
Concept explainers
RIPs as Cancer Drugs Researchers are taking a page from the structure-function relationship of RIPs in their quest for cancer treatments. The most toxic RIPs, remember, have one domain that interferes with ribosomes, and another that carries them into cells. Melissa Cheung and her colleagues incorporated a peptide that binds to skin cancer cells into the enzymatic part of an RIP, the E. coli Shiga-like toxin. The researchers created a new RIP that specifically kills .skin cancer cells, which are notoriously resistant to established therapies. Some of their results are shown in FIGURE 9.17.
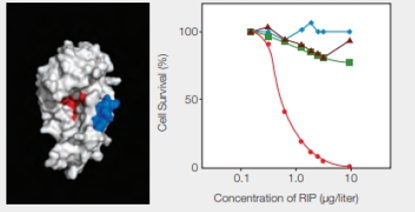
FIGURE 9.17 Effect of an engineered RIP on cancer cells. The model on the left shows the enzyme portion of E. coli Shiga-like toxin engineered to carry a small sequence of amino acids (in blue) that targets skin cancer cells. (Red indicates the active site.) The graph on the right shows the effect of this engineered RIP on human cancer cells of the skin ( ); breast (
); breast ( ) liver (
) liver ( ); and prostate (
); and prostate ( ).
).
At what concentration of RIP did all of the different kinds of cells survive?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Concepts and Investigations
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (4th Edition)
Human Anatomy (8th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Seeley's Anatomy & Physiology
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach - Standalone book
- Only answer please, no need to explain… Thank you for your time. i: Modification of the 5 prime ends of eukaryotic mRNA is called? a) Capping b) Polyadenylation c) Splicing d) Transcription ii: Genetic Code is? a) The sequence of Nitrogenous Bases in mRNA that codes for a protein b) Is a Triplet Code c) is Non-Overlapping d) All of these iii. The process of formation of RNA is known as a) Replication b) DNA repair c) Translation d) Transcription iv. Which of the following statement is NOT true regarding transcription/RNA synthesis? a) RNA synthesis occurs in the nucleus b) Unlike DNA synthesis, the only selective sequence of DNA is transcribed to RNA c) RNA synthesis requires a short stretch of RNA primers d) DNA sequences, specific proteins, and small RNAs regulate RNA synthesisarrow_forwardIn the: Mutation of the 23S RNA preventing the binding of the 40S with 60S ribosomes Explain: (a) What is the process affected? (b) What is the Effect on the process? (c) Does it affect prokaryotes, eukaryotes or both?arrow_forwardTrue or False. 1. a.) RNA polymerase decodes mRNA so the ribosome can make proteins. b.) Only coding RNA can interact with the ribosome. c.) The ribosome is composed of both protein and ncRNA. d.)The ncRNA components of the ribosome behave as a ribozyme. Pick one of the FALSE statements from the 4 previous questions and explain why it is incorrect.arrow_forward
- Many blood clotting proteins undergo a post-translational modification in which specific glutamic acid residues (Glu) in the protein are converted to gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues (Gla). See reaction scheme below. An example is the blood clotting protein Factor IX, which has 12 Glu in its N-terminus converted to Gla. This modification gives Factor IX the ability to bind calcium and phospholipid membranes. Bacteria do not have the enzyme required to convert Glu to Gla and therefore Factor IX proteins expressed in bacteria would not have the proper modifications. How might you engineer the translational apparatus of a bacterial cell line so that it produces Factor IX with Gla in the appropriate positions. How would you ensure that only the 12 Glu in Factor IX that are normally converted to Gla and not just all Glu (Limit 5-6 senetnces)?arrow_forwardPart A Shown above is a schematic diagram of the E. coli leader peptidase (Lep) which has several basic amino acids in a cytoplasmic loop. Propose a mutant of Lep that would be a test of the "inside positive" rule for the orientation of proteins in membranes. Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. Make certain each sentence is complete before submitting your answer. terminal reversed same (+) (-) center 1. Make mutant Lep that substitutes noncharged residues for the chains in the loop, and put charged side chains in 2. If the inside-positive rule applies, the mutant ought to have the membrane. Reset Help charged side positions. orientation in thearrow_forwardWhat enzyme catalyzes protein synthesis in bacteria? You discover a new broad-spectrum antibiotic that inhibits protein synthesis and named it Compound J. You want to determine the mechanism of action of Compound J. After treating bacteria cells with Compound J, you observe many ribosomes with long polypeptide chains bound to them. Based on this observation, make a hypothesis about which part of the ribosome Compound J is binding and how this specifically affects translation. What evidence supports that proper protein folding is essential to all domains of life? Name and describe the function/s of two specific molecules that help proteins fold in bacteria.arrow_forward
- Hi, Could you please comfirm the following question. I have selected option c) because tRNA is the the complimentary pairs of mRNA so I figured the oppside end of the tRNA would be the same as the mRNA. When I have tired to double check my answer, no tutor has selected this answer. Thank you in advance, Like mRNA, tRNA has a ribose sugar, U instead of T, and is single stranded. Unlike mRNA, which remains a long single strand of nucleotides, tRNA folds so that some areas pair up. The resulting structure has an anticodon on one end and a site for an amino acid to attach on the other end. There is base complementarity (A pairs with U and G pairs with C) between an mRNA codon and tRNA anticodon.If the amino acid lysine attaches to a tRNA, which of the following anticodons could be at the opposite end of the tRNA molecule? a. UUU and UUC b. AGA and AGU c. AAA and AAG d. UCU and UCAarrow_forwardThe steroid progesterone has an important role in the female reproductive system. Researchers interested in studying membrane progestin receptors (MPRS) developed a method to produce and purify the protein in active form. First, the researchers devised a way to prepare a specific MPR known as hMPRA using the machinery of yeast cells. In order to facilitate purification and identification in later studies, they manipulated the yeast cells so that they attached two different tags to the C-terminal end of the protein. The first tag, Compound 1, is a peptide sequence that acts as an epitope, part of a much larger peptide sequence that is recognized by the immune system. The second sequence consisted of six consecutive histidine residues (His). This sequence binds tightly to Ni2+ cations. In chromatography, (His), tag labeled proteins can be eluted from Ni²+. supported columns by adding a small molecule to the eluent that mimics the side chain of histidine.…arrow_forwardThe steroid progesterone has an important role in the female reproductive system. Researchers interested in studying membrane progestin receptors (MPRs) developed a method to produce and purify the protein in active form. First, the researchers devised a way to prepare a specific MPR known as hMPRA using the machinery of yeast cells. In order to facilitate purification and identification in later studies, they manipulated the yeast cells so that they attached two different tags to the C-terminal end of the protein. The first tag, Compound 1, is a peptide sequence that acts as an epitope, part of a much larger peptide sequence that is recognized by the immune system. The second sequence consisted of six consecutive histidine residues (His). This sequence binds tightly to Ni2+ cations. In chromatography, (His), tag labeled proteins can be eluted from Ni²+- supported columns by adding a small molecule to the eluent that mimics the side chain of histidine. After preparing hMPRA, the…arrow_forward
- Once the chains of peptides that make up lysyl-tRNA synthetase protein are synthesized in ribosomes, lysyl-tRNA synthetase needs to have the proper active site in order to perform its function, explain the process of protein folding necessary to have a proper 3-D structure, include effect of thermodynamics and different states in folding, including what happen when there are prolines that form peptide bonds with other amino acids, and any disulfide bridgesarrow_forwardLike ribonuclease A, lysozyme from T4 phage is a model enzyme for understanding the energetics and pathways of protein folding. Unlike ribonuclease A, T4 lysozyme does not contain any disulfide bonds. A number of studies have quantified the thermodynamic contributions individual amino acid residues and their interactions make to lysozyme folding. An ion pair between an Asp residue and a His residue in lysozyme contributes 13-21 kJ/mol of favorable folding energy at pH 6.0. However, this ion pair contributes much less to lysozyme folding at either pH 2.0 or pH 10.0. Why does the Asp-His ion pair contribute more energy at pH 6.0 than at low or high pH? At pH 10.0, Asp is protonated and His may be deprotonated. At pH 6.0, Asp is protonated and His may be deprotonated. At pH 2.0, Asp and His are both deprotonated. At pH 10.0, Asp and His are both protonated. ● At pH 6.0, Asp is deprotonated and His may be protonated.arrow_forwardWhat molecular biology strategy can best be used to determine Failure of t-RNA to bind at the A site of the small subunit of the ribosome? Explain.arrow_forward
 Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
