
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
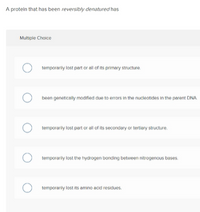
Transcribed Image Text:A protein that has been reversibly denatured has
Multiple Choice
temporarily lost part or all of its primary structure.
been genetically modified due to errors in the nucleotides in the parent DNA
temporarily lost part or all of its secondary or tertiory structure.
temporarily lost the hydrogen bonding between nitrogenous bases.
temporarily lost its amino acid residues.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A nonsynonymous mutation is also referred to as missense mutation. Which of the following correctly describe these mutations? They are permanent and cannot revert or reverse mutate back into a wild-type sequence. They cause a non-functional amino acid to replace a functional amino acid. O They result in the insertion or deletion of a small number of nucleotides to the DNA. They change the nucleotide sequence of a gene but do not change the sequence of the resulting protein. None of the provided answers are correct. They convert a codon for a particular amino acid within a gene into a stop codon. They insert an additional amino acid into the final protein product.arrow_forwardFor each mutant, state what change has occurred in the DNA, whether it was a substitution by transition or transversion, sense mutation, nonsense or reading frame change. It must present the codon sequence. Normal nucleotide sequence starting from the third codon: CCC-ACG-GUG-ACG-ACA-CGG-UGG Please show the codon and nucleotide sequence of the mutation.arrow_forwardIdentify the type of mutation and how it would affect the protein made (amino acid) if the following changes occurred in the DNA template strand.DNA Strand: TCT AAC TAT CCC CTA Third codon change from TAT to TAG. Second codon change from AAC to ATC. Nucleotide with adenine (A) base inserted between 14th and 15th nucleotide. Ninth nucleotide changes from T to C. Types of Mutation Changes in the Amino Acid 1. 2. 3. 4.arrow_forward
- Which of the following mutations would be most likely to have the most negative effect on the functioning of a protein produced by the gene? Group of answer choices a deletion of one nucleotide at the beginning of the coding sequence a substitution of one nucleotide at the beginning of the coding sequence an insertion of three nucleotides near the end of the coding sequence a substitution of one nucleotide near the end of the coding sequencearrow_forwardWhich of the following mutations near the beginning of a gene likely results in numerous amino acid changes in the resulting protein? insertion of three consecutive nucleotides. deletion of three consecutive nucleotides replacement of two consecutive nucleotides with two other nucleotides replacement of one nucleotide for another nucleotide insertion of two consecutive nucleotidesarrow_forwardWhich of the following mutations will MOST drastically change the polypeptide sequence for which the DNA codes? 1 base pair change 2 base pair changes 3 consecutive insertions 1 insertionarrow_forward
- When DNA is copied, sometimes a mutation can occur where an incorrect, base pairing appears within the structure of a DNA molecule replacing original base pairs. This mistake is called a mutation. Deletion Translocation Point (Substitution) Inversionarrow_forwardA polypeptide has the following amino acid sequence: Met-Ser-Pro-Arg-Leu-Glu-Gly The amino acid sequence of this polypeptide was determined in a series of mutants listed in parts a through e. indicate the type of mutation that occurred in the DNA (single-base substitution, insertion, deletion) and the phenotypic effect of the mutation (nonsense mutation, missense mutation, frameshift, etc.). a. MMutant 4: Met-Ser-Pro-Glu-Glarrow_forwardProtein synthesis is a complicated process involving DNA being transcribed to RNA, which is then translated into amino acids. Complete the DNA-to-amino acid table for three consecutive codons with the appropriate nucleotides and amino acids using a codon table. Nucleotide and amino acid options can be used multiple times or not at all. 5' to 3' DNA strand T T A G A G 3' to 5' DNA strand A A T C T C G C G transcribed mRNA U U A G A G C G C TRNA anticodon A. A U C U G C G amino acid leucine glutamic acid Answer Bank A glutamic acid leucine cysteine arginine proline Uarrow_forward
- Identify the type of mutation and how it would affect the protein made (amino acid) if the following changes occurred in the DNA template strand.DNA Strand: TCT AAC TAT CCC CTA Third codon change from TAT to TAG. Second codon change from AAC to ATC. Nucleotide with adenine (A) base inserted between 14th and 15th nucleotide. Ninth nucleotide changes from T to C.arrow_forwardDraw out the following DNA sequence on a white sheet of paper along with itscomplementary strand. Challenge yourself by not using any notes to begin with. Use hexagon and hexagon/pentagon shapes within the nitrogenous bases to depict purines and pyrimidines. Use circles and pentagons to show phosphates and sugars in the backbones. Label the ends (5’ and 3’) and make sure to associate those ends with the correct functional group. Include the proper number of hydrogen bonds between base pairs. 3’ CCAGGTACT 5’arrow_forwardThe following is the base sequence on the coding strand of a DNA molecule. AAT GCC AGT GGT TCG CAC Rewrite the base sequence above and underneath write the base sequence for the template DNA strand. Write the base sequence for the strand of mRNA transcribed from the original strand of DNA or template strand. Remember transcribing means making mRNA from DNA. Write the amino acid sequence translated from this mRNA. Translating means making an amino acid chain from mRNA. A) If the fourth nucleotide in the coding DNA strand was changed from a G to a C, what would be the base sequence of the new strand of mRNA? b) What would the resulting amino acid fragment be? A) If a G were added to the coding DNA strand after the third nucleotide, what would be the base sequence of the resulting mRNA? B) What would the resulting amino acid fragment be?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education