
(a)
Interpretation: The dipole in the H2Se molecule needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction: The chemical compounds can be classified as covalent compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds have complete negative and positive charges on it, whereas covalent compounds are formed by equal sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The polarity of a molecule depends on the presence of electropositive and electronegative atoms present in the molecule.
Due to the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, partial charges are induced on the bonded atoms. The partial charges affect the physical properties of the polar molecules.
(a)
Answer to Problem 4E
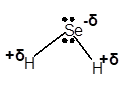
Explanation of Solution
In H2Se molecule, Se is more electronegative element than H atom. This is because Se is a non-metal with 6 valence electrons. Therefore, Se tends to accept electrons to get octet configuration. That makes it more electronegative than H atom. Due to this difference in electronegativity of bonded atoms, Se gets a partial negative charge and H gets a partial positive charge.
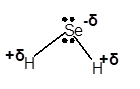
(b)
Interpretation: The dipole in the H2 molecule needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction: Concept Introduction: The chemical compounds can be classified as covalent compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds have complete negative and positive charges on it, whereas covalent compounds are formed by equal sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The polarity of a molecule depends on the presence of electropositive and electronegative atoms present in the molecule.
Due to the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, partial charges are induced on the bonded atoms. The partial charges affect the physical properties of the polar molecules.
(b)
Answer to Problem 4E
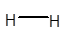
No dipole exists on H2 molecule.
Explanation of Solution
In H2 molecule, both H atoms are the same and have 1 valence electron. They form a covalent bond with another H atom to get the duplet configuration. Due to the presence of the same atom, there will be no partial charge on both H atoms and the molecule will be non-polar overall with zero dipole moment.
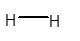
(c)
Interpretation: The dipole in the Ar molecule needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction: Concept Introduction: The chemical compounds can be classified as covalent compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds have complete negative and positive charges on it, whereas covalent compounds are formed by equal sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The polarity of a molecule depends on the presence of electropositive and electronegative atoms present in the molecule.
Due to the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, partial charges are induced on the bonded atoms. The partial charges affect the physical properties of the polar molecules.
(c)
Answer to Problem 4E
No dipole exists on Ar molecule.
Explanation of Solution
Ar is the monoatomic Noble gas. It has a completely filled octet configuration, therefore, it does not form any
Because of no bond formation, the overall dipole on the Ar monoatomic gas is zero.
(d)
Interpretation: The dipole in the HOF molecule needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction: Concept Introduction: The chemical compounds can be classified as covalent compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds have complete negative and positive charges on it, whereas covalent compounds are formed by equal sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The polarity of a molecule depends on the presence of electropositive and electronegative atoms present in the molecule.
Due to the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, partial charges are induced on the bonded atoms. The partial charges affect the physical properties of the polar molecules.
(d)
Answer to Problem 4E
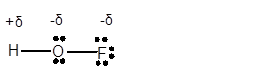
Explanation of Solution
In HOF molecule, H atom has 1 valence electron, whereas O and F are electronegative elements with 6 and 7 valence electrons respectively. Therefore in HOF molecule, O and F will get a partial negative charge, whereas H will get a partial positive charge.
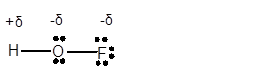
(e)
Interpretation: The dipole in the CHClF2 molecule needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction: Concept Introduction: The chemical compounds can be classified as covalent compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds have complete negative and positive charges on it, whereas covalent compounds are formed by equal sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The polarity of a molecule depends on the presence of electropositive and electronegative atoms present in the molecule.
Due to the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, partial charges are induced on the bonded atoms. The partial charges affect the physical properties of the polar molecules.
(e)
Answer to Problem 4E
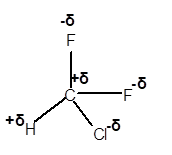
Explanation of Solution
In CHClF2 molecule, Cl and F are more electronegative elements compared to C and H. Therefore, C and H will get a partial positive charge, whereas Cl and F will get a partial negative charge in the molecule as given.
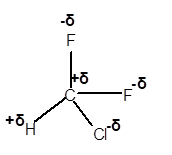
(f)
Interpretation: The dipole in the CH2O molecule needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction: Concept Introduction: The chemical compounds can be classified as covalent compounds and ionic compounds. Ionic compounds have complete negative and positive charges on it, whereas covalent compounds are formed by equal sharing of electrons between bonded atoms.
The polarity of a molecule depends on the presence of electropositive and electronegative atoms present in the molecule.
Due to the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms, partial charges are induced on the bonded atoms. The partial charges affect the physical properties of the polar molecules.
(f)
Answer to Problem 4E
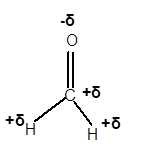
Explanation of Solution
In CH2O molecule, O is a more electronegative element compared to C and H. Therefore, C and H will get a partial positive charge, whereas O atom will get a partial negative charge in the molecule as given.
Chapter U2 Solutions
Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- true or false The equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.20. N2O4(g) ⇔ 2NO2(g) Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 5. 4NO2(g) ⇔ 2N2O4(g)arrow_forwardtrue or false The equilibrium constant for this reaction is 0.20. N2O4(g) ⇔ 2NO2(g) Based on the above, the equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 0.4. 2N2O4(g) ⇔ 4NO2(g)arrow_forwardtrue or false Using the following equilibrium, if heat is added the equilibrium will shift toward the reactants. N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇔ 2NH3(g) + heatarrow_forward
- True or False Using the following equilibrium, if heat is added the equilibrium will shift toward the products. N2O4(g) + heat ⇔ 2NO2(g)arrow_forwardtrue or false Using the following equilibrium, if solid carbon is added the equilibrium will shift toward the products. C(s) + CO2(g) ⇔ 2CO(g)arrow_forwardProvide the complete mechanism for the reaction below. You must include appropriate arrows,intermediates, and formal charges. Please also provide a reason to explain why the 1,4-adduct is preferred over the 1,3-adduct.arrow_forward
- Which of the following pairs are resonance structures of one another? I. III. || III IV + II. :0: n P !༠ IV. EN: Narrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) and byproducts (either organic or inorganic) for thefollowing reactions.arrow_forwardA 8.25 g sample of aluminum at 55°C released 2500 J of heat. The specific heat of aluminum is 0.900 J/g°C. The density of aluminum is 2.70 g/mL. Calculate the final temperature of the aluminum sample in °C.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





