2 ng/uL. What is the DNA yield?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





