
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Using the
Concept Introduction:
Every matter is made of chemicals. Chemistry is very important for the study of everything. Chemistry is all about how something interacts to affect the structure, composition, as well as properties of substances.
(a)
Answer to Problem 59A
The element with the given chemical symbol,
Explanation of Solution
Protons are defined as positively charged
Electrons are negatively charged subatomic particles found orbiting the nucleus of an atom.
For neutral atom, the number of Electron = number of protons.
Neutrons are subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom which is neutral.
An atom has a nucleus with a positive charge due to its protons and has electrons in the space surrounding the nucleus at a relatively large distance from it.
For
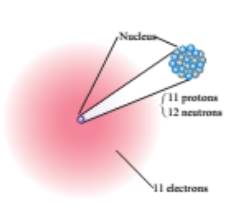
From the given figure, the first element contains
The atomic number of the element is
Hence, the first element is
(b)
Interpretation:
Using the
Concept Introduction:
Every matter is made of chemicals. Chemistry is very important for the study of everything. Chemistry is all about how something interacts to affect the structure, composition, as well as properties of substances.
(b)
Answer to Problem 59A
The elements with the chemical symbol and atomic number and mass number -
Explanation of Solution
Protons are defined as positively charged
Electrons are negatively charged subatomic particles found orbiting the nucleus of an atom.
For neutral atom, the number of Electron = number of protons.
Neutrons are subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom which is neutral.
An atom has a nucleus with a positive charge due to its protons and has electrons in the space surrounding the nucleus at a relatively large distance from it.
For
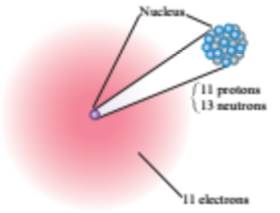
From the given figures
The second element contains
The atomic number of the element is
Hence, the second element is
(c)
Interpretation:
Using the
Concept Introduction:
Every matter is made of chemicals. Chemistry is very important for the study of everything. Chemistry is all about how something interacts to affect the structure, composition, as well as properties of substances.
(c)
Answer to Problem 59A
The element with the chemical symbol and atomic number and mass number is:
Explanation of Solution
Protons are defined as positively charged
Electrons are negatively charged subatomic particles found orbiting the nucleus of an atom.
For neutral atom, the number of Electron = number of protons.
Neutrons are subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom which is neutral.
An atom has a nucleus with a positive charge due to its protons and has electrons in the space surrounding the nucleus at a relatively large distance from it.
For
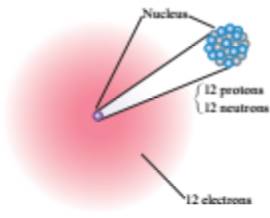
The element contains
The atomic number of the element is
And the mass number is
Hence the third element is
Chapter 3 Solutions
World of Chemistry
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward5. A solution of sucrose is fermented in a vessel until the evolution of CO2 ceases. Then, the product solution is analyzed and found to contain, 45% ethanol; 5% acetic acid; and 15% glycerin by weight. If the original charge is 500 kg, evaluate; e. The ratio of sucrose to water in the original charge (wt/wt). f. Moles of CO2 evolved. g. Maximum possible amount of ethanol that could be formed. h. Conversion efficiency. i. Per cent excess of excess reactant. Reactions: Inversion reaction: C12H22O11 + H2O →2C6H12O6 Fermentation reaction: C6H12O6 →→2C2H5OH + 2CO2 Formation of acetic acid and glycerin: C6H12O6 + C2H5OH + H₂O→ CH3COOH + 2C3H8O3arrow_forward
- Show work. don't give Ai generated solution. How many carbons and hydrogens are in the structure?arrow_forward13. (11pts total) Consider the arrows pointing at three different carbon-carbon bonds in the molecule depicted below. Bond B 2°C. +2°C. cleavage Bond A •CH3 + 26.← Cleavage 2°C. + Bond C +3°C• CH3 2C Cleavage E 2°C. 26. weakest bond Intact molecule Strongest 3°C 20. Gund Largest argest a. (2pts) Which bond between A-C is weakest? Which is strongest? Place answers in appropriate boxes. C Weakest bond A Produces Most Bond Strongest Bond Strongest Gund produces least stable radicals Weakest Stable radical b. (4pts) Consider the relative stability of all cleavage products that form when bonds A, B, AND C are homolytically cleaved/broken. Hint: cleavage products of bonds A, B, and C are all carbon radicals. i. Which ONE cleavage product is the most stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. 13°C. formed in bound C cleavage ii. Which ONE cleavage product is the least stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. • CH3 methyl radical Formed in Gund A Cleavage c.…arrow_forwardBr. COOH Br, FCH COOH E FeBr ASOCI B NH (CH,CO),OD Br₂ 2 C alcKOHarrow_forward
- Find A to F (all)arrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardHi!! Please provide a solution that is handwritten. Ensure all figures, reaction mechanisms (with arrows and lone pairs please!!), and structures are clearly drawn to illustrate the synthesis of the product as per the standards of a third year organic chemistry course. ****the solution must include all steps, mechanisms, and intermediate structures as required. Please hand-draw the mechanisms and structures to support your explanation. Don’t give me AI-generated diagrams or text-based explanations, no wordy explanations on how to draw the structures I need help with the exact mechanism hand drawn by you!!! I am reposting this—ensure all parts of the question are straightforward and clear or please let another expert handle it thanks!!arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





