
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The differences between the first step in reactions of
Concept introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as
In addition reaction of
Regioselective reaction: They are reactions which contain more than one product which are actually molecules with same molecular formula but different in the way they are connected and among those products only one product is major.
Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
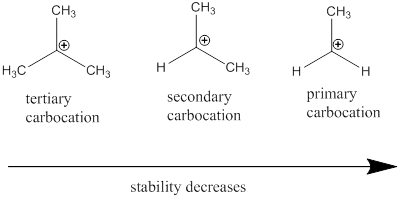
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Leaving group: it is a fragment that leaves from a substrate with a pair of electrons via
Carbocation stability order:
(b)
Interpretation:
The product and reason for attack of
Concept introduction:
Addition Reaction: It is defined as chemical reaction in which two given molecules combines and forms product. The types of addition reactions are electrophilic addition, nucleophilic addition, free radical additions and cycloadditions. Generally, compounds with carbon-hetero atom bonds favors addition reaction.
In addition reaction of alkenes when two substituents are placed on same side of
Regioselective reaction: They are reactions which contain more than one product which are actually molecules with same molecular formula but different in the way they are connected and among those products only one product is major.
Markovnikov’s Addition Rule: The unsymmetrical alkene in a chemical compound reacts with hydrogen halide in a way, where halide ions attacks and bond to the more substitution position of carbon-carbon double bond.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)

 EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

