
To find:
a) Draw Lewis structure for possible arrangement of
b) Assign formal charges of each structure.
c) Give reason why structure is not stable.
Answer to Problem 4.121QA
Solution:
a) i) ii)
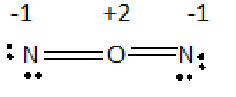
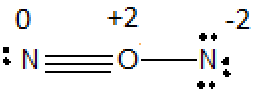
b) i) Formal charge on each N is -1 and on O is +2.
ii) Formal charge on one of N is -2 and on O is +2.
c) In both structure the formal charge on oxygen is +2. Since oxygen is more electronegative than Nitrogen none of these structure is stable.
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
Each molecule contains two Nitrogen and one oxygen has an overall charge zero. Nitrogen and oxygen are in group 15 and 16 and have bonding capacity three and two. Nitrogen can show hypervalency.
2) Calculations:
The number of valence electrons are,
| Elements | Valence electrons | ||
| Symbol | Number of atom | In one atom | Total |
| N | 2 | 5 | 10 |
| O | 1 | 6 | 6 |
| Valence electrons in molecule | 16 | ||
First possible arrangement of
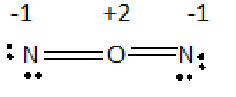
Second possible arrangement of
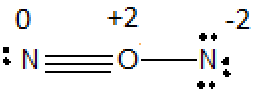
Formula:
To find formal charge we need to use following equation,
Calculation:
Step 1) Calculations of formal charge on atoms in first structure,
Step 2) Calculations of formal charge on atoms in second structure,
Oxygen has electronegativity 3.5 and nitrogen has electronegativity 3.0. Thus, structures with formal negative charges on nitrogen and formal positive charges on oxygen are not preferred. Therefore none of these structures is stable.
Conclusion:
a) Lewis structure for possible arrangement of
i) ii)
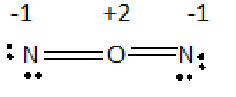
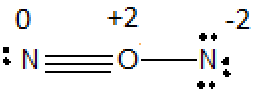
b) i) Formal charge on each N is -1 and on O is +2.
ii) Formal charge on one of N is -2 and on O is 2+
c) Oxygen is more electronegative than Nitrogen and each of structure contains +2 charge on oxygen so none of these structure is likely to be stable.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Chemistry: An Atoms-Focused Approach
- (12) Which one of the following statements about fluo- rometry is FALSE? a) Fluorescence is better detected at 90 from the exci- tation direction. b) Fluorescence is typically shifted to longer wave- length from the excitation wavelength. c) For most fluorescent compounds, radiation is pro- duced by a transitionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





