
Concept explainers
RIPs as Cancer Drugs Researchers are taking a page from the structure-function relationship of RIPs in their quest for cancer treatments. The most toxic RIPs, remember, have one domain that interferes with ribosomes, and another that carries them into cells. Melissa Cheung and her colleagues incorporated a peptide that binds to skin cancer cells into the enzymatic part of an RIP, the E. coli Shiga-like toxin. The researchers created a new RIP that specifically kills .skin cancer cells, which are notoriously resistant to established therapies. Some of their results are shown in FIGURE 9.17.
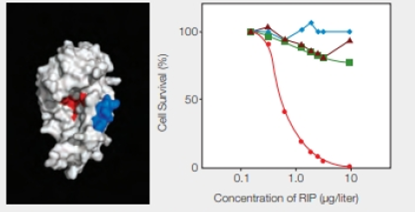
FIGURE 9.17 Effect of an engineered RIP on cancer cells. The model on the left shows the enzyme portion of E. coli Shiga-like toxin engineered to carry a small sequence of amino acids (in blue) that targets skin cancer cells. (Red indicates the active site.) The graph on the right shows the effect of this engineered RIP on human cancer cells of the skin ( ); breast (
); breast ( ) liver (
) liver ( ); and prostate (
); and prostate ( ).
).
Which cells had the greatest response to an increase in concentration of the engineered RIP?
To determine: The type of cells that had the greatest response to an increase in the concentration of the engineered RIP.
Introduction: Ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) inactivate the ribosomes and prevent protein synthesis in a cell. The toxic RIPs have a domain that makes them enter into the cell and another domain that interferes with the ribosome. They have antiviral and anticancer properties and are used to design drugs for HIV and cancer.
Answer to Problem 1DAA
Correct answer: The greatest response in the form of fall in cell’s survival percentage with an increase in the concentration of engineered RIP is seen in the skin cancer cells.
Explanation of Solution
As given in the problem statement, Researcher M and her colleagues incorporated a peptide into the enzymatic part of a RIP, the E. coli Shiga-like toxin. The peptide specifically binds to the skin cancer cells, and thus, the newly synthesized RIP kills the skin cancer cells.
Refer Fig. 9.17, “Effect of an engineered RIP on cancer cells”, in the textbook. The model shown on the left indicates a blue-colored enzyme region of E. coli Shiga-like toxin that is engineered to carry the peptide sequence specific for the skin cancer cells. The red color indicates the active site of RIP.
The graphical representation that is shown in Fig. 9.17 on the right side indicates the effect of the engineered RIP on different human cancer cells indicated by different colors and shapes. They include skin, breast, liver, and prostate cancer cells with red, blue, brown, and green color, respectively. The concentration of RIP (µg/liter) is plotted with the percentage of cell survival. As shown in the graph, as the concentration of RIP increases, there is a significant drop in the skin cancer cells percentage. It reaches to zero at RIP concentration of 10 µg/liter. In the case of the other cancer cells, there is lesser variability.
Thus, the greatest response in the form of fall in cell’s survival percentage with an increase in the concentration of engineered RIP is seen in the skin cancer cells.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Biological Science
Campbell Essential Biology (6th Edition) - standalone book
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
- Many blood clotting proteins undergo a post-translational modification in which specific glutamic acid residues (Glu) in the protein are converted to gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues (Gla). See reaction scheme below. An example is the blood clotting protein Factor IX, which has 12 Glu in its N-terminus converted to Gla. This modification gives Factor IX the ability to bind calcium and phospholipid membranes. Bacteria do not have the enzyme required to convert Glu to Gla and therefore Factor IX proteins expressed in bacteria would not have the proper modifications. How might you engineer the translational apparatus of a bacterial cell line so that it produces Factor IX with Gla in the appropriate positions. How would you ensure that only the 12 Glu in Factor IX that are normally converted to Gla and not just all Glu (Limit 5-6 senetnces)?arrow_forwardThe structure of a prodrug used for treating people with HIV virus (human immunodeficiency virus) and AIDS is shown below. This molecule is a precursor of a protease inhibitor that competitively inhibits HIV protease due to its resemblance to the proteolytic site of the enzyme. Which process in the viral life cycle does this inhibitor target directly ? Group of answer choices a. viral protein processing for making new viruses b. viral mRNA synthesis c. viral DNA integration into the host cell DNA d. viral DNA synthesisarrow_forwardOnce the chains of peptides that make up lysyl-tRNA synthetase protein are synthesized in ribosomes, lysyl-tRNA synthetase needs to have the proper active site in order to perform its function, explain the process of protein folding necessary to have a proper 3-D structure, include effect of thermodynamics and different states in folding, including what happen when there are prolines that form peptide bonds with other amino acids, and any disulfide bridgesarrow_forward
- Some types of tumors express cell-surface receptors that are specific for unique peptide sequences. Development of modified peptides that target cancerous cells specifically is an area of active research. One peptide that has been studied extensively is luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone. A portion of the peptide sequence is: HWSYKLRPG. a. Of the nine amino acid sidechains in HWSYKLRPG, how many carry a positive charge at pH 4? at pH 7.4? at pH 11? b. What is the net charge on the peptide HWSYKLRPG at pH 7? c. (optional) For extra practice, draw the structure of HWSYKLRPG in its predominant form at pH 7.4.arrow_forwardE. coli ribonuclease H1 is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphodiester bonds in RNA. Its proposed mechanism involves a 'carboxylate relay,' as shown below. His124 Asp70 || -HN-CH-C -HN-CH-C- CH2 CH2 c=0 RNA substrate HN H. H. (1) Fill the blanks. In the reaction scheme above, His124 acts as a ( ). The purpose of this relay system is to deprotonate the water molecule (II) so that it becomes a better ( :0arrow_forwardI-cell disease is a classic example of an inherited human defect in protein targeting that affects an entire class of proteins: the soluble enzymes of the lysosome. What is the molecular defect in I-cell disease? Why does it affect the tar- geting of an entire class of proteins? What other types of mutations might produce the same phenotype?arrow_forward
- Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an inherited disorder caused by different types of mutations, many of which prevent ions from moving across cell membranes. Normally there are channel proteins that allow passage of the ions, but in patients with one kind of CF these proteins seem odd. Closer examination shows that these proteins display the correct amino acid sequence. However, they fail to do their job. A) Given that the primary structure of the protein is correct, what can you infer about the DNA sequence for the gene coding this protein on this patient, is there a mutation? Explain. B) Why is the primary structure insufficient to guarantee the proper function of the protein?arrow_forwardWhich of the following would be a good chemotherapy approach: blocking formationof the ribonucleotide GTP or blocking formation of the deoxyribonucleotide dGTP?Why? Please explain the chemical differences between each of the two nucleotides. Use the specific processes below to support your choice by explaining how either GTP or dGTPare related to these and how loss of the particular molecule would affect each process. *PEP carboxykinase in gluconeogenesis*Succinyl-CoA synthetase in the TCA Cycle*Glucagon signal transductionarrow_forwardWhich factor has NOT been shown to play a role in determining the specificity of protein kinases? a. protein tertiary structure b. protein quaternary structure c. primary sequence at phosphorylation site d. disulfide bonds near the phosphorylation site e. residues near the phosphorylation sitearrow_forward
- You are working with a protein that is known to form an functioning complex of three identical polypeptide subunits, each with a binding site for a ligand of interest. You are studying an inherited mutation in the protein that changes one Asp residue to a Leu residue in each subunit. A comparison of the binding curves for the normal (wild-type) and mutant versions of the complex are shown below. Suggest a mechanism for the effect that this mutation has on the structure of the complex.arrow_forwardKnowing that the genetic code is almost universal, a scientist uses molecular biological methods to insert the human β-globin gene (Shown in Figure 17.11) into bacterial cells, hoping the cells will express it and synthesize functional β-globin protein. Instead, the protein produced is nonfunctional and is found to contain many fewer amino acids than does β-globin made by a eukaryotic cell. Explain why.arrow_forwardHuman cells are highly resistant to transformation. Experiments have shown that 5 regulatory circuits (pathways) have to be altered before human cells can grow as tumor cells in immunocompromised mice. State each of these circuits. Explain how the alteration of the protein of that particular circuit leads to uncontrolled growth.arrow_forward
 Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax

