
(a)
Interpretation: The acid base reaction of aniline with hydrochloric acid needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction:Bronsted and Lowery purposed the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory. It states that acid can give
(b)
Interpretation: The acid, base, conjugated acid and conjugated base in the reaction of aniline with hydrochloric acid needs to be determined.
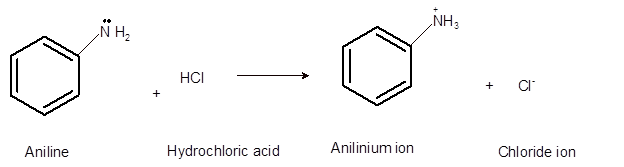
Concept Introduction:Bronsted and Lowery purposed the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory. It states that acid can give
(c)
Interpretation: The solubility of aniline and its conjugated base in diethyl ether and water needs to be explained.

Concept Introduction:Bronsted and Lowery purposed the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory. It states that acid can give
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK EXPERIMENTAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: A M
- Part I. Give an example of the following substances. 1. An acid according to Arrhenius and Bronsted-Lowry theory 2. A neutral Bronsted-Lowry base but not an Arrhenius base 3. A Lewis acid but not an Arrhenius acid 4. A charged, amphoteric moleculearrow_forwardLola and Richie were tasked to analyze the acidity of a 10.0-mL fermented milk sample diluted with water in a 250-mL volumetric flask. Mola obtained a 15.0-mL aliquot of this solution, diluted it to 50.0 mL, and then titrated this diluted sample. Titration data were given to Rity and she found out that the 50.0-mL sample contains 0.21 mmol of lactic acid. MW: Lactic Acid (90.08)1.What is the lactic acid concentration (in M) of the titrated sample?2. Determine the lactic acid content (in M) of the 10.0-mL fermented milk sample.3. What is the lactic acid concentration (in %w/v) of the 10.0-mL fermented milk sample?arrow_forwardYeni... O Ara Posta Gonderileri Gözden Geçir Görünüm Yardim 4- Write equations for the acid base reactions that would occur (if any) if ethanol were added to solutions of each of the following compounds In each reaction, label the stronger acid, the stronger base, and so forth.(Please consult the table given below) Ya) NaNH (c) (d) NaOH EGO 16 A 12 IA 17 & 5 8 Karrow_forward
- 4. Calculate the pH you would expect for a 0.15 M aqueous solution of each substance. - nitric acid - ascorbic acid - lithium hydroxide - methylamine (see Table 15.4, p. 682) I 5. Consider your work on the ascorbic acid solution in the previous problem. What would the equilibrium concentration of the conjugate (ascorbate, C,H;O6) be in the solution?arrow_forwardExplain why phenolphthalein is used to determine when the reaction is “done”. Make sure to explain the role of NaOH in this solution.arrow_forwardI need help with this problem. Compare the pH of propionic acid and nitric acid when they are dissolved in water at a concentration of 20 mM using the "Arrhenius Concept". Include:a balanced equation describing the acid-base reactions involvedThe calculation of the pKa for bothThe calculation of the two pH's (of propionic acid and nitric acid when they are dissolved in water at a concentration of 20 mM)and A calculation of the percent of dissociation of both propionic acid and nitric acid.The gibbs free energy ΔG are listed as the following:Nitric acid: -152 kJ/molPropionic Acid : -291 kJ/molPropionate: -361 kJ/molarrow_forward
- 1. What is the structure of N,N-diethylaniline? CH₂CH3 CH3 B 2. Which of the following compounds is least soluble in water? NH₂ A O₂N A. IB. II C. III D. both I and III 3. Which of the following compounds is the strongest base? NH₂2 NH₂ NH₂ III NH₂ A. I B. II C. III D. IV E. V IV NH₂ с NH₂arrow_forward3. What is observed when the H2O concentration in the acetic acid equilibrium becomes relatively low? Relatively high? 4. Humidity indicator cards (HIC) are commonly added to semiconductor shipments to document that the parts were not exposed to humidity. These cards are impregnated with cobalt(II) chloride, or an alternative, and change color to indicate the presence of water. Predict the color you would see if a cobalt(II) chloride HIC were exposed to moist, humid air?arrow_forwardWhich of the following functional groups will increase acidity? I. -NO2 II. -CH2CH3 III. -OCH3 IV. - Clarrow_forward
- The conjugate base of benzoic acid is used as a 72 preservative. Write the equilibrium reaction for this weak acid in aqueous solution. ОН Benzoic acid a. What substances are present at equilibrium? b. At equilibrium, are reactants or products favored, and why? c. Are the concentrations of benzoic acid and benzoate constant or changing at equilibrium? d. What happens to the equilibrium if more hydronium ions are added to the reaction? e. Label the conjugate acid-base pairs.arrow_forwardPart A The chemical 5-amino-2,3-dihydro-1,4-phthalazinedione, better known as luminol, is used by forensic scientists in analyzing crime scenes for the presence of washed-away blood. Luminol is so sensitive that it can detect blood that has been diluted 10,000 times. A basic solution of luminol is often sprayed onto surfaces that are suspected of containing minute amounts of blood. The forensic technician at a crime scene has just prepared a luminol stock solution by adding 15.0 g of luminol into a total volume of 75.0 mL of H2O. What is the molarity of the stock solution of luminol? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Luminol has a molecular weight of 177 g/mol. • View Available Hint(s) HẢ molarity of luminol solution = Value Units Submit Part B Before investigating the scene, the technician must dilute the luminol solution to a concentration of 6.00x10-2 M. The diluted solution is then placed in a spray bottle for application on the desired surfaces. How many moles of…arrow_forward3. When an acid is neutralized by a base in the presence of phenolphthalein, a faint purple-pink color is observed at the end point; however, after a few minutes, the solution becomes colorless. a. What can you say about the solution when it has a faint purple-pink color? What must have changed about the solution for the color to go away? Assume that the phenolphthalein is still present. b. The cause of the change is the carbon dioxide that is in the air. Rising levels of CO2 in the atmosphere pose serious concerns not only for the temperature of the earth, but also a process known as ocean acidification. What is ocean acidification, and why is it a concern? 8/16/2023arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

