
Concept explainers
a.
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept Introduction:
We can predict the shape of a particular molecule by the knowledge of their
The main concept behind this theory is that the electron pairs are always present in the outermost shell i.e. valence shell of an atom of a molecule and they repel each other due to which they try to attain the best possible position so that the value of their repulsion is the least. Hence, the electrons occupy such positions around the atom that reduces their repulsion and provides a molecule to their shape.
Here the electrons that take part in the bonding of a molecule are known as the bonding pair and the electrons that do not take part in the bonding are known as the lone pairs. The bond pairs are in the influence of the two bonding atoms whereas the lone pairs are in the influence of only of the atom.
Due to the presence of lone pairs, there is more space occupied between the atoms of the molecules. Now they suffer the repulsion between the lone pair-lone pair and bond pair-lone pair. Their repulsion can be represented as:-
lp-lp>lp-bp>bp-bp
a.
Answer to Problem 7.75PAE
Solution:
The geometry of
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration of Xeis
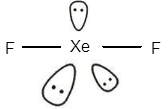
The geometry of
The central atom has three lone pairs of electrons
b.
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept Introduction:
We can predict the shape of a particular molecule by the knowledge of their atomic numbers and VSEPR theory. According to this theory, the atoms take such a position in which there is a minimum possible repulsion between the bonded atoms and the lone pair of electrons if any. For Linear Molecular geometry, the molecules of an atom are arranged in a straight line making an angle of 180o with the lone pairs if any. A lonepair is the pair of an electron occupying the orbital but not taking part in the bonding.
The main concept behind this theory is that the electron pairs are always present in the outermost shell i.e. valence shell of an atom of a molecule and they repel each other due to which they try to attain the best possible position so that the value of their repulsion is the least. Hence, the electrons occupy such positions around the atom that reduces their repulsion and provides a molecule to their shape.
Here the electrons that take part in the bonding of a molecule are known as the bonding pair and the electrons that do not take part in the bonding are known as the lone pairs. The bond pairs are in the influence of the two bonding atoms whereas the lone pairs are in the influence of only of the atom.
Due to the presence of lone pairs, there is more space occupied between the atoms of the molecules. Now they suffer the repulsion between the lone pair-lone pair and bond pair-lone pair. Their repulsion can be represented as:-
lp-lp>lp-bp>bp-bp
b.
Explanation of Solution
The geometry of
is linear and it has 0 lone pairs of an electron on the central atom The electronic configuration of C is
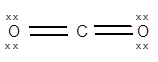
The geometry of
The central atom has no lone pair of electrons
c.
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept Introduction We can predict the shape of a particular molecule by the knowledge of their atomic numbers and VSEPR theory. According to this theory, the atoms take such a position in which there is a minimum possible repulsion between the bonded atoms and the lone pair of electrons if any. For Linear Molecular geometry, the molecules of an atom are arranged in a straight line making an angle of 180o with the lone pairs if any. A lonepair is the pair of an electron occupying the orbital but not taking part in the bonding.
The main concept behind this theory is that the electron pairs are always present in the outermost shell i.e. valence shell of an atom of a molecule and they repel each other due to which they try to attain the best possible position so that the value of their repulsion is the least. Hence, the electrons occupy such positions around the atom that reduces their repulsion and provides a molecule to their shape.
Here the electrons that take part in the bonding of a molecule are known as the bonding pair and the electrons that do not take part in the bonding are known as the lone pairs. The bond pairs are in the influence of the two bonding atoms whereas the lone pairs are in the influence of only of the atom.
Due to the presence of lone pairs, there is more space occupied between the atoms of the molecules. Now they suffer the repulsion between the lone pair-lone pair and bond pair-lone pair. Their repulsion can be represented as:-
c.
Answer to Problem 7.75PAE
lp-lp>lp-bp>bp-bp
Solution: The geometry of
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration of Be is
Structure of
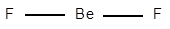
The geometry of
The central atom has no lone pair of electrons
d.
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept Introduction We can predict the shape of a particular molecule by the knowledge of their atomic numbers and VSEPR theory. According to this theory, the atoms take such a position in which there is a minimum possible repulsion between the bonded atoms and the lone pair of electrons if any. For Linear Molecular geometry, the molecules of an atom are arranged in a straight line making an angle of 180o with the lone pairs if any. A lonepair is the pair of an electron occupying the orbital but not taking part in the bonding.
The main concept behind this theory is that the electron pairs are always present in the outermost shell i.e. valence shell of an atom of a molecule and they repel each other due to which they try to attain the best possible position so that the value of their repulsion is the least. Hence, the electrons occupy such positions around the atom that reduces their repulsion and provides a molecule to their shape.
Here the electrons that take part in the bonding of a molecule are known as the bonding pair and the electrons that do not take part in the bonding are known as the lone pairs. The bond pairs are in the influence of the two bonding atoms whereas the lone pairs are in the influence of only of the atom.
Due to the presence of lone pairs, there is more space occupied between the atoms of the molecules. Now they suffer the repulsion between the lone pair-lone pair and bond pair-lone pair. Their repulsion can be represented as:-
lp-lp>lp-bp>bp-bp
d.
Answer to Problem 7.75PAE
Solution:
The geometry of
Explanation of Solution
The electronic configuration of O is
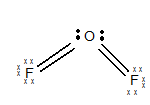
The geometry of
The central atom has two lone pairs of electrons
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry for Engineering Students
- The Ksp for lead iodide ( Pbl₂) is 1.4 × 10-8. Calculate the solubility of lead iodide in each of the following. a. water Solubility = mol/L b. 0.17 M Pb(NO3)2 Solubility = c. 0.017 M NaI mol/L Solubility = mol/Larrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forward
- Only 100% sure experts solve it correct complete solutions need to get full marks it's my quiz okkkk.take your time but solve full accurate okkk chemistry expert solve itarrow_forwardPleasssssseeee solve this question in cheeemsirty, thankss sirarrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

