
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
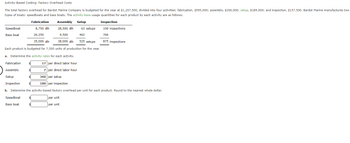
Transcribed Image Text:Activity-Based Costing: Factory Overhead Costs
The total factory overhead for Bardot Marine Company is budgeted for the year at $1,207,500, divided into four activities: fabrication, $595,000; assembly, $266,000; setup, $189,000; and inspection, $157,500. Bardot Marine manufactures two
types of boats: speedboats and bass boats. The activity-base usage quantities for each product by each activity are as follows:
Inspection
Speedboat
Bass boat
Fabrication
Assembly
462
525 setups
Each product is budgeted for 7,500 units of production for the year.
a. Determine the activity rates for each activity.
17 per direct labor hour
7 per direct labor hour
Setup
Inspection
Fabrication
8,750 dlh
$
$
Speedboat
Bass boat
Assembly Setup
28,500 dlh
9,500
38,000 dlh
26,250
35,000 dlh
63 setups
360 per setup
180 per inspection
b. Determine the activity-based factory overhead per unit for each product. Round to the nearest whole dollar.
$
per unit
$
per unit
109 inspections
766
875 inspections
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Activity-Based Costing Zeus Industries manufactures two types of electrical power units, custom and standard, which involve four factory overhead activities-production setup, procurement, quality control, and materials management. An activity analysis of the overhead revealed the following estimated activity costs and activity bases for these activities: Activity Activity Cost Activity Base Production setup $ 44,000 Number of setups Procurement 13,500 Number of purchase orders (PO) Quality control 97,500 Number of inspections Materials management 84,000 Number of components Total $239,000 The activity-base usage quantities for each product are as follows: Purchase Setups Inspections Components Unit Volume Orders Custom 290 760 1,200 500 2,000 Standard 110 140 300 200 2,000 400 900 1,500 700 4,000 Total a. Determine an activity rate for each activity. Activity Rates Production Setup Procurement Quality Control Materials Management Activity cost + Activity base /setup /PO $ /inspection…arrow_forwardFeldpausch Corporation has provided the following data from its activity-based costing system: Activity Cost Pool Total Cost Total Activity Assembly $ 1,398,250 65,800 machine-hours Processing orders $ 69,451 2,520 orders Inspection $ 184,800 2,400 inspection-hours The company makes 920 units of product W26B a year, requiring a total of 1,290 machine-hours, 61 orders, and 40 inspection-hours per year. The product's direct materials cost is $57.55 per unit and its direct labor cost is $13.56 per unit. The product sells for $123.50 per unit. According to the activity-based costing system, the product margin for product W26B is: (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardActivity Base Entry Dining Total Machine hours 5,320 4,710 10,030 Direct labor hours 4,570 6,860 11,430 Number of inspections 1,940 610 2,550 Number of setups 310 70 380 Number of loads 700 190 890 Units produced 10,600 5,300 15,900 a. Determine the activity rate for each activity. If required, round the rate to the nearest dollar. Activity Activity Rate Casting per machine hour Assembly per direct labor hour Inspecting 24 per inspection Setup per setup Materials handling per load b. Use the activity rates in (a) to determine the total and per-unit activity costs associated with each product. Round the per unit amounts to the nearest cent. Product Total Activity Cost Activity Cost Per Unit Entry Lighting Fixtures Dining Room Lighting Fixturesarrow_forward
- Activity-Based Costing Zeus Industries manufactures two types of electrical power units, custom and standard, which involve four factory overhead activities—production setup, procurement, quality control, and materials management. An activity analysis of the overhead revealed the following estimated activity costs and activity bases for these activities: Activity Activity Cost Activity Base Production setup $ 44,000 Number of setups Procurement 13,500 Number of purchase orders (PO) Quality control 97,500 Number of inspections Materials management 84,000 Number of components Total $239,000 The activity-base usage quantities for each product are as follows: Setups PurchaseOrders Inspections Components Unit Volume Custom 290 760 1,200 500 2,000 Standard 110 140 300 200 2,000 Total 400 900 1,500 700 4,000 a. Determine an activity rate for each activity. Activity Rates Production Setup Procurement Quality Control…arrow_forwardKlamath Corp. produces two products: saws and drills. Three activities are used in their manufacture. These activities and their associated costs and bases are as follows: Activity Stamping Assembly Setup Activity Base Machine hours Labor hours Number of setups Units produced Budgeted Costs Saws Drills $200,000 400,000 30,000 Saws 4,000 7,000 $ 3 500 Activity Base Machine hours Labor hours Number of setups a. Determine the activity rate for each activity. Stamping Assembly Setup Drills 6,000 13,000 12 600 per machine hour per labor hour per setup b. Determine the factory overhead to be allocated to each unit of product. Round your answers to two decimal places, if necessary. per unit per unit Total 10,000 20,000 15 Previousarrow_forwardActivity Rates and Product Costs using Activity-Based Costing Garfield Inc. manufactures entry and dining room lighting fixtures. Five activities are used in manufacturing the fixtures. These activities and their associated budgeted activity costs and activity bases are as follows: Activity BudgetedActivity Cost Activity Base Casting $560,000 Machine hours Assembly 75,000 Direct labor hours Inspecting 30,000 Number of inspections Setup 18,750 Number of setups Materials handling 14,000 Number of loads Corporate records were obtained to estimate the amount of activity to be used by the two products. The estimated activity-base usage quantities and units produced follow: Activity Base Entry Dining Total Machine hours 7,500 12,500 20,000 Direct labor hours 2,000 3,000 5,000 Number of inspections 500 250 750 Number of setups 150 100 250 Number of loads 400 300 700 Units produced 5,000 2,500 7,500 a.…arrow_forward
- both requirements solvearrow_forwardGreenwood Company manufactures two products-13,000 units of Product Y and 5,000 units of Product Z. The company uses a plantwide overhead rate based on direct labor-hours. It is considering implementing an activity- based costing (ABC) system that allocates all of its manufacturing overhead to four cost pools. The following additional information is available for the company as a whole and for Products Y and Z: Activity Cost Pool Machining Machine setups Production design General factory Activity Measure Machining Windows DESKTOP- Windows Number of setups Number of products Direct labor-hours Total overhead cost Activity Measure Machine-hours Number of setups Number of products Direct labor-hours Product Y FEB +1 (252) 484-2153 Oh nun Product Y Product Z 8,800 3,200 240 40 1 1 8,800 3,200 11. Using the plantwide overhead rate, what percentage of the total overhead cost is allocated to Product Y an Product Z? (F your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places. Round your answers to 2…arrow_forwardSilven Company has identified the following overhead activities, costs, and activity drivers for the coming year: Activity Expected Cost Activity Driver Activity Capacity $138,000 Number of setups 10,200 Number of orders 92,400 Machine hours 18,480 Receiving hours phones with the following expected activity demands: Setting up equipment Ordering materials Machining Receiving Silven produces two models of cell Model X 5,000 80 200 6,600 385 Units completed Number of setups Number of orders Machine hours Receiving hours Required: Model Y 10,000 40 400 4,950 770 120 600 11,550 1,155arrow_forward
- Activity-Based Costing: Factory Overhead Costs The total factory overhead for Bardot Marine Company is budgeted for the year at $1,347,400, divided into four activities: fabrication, $660,000; assembly, $276,000; setup, $224,400; and inspection, $187,000. Bardot Marine manufactures two types of boats: speedboats am bass boats. The activity-base usage quantities for each product by each activity are as follows: Fabrication Assembly Setup Inspection Speedboat 11,000 dlh 34,500 dlh 79 setups 138 inspections Bass boat 33,000 11,500 581 962 44,000 dlh 46,000 dlh 660 setups 1,100 inspections Each product is budgeted for 6,500 units of production for the year. a. Determine the activity rates for each activity. Fabrication per direct labor hour Assembly %$4 per direct labor hour Setup %$4 per setup Inspection per inspection b. Determine the activity-based factory overhead per unit for each product. Round to the nearest whole dollar. Speedboat per unit Bass boat %$4 per unitarrow_forwardGreenwood Company manufactures two products-13,000 units of Product Y and 5,000 units of Product Z. The company uses a plantwide overhead rate based on direct labor-hours. It is considering implementing an activity- based costing (ABC) system that allocates all of its manufacturing overhead to four cost pools. The following additional information is available for the company as a whole and for Products Y and Z: Activity Cost Pool Machining Machine setups Production design General factory Activity Measure Machining DESKTOP- Windows Number of setups Number of products Direct labor-hours General factory cost Activity Measure Machine-hours Number of setups Number of products Direct labor-hours Product Y +1 (252) 484-2153 Oh nun Product Y Product Z 8,800 3,200 40 240 1 1 8,800 3,200 % 15. Using the ABC system, what percentage of the General Factory cost is assigned to Product Y and Product Z? (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) Product Z (@ 2 0…arrow_forwardFactory depreciation Indirect labor Factory electricity Indirect materials Selling expenses Administrative expenses Total costs Tortilla chips Potato chips Factory overhead is allocated to the three products on the basis of processing hours. The products had the following production budget and processing hours per case: Budgeted Volume Processing Hours (Cases) Per Case Pretzels Total Tortilla chips Potato chips $24,012 59,508 6,000 6,000 1,200 13,200 Pretzels 6,786 14,094 33,408 18,792 $156,600 Total If required, round all per-case answers to the nearest cent. a. Determine the single plantwide factory overhead rate. per processing hour 0.12 0.15 b. Use the overhead rate in (a) to determine the amount of total and per-case overhead allocated to each of the three products under generally accepted accounting principles. Total Per-Case Factory Overhead Factory Overhead 0.10arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education