
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
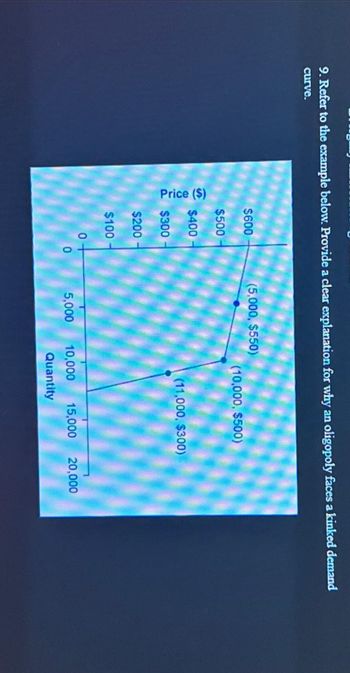
Transcribed Image Text:9. Refer to the example below. Provide a clear explanation for why an oligopoly faces a kinked demand
curve.
Price ($)
$600
$500
$400
$300
$200
$100
0
0
(5,000, $550)
5,000
(10,000, $500)
(11,000, $300)
10,000
Quantity
15,000
20,000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please provide answer in 1 hrarrow_forward12. Consider a duopoly market. Two firms are selling identical products and all costs are assumed to be zero for simplicity. Market demand schedule is given in the following table. Note that firms always choose an integer value for the quantity of production. Quantity Price Total Profit 3 $12 4 11 5 8 6 6. 7 4 8 2 1 10 a. Fill in the column of total profit.arrow_forward7. Comparing monopoly and perfect competition Consider the daily market for hot dogs in a small city. Suppose that this market is in long-run competitive equilibrium, with many hot dog stands in the city, each one selling the same kind of hot dogs. Therefore, each vendor is a price taker and possesses no market power. The following graph shows the demand (D) and supply curves (S= MC) in the market for hot dogs. Place the black point (plus symbol) on the graph to indicate the market price and quantity that will result from perfect competition. PRICE AND COSTS (Dollars per hot dog) 0.5 བྷྲ ༷ ྴ་ཤཱ་བྷ་ཛྙྰ་བླླ་ཤཱ་བ། 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.0 0 0 30 60 90 Perfect Competition S=MC D 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 QUANTITY (Hot dogs) PC Outcome Assume that one of the hot dog vendors successfully lobbies the city council to obtain the exclusive right to sell hot dogs within the city limits. This firm buys up all the rest of the hot dog vendors in the city and operates as a monopoly. Assume…arrow_forward
- The table below shows the payoffs for two firms competing through advertisement. Firm A and Firm B can each choose to advertise, or to not advertise. A's Strategy Advertise Don't Advertise Table 14.2 B's Strategy Advertise A's profit $100 million B's profit $100 million A's profit $50 million B's profit $200 million What is Firm A's dominant strategy? Don't Advertise A's profit $200 million B's profit $50 million C. Advertise d. Firm A does not have a dominant strategy A's profit $75 million B's profit $75 million a. Don't advertise b. Indeterminate from this information, as no information is provided on Firm A's risk preference.arrow_forwardEconomics: Industrial Economics Question: A duopoly exists in the market for lumber in a town. It costs the first company, Big Cutters, $16 per cord of wood while it costs the second company, Pine Stackers, $10 per cord of wood. The local market demand curve for wood is Q-31,000-100P. Assume each has the capacity to serve the entire market and that they can only price in whole dollar amounts (i.e.$30, not $29.99). Assume initially that Cutters and Stackers decide to collude and split the market. How many cords of wood will they sell? Choices: A. 12,000 B. 9,000 C. 15,000 D. 20,000 2. What will be the price they charge? Choices: A. 190 B. 210 C. 110 D. 160 3. How much will Big Cutters produce? Choices: A. 9,000 B. 4,500 C. 0 D. 15,000 Now assume that collusion is not possible. 4. What is the Nash Equilibrium quantity that Pine Stackers Choices: A. 0 B. 15,300 C. 14,700 D. 29,500 5. What is the Nash Equilibrium price? Choices: A. 15 B. 112 C. 11 D. 157 Thank you for your…arrow_forward1. Suppose we live in a world where the widgets market is a monopolistically competitive market with homogenous firms (i.e. no productivity differences among firms). There are two countries: A and B. In each country, consumer demand for widgets can be written as Q = S x- x (P – P), 30 where n is the number of widget firms, P the price of widget charged by the firm, and P the average price of widget by other firms in the market. Moreover, widget firms in both countries have the same total cost function, which is C = 750 + (5 × Q). It is also given that marginal revenue of each 30Q firm can be written as MR = P – Total demand for widget in country A is SA = 900 and Sg = 1600 in country В. a) Derive the average cost function from the total cost function. What is the marginal cost? b) Calculate the number of firms and the prices of widget in each country when trade is not allowed (that is, calculate na, ng, Pa, PBÌ- c) Calculate the number of firms and the price of widget in the unified…arrow_forward
- 3. Demand for a good produced by a duopoly is given by P = 100 - Q. Both firms have constant marginal costs, MC = 20 and zero fixed costs. Firms can choose to maximize profit or revenue. Suppose firm 1 choose to maximise profit and firm 2 choose to maximise revenue. Determine the equilibrium price and quantity of each firm.arrow_forward(Figure: The Market for Designer Boots in Monopolistic Competition IV) Use Figure: The Market for Designer Boots in Monopolistic Competition. A positive economic profit will be earned if the profit-maximizing price is in panel Price, cost XXX G; (A) H; (B) (a) O I; (C) O F; (A) ATC Quantity (per period) Price, (b) cost ATC Quantity (per period) Price, (c) cost ATC Quantity (per period)arrow_forwardAssume an oligopolist confronts two possible demand curves for its own output, as illustrated below. The first (A) prevails if other oligopolists don't match price changes. The second (B) prevails if rivals do match price changes. Price (dollars per unit) 19- 17 Demand B 15- Demand A 13- 11. 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 Quantity (units per period) (a) By how much does quantity demanded increase if price is reduced from $11 to $9 and Instructions: Enter your responses rounded to the nearest whole number. (i) Rivals match the price cut? (ii) Rivals don't match the price cut? (b) By how much does quantity demanded decrease when price is raised from $11 to $15 and Instructions: Enter your responses rounded to the nearest whole number (do not include negative signs). (i) Rivals match the price hike? (ii) Rivals don't match the price hike?arrow_forward
- Offer Bud Light Don't Offer New Ads New Ads Offer New Ads B: $100 B: $50 M: $100 M: $200 Miller Lite Don't Offer New Ads B: $200 M: $50 B: $120 M: $120 Refer to Table 14.2.4. The marketers of Budweiser Light beer and Miller Lite beer must decide whether or not to offer new advertising campaigns promoting their products. The payoffs in the table are the economic profit made by Bud and Miller. Which one of the following observations is correct? This game has no Nash equilibrium. Bud has a dominant strategy but Miller does not. This game has no dominant strategies. Bud and Miller each have a dominant strategy. Miller has a dominant strategy but Bud does not.arrow_forward(12) Suppose all firms in a monopolistically competitive industry were merged into one large firm. Would that new firm produce as many different brands? Would it produce only a single brand? Explain.arrow_forward1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education