
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134320533
Author: Michael S. Mamlouk, John P. Zaniewski
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.37QP
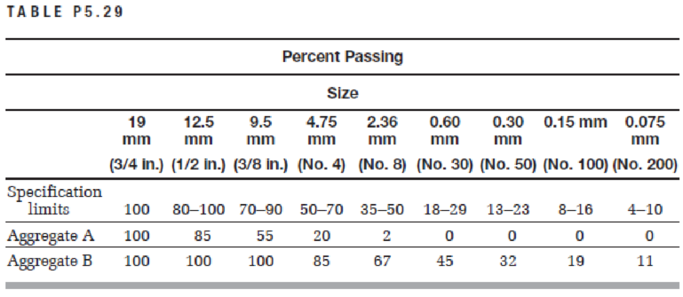
Calculate the fineness modulus of aggregate B in Problem 5.29. Is your answer within the typical range for fineness modulus? If not, why not? (Note that the percent passing the 1.18-mm [No. 16] sieve is not given and must be estimated.)
5.29 Table P5.29 shows the grain size distribution for two aggregates and the specification limits for an asphalt concrete. Determine the blend proportion required to meet the specification and the gradations of the blend. On a semilog gradation graph, plot the gradations of aggregate A, aggregate B, the selected blend, and the specification limits.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Based on the data shown in Table P9.31, select the blend for a Superpave
design aggregate structure. Assume <0.3 million ESAL and 19 mm nominal
maximum aggregate size.
TABLE P9.31
Blend
Data
1
3
Gmb
Gmm
2.451
2.465
2.467
2.585
2.654
2.584
Gp
1.030
1.030
1.030
P
5.9
5.5
5.8
94.1
94.5
94.2
Ра
4.5
4.5
4.5
Gşb
2.657
2.667
2.705
Hini
127
135
124
Håes
113
114
118
Q3) The result of sieve analysis of a sample of aggregate given in the Table below. According
to ASTM C 33, the sample is acceptable or not?
BS
Total mass of sample 4 80 g
Sieve size
10 mm
5 mm
2.36 mm
1.18 mm
600 μm
300 μm
150 μm
€150μm
ASTM
in
4
8
16
30
50
100
<-100
Mass retained
O
80
40
80
110
68
61
Determine the suitability of the aggregate, with the gradation tabulated below, for use in Portland cement concrete. Review the grain size distribution to determine if it meets all of the relevant specifications for use in concrete (i.e. gradation limits, fineness modulus and % fines). Refer to the specification for concrete aggregates (Table 7 – 10) below:
Grain Size (mm)
% Passing
Cum %Retained
25
100
19
100
12.5
100
9.5
100
4.75
95
2.36
85
1.18
55
0.6
30
0.3
15
0.15
8
0.075
6
Fineness Modulus - write answer to two decimal places
Percent fines - write answer to the nearest whole number %
Meets Gradation Limits? - y/n (only type lower case "y" for yes and lower case "n" for no)
Suitable for use in portland cement concrete subject to abrasion? - y/n (only type lower case "y" for yes and lower case "n" for no)
Chapter 5 Solutions
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers (4th Edition)
Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.1QPCh. 5 - Discuss five different desirable characteristics...Ch. 5 - Discuss five different desirable characteristics...Ch. 5 - The shape and surface texture of aggregate...Ch. 5 - Define the following terms: a. Saturated...Ch. 5 - Three samples of fine aggregate have the...Ch. 5 - A sample of wet aggregate weighed 297.2 N. After...Ch. 5 - 46.5 kg (102.3 lb) of fine aggregate is mixed with...Ch. 5 - Samples of coarse aggregate from a stockpile are...Ch. 5 - Base course aggregate has a target dry density of...
Ch. 5 - Calculate the percent voids between aggregate...Ch. 5 - Calculate the percent voids between aggregate...Ch. 5 - Coarse aggregate is placed in a rigid bucket and...Ch. 5 - The following laboratory tests are performed on...Ch. 5 - Students in the materials lab performed the...Ch. 5 - The specific gravity and absorption test (ASTM...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.18QPCh. 5 - Calculate the sieve analysis shown in Table P5.19...Ch. 5 - Calculate the sieve analysis shown in Table P5.20,...Ch. 5 - A sieve analysis test was performed on a sample of...Ch. 5 - A sieve analysis test was performed on a sample of...Ch. 5 - Draw a graph to show the cumulative percent...Ch. 5 - Referring to Table 5.6, plot the specification...Ch. 5 - Referring to the aggregate gradations A, B, and C...Ch. 5 - Table P5.26 shows the grain size distributions of...Ch. 5 - Table P5.27 shows the grain size distributions of...Ch. 5 - Three aggregates are to be mixed together in the...Ch. 5 - Table P5.29 shows the grain size distribution for...Ch. 5 - Laboratory specific gravity and absorption tests...Ch. 5 - Table P5.31 shows the grain size distribution for...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.32QPCh. 5 - Laboratory specific gravity and absorption tests...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.34QPCh. 5 - Define the fineness modulus of aggregate. What is...Ch. 5 - Calculate the fineness modulus of aggregate A in...Ch. 5 - Calculate the fineness modulus of aggregate B in...Ch. 5 - A portland cement concrete mix requires mixing...Ch. 5 - Discuss the effect of the amount of material...Ch. 5 - Aggregates from three sources having the...Ch. 5 - Aggregates from three sources having the...Ch. 5 - A contractor is considering using three stockpiles...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.43QPCh. 5 - What are the typical deleterious substances in...Ch. 5 - Review ASTM D75 and summarize the following: a....
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the suitability of the aggregate, with the gradation tabulated below, for use in Portland cement concrete. Review the grain size distribution to determine if it meets all of the relevant specifications for use in concrete (i.e. gradation limits, fineness modulus and % fines). Refer to the specification for concrete aggregates (Table 7 – 10) below: Grain Size (mm) % Passing Cum %Retained 25 100 19 100 12.5 100 9.5 100 4.75 95 2.36 85 1.18 55 0.6 30 0.3 15 0.15 8 0.075 6arrow_forward500 gm oven dry fine aggregate was tested to find its physical properties. The output from the test was as follows: SSD = 510 gm, mass of the vessel full of water = 1200 gm, mass of vessel plus sand and topped up with water= 1500 gm, mass in wet condition 518 gm, Apparent specific gravity= 2.5 . The grading of the fine aggregate is in the table below. Answer the followings choose the correct answer 1- The fineness modulus (F.M) is a- 2.6 b- 2.8 c- 2.4 d- 2.7 e- 2.5 2- The bulk specific gravity is a- 2.63 b- 2.53 c- 2.33 d- 2.43 e- 2.73 3- Absorption% is a- 4.5% c- 2.0% d- 6.0% e- 3.6% f- 5.2%…arrow_forwardThe following are the results in the test for specific gravity of fine aggregates:Mass of Oven-dried specimen in air = 502gMass of Pycnometer filled with water, to calibration mark = 640gMass of Saturated Surface Dry Specimen = 510gMass of Pycnometer filled with specimen and water to calibration mark = 950gCalculate the absorption, apparent specific gravity, bulk specific gravity in SSD condition, and bulk specific gravity in OD conditionarrow_forward
- There are two sources of aggregates (A, B). A sample has been taken from both sources and measured their mass as shown in table below. Measurement Wet mass (9) Oven-dry mass (g) Aggregate A 500 480 Aggregate B 600 564 (a) Determine the total moisture content for the samples from both aggregate sources, respectively. (b) Determine the total moisture content for an aggregate blend with 30% of aggregate A and 70% of aggregate B.arrow_forward500 gm oven dry fine aggregate was tested to find its physical properties. The output from the test was as follows: SSD = 510 gm, mass of the vessel full of water = 1200 gm, mass of vessel plus sand and topped up with water= 1500 gm, mass in wet condition 518 gm, Apparent specific gravity= 2.5 . The grading of the fine aggregate is in the table below. Answer the followings: 1- The fineness modulus (F.M) is 2- The bulk specific gravity is 3- Absorption% is 4- Moisture content % is 5- The mass of oven dried sand isarrow_forwardFrom the given data shown in the table for a mix design of asphalt concrete. Compute the effective specific gravity of aggregates. Express your answer in 4 decimal places. SG Materials Fine Aggregates 2.650 Coarse Aggregates 2.725 Asphalt Cement 1.03 Total: Percent by weight 40.7 41.1 12 100arrow_forward
- Questions 30 is based on the information below: An asphalt concrete mix design has the following properties. The densities of the binder and aggregate are 1.090 g/cm³ and 2.760 g/cm³, respectively. The bulk density of the entire mix is 2.220 g/cm³. The percent binder content is 6.2% (by weight). Assume no absorption. V₁= 1.0 cm³ Volume Vv Vb Vs AIR Binder Aggregate Mass Mb Ms Mt 30. As an engineer, you are asked to use this mix design for a 25 kilometer-long section of roadway where the total pavement width is 8.0 meters and the thickness is 15 centimeters. What is the (a) total volume of binder and (b) the total volume of aggregate that you would need to purchase? Also, determine the (c) total %air voids in the mix.arrow_forwardThe table below presents the results of the sieve analysis conducted on a sample of aggregate. Given the bulk specific gravities of 2.65 for coarse aggregate, 2.69 for fine aggregate, and 2.73 for filler, determine the bulk density of the aggregate sample. Additionally, calculate the maximum aggregate size and nominal aggregate maximum size. Sieve size (mm) 37.5 % Passing 100 Specification limit 25 92 100 90-100 19 83 76-90 12.5 9.5 4.75 2.36 0.3 71 62 53 32 15 56-80 48-74 29-59 19-45 5-17 0.075 4 2-8arrow_forwardSamples of coarse aggregate from a stockpile are brought to the laboratory for determination of specific gravities. The following weights are found: Mass of moist aggregate sample as brought to the laboratory: 5,298 grams Mass of oven dried aggregate: 5,216 g Mass of aggregates submerged in water: 3,295 g Mass of SSD (Saturated Surface Dry) Aggregate: 5,227 g Find a. The aggregate bulk dry specific gravity b. The aggregate apparent specific gravity c. The moisture content of stockpile aggregate (report as a percent) d. Absorption (report as percent)arrow_forward
- A portland cement concrete mix requires mixing sand having a gradation following the midpoint of the ASTM gradation band and gravel having a gradation following the midpoint of size number 467 of the ASTM gradation band at a ratio of 2:3 by weight. On a 0.45 power gradation chart, plot the gradations of the sand, gravel, and the blend. Is the gradation of the blend well graded? If not, what would you call it?arrow_forward9.31 Based on the data shown in Table P9.31, select the blend for a Superpave design aggregate structure. Assume <0.3 million ESAL and 19 mm nominal maximum aggregate size. Table P9.31 Blend Data 1 2 3 2.451 2.465 2.467 Gmb Gmm Gp P P3 Pd Gsb Hini Hdes 2.585 2.654 2.584 1.030 1.030 1.030 5.9 5.5 5.8 94.1 94.5 94.2 4.5 4.5 4.5 2.657 2.667 2.705 127 135 124 113 114 118arrow_forwardThoroughly mix the aggregate sample and reduce it to an amount suitable for testing, using a sample splitter or by quartering. The minimum sample size should be as follows: Minimum Mass, kg Fine aggregate with at least 95% passing 2.36-mm sieve 0.1 Fine aggregate with at least 85% passing 4.75-mm sieve 0.5 Coarse aggregate with a nominal maximum size of 9.5 mm 1 Coarse aggregate of a nominal maximum size of 12.5 mm 2 Coarse aggregate of a nominal maximum size of 19.0 mm Coarse aggregate of a nominal maximum size of 25.0 mm 10 Coarse aggregate of a nominal maximum size of 37.5 mm 15arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Aggregates: Properties; Author: nptelhrd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=49yGZYeokKM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY