
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The equation given below has to be balanced.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The given chemical equation is written as follows;
Balancing hydrogen atoms: In the above equation, there are four hydrogen atoms on left side of the equation while three hydrogen atoms are present in right side of the equation. Adding coefficient
(b)
Interpretation:
Oxidation number of nitrogen in
Concept Introduction:
Oxidation state of a species is the one that has a specified oxidation number. Increase in oxidation number corresponds to oxidation while decrease in oxidation number corresponds to reduction. Rules for assigning oxidation number for an element is given as follows;
- The oxidation number is zero for the element that is present in uncombined state.
- Sum of the oxidation number of the atoms that is present in it is equal to the charge on the species.
- Oxidation number of the element is the charge that is possessed when the more electronegative atom is imagined to be an ion.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Oxidation number of nitrogen in
The sum of oxidation state of the individual atoms is equal to the total charge. Therefore, the oxidation number of nitrogen can be found as shown below;
Thus the oxidation state of nitrogen in
Oxidation number of nitrogen in
The sum of oxidation state of the individual atoms is equal to the total charge. Therefore, the oxidation number of nitrogen can be found as shown below;
Thus the oxidation state of nitrogen in
Oxidation number of nitrogen in
Nitrogen molecule consists only atoms of nitrogen. Oxidation number of an element that is in its free form is zero. Therefore, the oxidation state of nitrogen in
(c)
Interpretation:
Oxidizing agent and reducing agent has to be identified in the given reaction.
Concept Introduction:
In
In redox reactions, reducing agent is the one that gets oxidized by causing reduction. These agents can be ions, elements, or even compounds. In reduction, the oxidation number decreases due to gain of electrons.
(c)
Answer to Problem K.22E
Oxidizing agent and reducing agent is
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is written as follows;
Oxidation number of the atoms present in the above equation is indicated as follows;
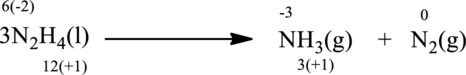
From the above equation, it is found that the oxidation state of nitrogen is increased from
The oxidation state of nitrogen decreases from
(d)
Interpretation:
Volume of nitrogen gas that will be obtained from
(d)
Answer to Problem K.22E
Volume of nitrogen is
Explanation of Solution
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is written as follows;
Density of hydrazine is given as
Molar mass of hydrazine is
Considering the balanced chemical equation, it is found that three moles of hydrazine gives one mole of nitrogen. Therefore, moles of nitrogen is calculated as shown below;
It is given that
Thus the volume of nitrogen that will be produced is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter F Solutions
Chemical Principles: The Quest for Insight
- Phosphorous acid, H3PO3, is oxidized to phosphoric acid, H3PO4, by nitric acid, which is reduced to nitrogen monoxide, NO. Write the balanced equation for this reaction.arrow_forwardAluminum is produced commercially by the electrolysis of Al2O3 in the presence of a molten salt. If a plant has a continuous capacity of 1.00 million A, what mass of aluminum can be produced in 2.00 h?arrow_forwardThe reaction of elemental phosphorus and excess oxygen produces P4O10. Name the compound. (a) phosphorus oxide (b) phosphoric acid (c) phosphorus decaoxide (d) tetraphosphorus decaoxidearrow_forward
- The carbon dioxide exhaled in the breath of astronauts is often removed from the spacecraft by reaction with lithium hydroxide 2LiOH(s)+CO2(g)Li2CO3(s)+H2O(l) Estimate the grams of lithium hydroxide required per astronaut per day. Assume that each astronaut requires 2.50 103 kcal of energy per day. Further assume that this energy can be equated to the heat of combustion of a quantity of glucose, C6H12O6, to CO2(g) and H2O(l). From the amount of glucose required to give 2.50 103 kcal of heat, calculate the amount of CO2 produced and hence the amount of LiOH required. The H for glucose(s) is 1273 kJ/mol.arrow_forwardNitric acid is produced commercially by the Ostwald process, represented by the following equations: 4NH3(g)+5O24NO(g)+6H2O(g)2NO(g)+O2(g)2NO2(g)3NO2(g)+H2O(l)2HNO3(aq)+NO(g) What mass of NH3 must be used to produce 1.0 106 kg HNO3 by the Ostwald process? Assume 100% yield in each reaction, and assume that the NO produced in the third step is not recycled.arrow_forwardWrite balanced net ionic equations for the following reactions in acid solution. (a) Liquid hydrazine reacts with an aqueous solution of sodium bromate. Nitrogen gas and bromide ions are formed. (b) Solid phosphorus (P4) reacts with an aqueous solution of nitrate to form nitrogen oxide gas and dihydrogen phosphate (H2PO4-) ions. (c) Aqueous solutions of potassium sulfite and potassium permanganate react. Sulfate and manganese(II) ions are formed.arrow_forward
- Calcium metal can be obtained by the direct electrolysis of molten CaCl2, at a voltage of 3.2 V. (a) How many joules of electrical energy are required to obtain 12.0 1b of calcium? (b) What is the cost of the electrical energy obtained in (a) if electrical energy is sold at the rate of nine cents per kilowatt hour?arrow_forwardBalanced chemical equation for conversion of Al(s) to KAl(SO4)2·12H2O(s) in aqueous solutionarrow_forwardWrite the balanced chemical equations for (a) the completecombustion of acetic acid (CH3COOH), the mainingredient in vinegar; (b) the decomposition of solidcalcium hydroxide into solid calcium oxide (lime) andwater vapor; (c) the combination reaction between nickelmetal and chlorine gas.arrow_forward
- (a) What compound precipitates when aqueous solutions of Fe2(SO4)3 and LiOH are mixed? (b) Write a balanced equation for the reaction.arrow_forwardSolid barium oxide and carbon dioxide gas are produced by the decomposition of solid barium carbonate BaCO3. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction.arrow_forwardThe percent yield in the direct reaction of silicon with Cl2 to form SiCl₄ is 62%. Calculate the mass (in grams) of SiCl₄ obtained in the reaction of 3.1 g of silicon with excess chlorine?arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





