
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
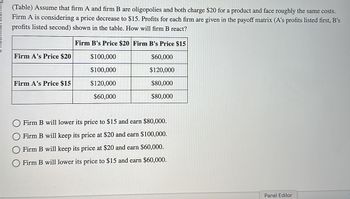
Transcribed Image Text:(Table) Assume that firm A and firm B are oligopolies and both charge $20 for a product and face roughly the same costs.
Firm A is considering a price decrease to $15. Profits for each firm are given in the payoff matrix (A's profits listed first, B's
profits listed second) shown in the table. How will firm B react?
Firm B's Price $20 Firm B's Price $15
$60,000
$120,000
$80,000
$80,000
Firm A's Price $20
Firm A's Price $15
$100,000
$100,000
$120,000
$60,000
Firm B will lower its price to $15 and earn $80,000.
Firm B will keep its price at $20 and earn $100,000.
Firm B will keep its price at $20 and earn $60,000.
Firm B will lower its price to $15 and earn $60,000.
Panel Editor
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1 Consider two identical firms with a unit cost of production of $10 and a market demand of p= 60-y. (a) What is firm 1’s optimal output level as a function of firm 2’s output? (b) What is firm 2’s optimal output level as a function of firm 1’s output? (c) What is the Cournot equilibrium output level for these firms? (d) What is the Cournot equilibrium price level? Show your work step by step.arrow_forward32arrow_forward6. Using a payoff matrix to determine the equilibrium outcome Suppose that Zipride and Citron are the only two firms in a hypothetical market that produce and sell electric scooters. The following payoff matrix gives profit scenarios for each company (in millions of dollars), depending on whether it chooses to set a high or low price for scooters. Zipride Pricing price. High Low For example, the lower-left cell shows that if Zipride prices low and Citron prices high, Zipride will earn a profit of $13 million, and Citron will earn a profit of $3 million. Assume this is a simultaneous game and that Zipride and Citron are both profit-maximizing firms. Citron Pricing High 9,9 13, 3 If Zipride prices high, Citron will make more profit if it chooses a Low If the firms do not lude, 3, 13 6, 6 If Citron prices high, Zipride will make more profit if it chooses a price. Considering all of the information given, pricing low True False Both Zipride and Citron will choose a low price. strategies…arrow_forward
- 1. Consider the following game matrix. Player A Answer: Top Bottom Left a, b e, f Player B Right c, d g, h (a) If top and left are strictly dominant strategies, then what do we know the relationship of the parameters? (b) If (top, left) is a Nash equilibrium, then what do we know the relationship of the parameters? Answer: (c) If top and left are strictly dominant strategies, will (top, left) be a Nash equilibrium? Why? Answer: (d) If (top, left) is a Nash equilibrium, must the strategies be strictly dominant strategies? Why? Answer:arrow_forward7) What is the significance of the mutual interdependence among the firms in an oligopolistic market?arrow_forward5arrow_forward
- 1arrow_forward1arrow_forward(REAL-WORLD APPLICATION) You are NOT required to read the oligopoly chapter in the textbook, but you already know quite a lot about it from our discussion of strategic interactions using game theory in weeks 2-3. This market structure is between monopoly and monopolistic competition, with only a handful of firms having a high degree of market power. Let's refresh your memory with the following example. Assume that the Australian low-cost airline industry consists of two firms and their situation can be represented by the following payoff matrix. Tigar Air Nothing Low Price More Advertising 0, 16 6, 6 Nothing 10, 10 2, 14 Jetstar Low Price 16, 0 12, 4 More Advertising 14, 2 4, 12 8, 8 a. Before solving the game, put yourself in the position of Jetstar and write down your action. Then independent of that, put yourself in the position of Tiger Air and write down your action. b. State all the dominated strategies in the full game, by which strategy they are dominated, and whether weakly or…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education