
Consider the differential amplifier shown in Figure 9.24(a). Assume thateach resistor is 50(1±x)kΩ . (a) Determine the worst case common-modegain ACM=vO/vCM , where vCM=v1=v2 . (b) Evaluate ACM andCMRR(dB) for x=0.01,0.02, and 0.05.
(a)
The value of the worst case common mode gain.
Answer to Problem 9.62P
The value of the worst case common mode gain is 2x1+x .
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The given diagram is shown in Figure 1
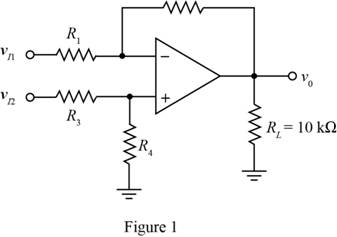
Mark the voltages and redraw the circuit.
The required diagram is shown in Figure 2
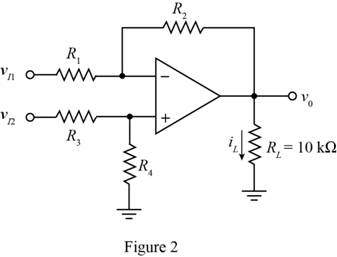
The expression for the common mode voltage gain is given by,
ACM=vOvCM
The expression for the value of the voltage v1 is given by,
v1=v2
The expression for the voltage v2 by voltage division rule is given by,
v2=(R4R3+R4)vI2
Apply KCL at the inverting terminal.
vI1−v1R1=v1−vOR2vI1R2−v1R1−v1R1R1R2=−vOR2vO=−vI1(R2R1)+v1(1+R2R1)
Substitute v2 for v1 in the above equation.
vO=−vI1(R2R1)+v2(1+R2R1)
Substitute (R4R3+R4)vI2 for v2 in the above equation.
vO=−vI1(R2R1)+((R4R3+R4)vI2)(1+R2R1) …… (1)
The expression for the common node input voltage is given by,
vCM=vI1
The expression for the common node input voltage is given by,
vCM=vI2
Substitute vCM for vI1 and vCM for vI2 in the above equation.
vO=−vCM(R2R1)+((R4R3+R4)vCM)(1+R2R1)vOvCM=[(R4R3+R4)(R1+R2R1)−R2R1]
Substitute ACM for vOvCM in the above equation.
ACM=[(R4R3+R4)(R1+R2R1)−R2R1]=R4R3+R4(1−R2R3R1R4) …… (2)
In the above equation the worst case ACM is obtained when R4R3+R4 is maximum and 1−R2R3R1R4 is minimum. The second case arises when R2 and R3R4 is minimum and R1 is maximum. The third case arises when the value of R1, R4 are minimum and R2 , R3 is minimum.
For worst condition the value of the resistance R1 is given by,
R1=50(1+x)
For worst condition the value of the resistance R2 is given by,
R2=50(1−x)
For worst condition the value of the resistance R3 is given by,
R3=50(1−x)
For worst condition the value of the resistance R4 is given by,
R4=50(1+x)
Substitute 50(1+x) for R1 , 50(1−x) for R2 , 50(1−x) for R3 and 50(1+x) for R4 in the above equation.
ACM=50(1+x)50(1−x)+50(1+x)(1−(50(1−x))(50(1−x))(50(1+x))(50(1+x)))=2x1+x …… (3)
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of the worst case common mode gain is 2x1+x .
(b)
The value of the CMRR and the common mode gain.
Answer to Problem 9.62P
The value of ACM for x equals to 0.01 is 0.0198 , for x equal to 0.02 is 0.0392 and for x equals to 0.05 is 0.0952 . The value of the CMRR for for x equals to 0.01 is 33.979 dB , for x equal to 0.02 is 27.959 dB and for x equals to 0.05 is 20 dB .
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The expression for the common mode gain is given by,
vCM=vI2+vI12vI1=2vCM−vI2
The expression for the differential voltage is given by,
vd=vI2−vI1
Substitute 2vCM−vI2 for vI1 in the above equation.
vd=vI2−2vCM+vI2vd=2vI2−2vCMvI2=vd2+vCM
The expression for the voltage vI1 is given by,
vI1=vCM−vd2
The expression for the common mode voltage is given by,
vCM=vI2+vI12
Substitute vCM−vd2 for vI1 and vd2+vCM for vI2 in the above equation.
vCM=vd2+vCM−vCM−vd22=0 V
Substitute vCM−vd2 for vI1 and vd2+vCM for vI2 in equation (1).
vO=−(vCM−vd2)(R2R1)+[(R4R3+R4)(R1+R2R1)](vd2+vCM)
Substitute 0 for vCM in the above equation.
vO=(vd2)(R2R1)+[(R4R3+R4)(R1+R2R1)](vd2)=[(R4R3+R4)(R1+R2R1)+(R2R1)]vd2
Substitute 50(1+x) for R1 , 50(1−x) for R2 , 50(1−x) for R3 and 50(1+x) for R4 in the above equation.
vO=[(50(1+x)50(1−x)+50(1+x))(50(1−x)+(50(1+x))50(1−x))+(50(1−x)50(1+x))]vd2vO=[21+x]vd2vOvd=[21+x]
Substitute Ad for vOvd in the above equation.
Ad=[11+x]
The expression for the CMRR is given by,
CMRR(dB)=20log10|AdACM|
Substitute for 11+x for Ad and 2x1+x for ACM in the above equation.
CMRR(dB)=20log10|11+x2x1+x|=20log10|12x| …… (4)
Substitute 0.01 for x in equation (3).
ACM=2(0.01)1+0.01=0.0198
Substitute 0.01 for x in equation (4).
CMRR(dB)=20log10|12(0.01)|=33.979 dB
Substitute 0.02 for x in equation (3).
ACM=2(0.02)1+0.02=0.0392
Substitute 0.02 for x in equation (4).
CMRR(dB)=20log10|12(0.02)|=27.959 dB
Substitute 0.05 for x in equation (3).
ACM=2(0.05)1+0.05=0.0952
Substitute 0.05 for x in equation (4).
CMRR(dB)=20log10|12(0.05)|=20 dB
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of ACM for x equals to 0.01 is 0.0198 , for x equal to 0.02 is 0.0392 and for x equals to 0.05 is 0.0952 . The value of the CMRR for for x equals to 0.01 is 33.979 dB , for x equal to 0.02 is 27.959 dB and for x equals to 0.05 is 20 dB .
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design
- SIM1 RESET O SIMULINO ARDUINO AREF 13 12 -11 www.arduino.cc blogembarcado.blogspot.com SIMULINO UNO BUZ1 BUZZER R1 R2 51.1 68.1 GAS1 MQ-2 GAS SENSOR MQ-2 TestPin www.TheEng Vcc OUT GND Can the expt help me write Arduino code for the Project sensou pas?arrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forward
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardA 3 km long multimode step index fibre operating at a bandwidth of 4 Mhz has a core refractive index of 1.48 and a refractive index difference of 1 %. Evaluate the rms pulse broadening per kilometer which results from chromatic dispersion.arrow_forward
- Find the Thevenin Equivalent of the circuit below, show all steps;arrow_forwardFind the Thevenin Equivalent Circuit of the following and find the current through R_L, show all steps;arrow_forwardFind the Thevenin Equivalent Circuit of the circuit below and the current through R_L , show all steps;arrow_forward
- Find the Norton Equivalent of the below and the voltage across R_L, show all steps;arrow_forwardUse Mesh Analysis to find the current through the laod resistor R_L. Show all steps;arrow_forwardFind Thevenin Equivalent of the circuit below and the current through the load resistor R_L. Show all steps;arrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





