
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305632134
Author: J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 3.32P
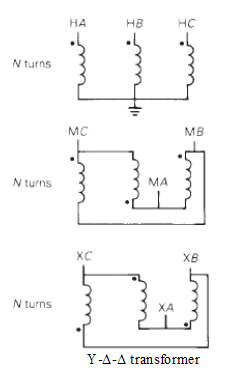
Determine the positive- and negative-sequence phase shifts for the three- phase transformers shown in Figure 3.36.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
64) answer just two from three the following terms:
A) Design ADC using the successive method if the Vmax=(3) volt, Vmin=(-2) volt, demonstrate the
designing system for vin-1.2 volt.
Successive Approximation ADC
Input Voltage-1.1 V
-4-3.5-3 -2.5 -2 -1.5 +1 -0.5
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
3.5
1
T
-8 -7 -6 -5
-3
+2 -1
0 1 2
3
4
5 6
7
X=1???
1st guess: -0.25 V
(too high)
X=11??
2nd guess: -2.25 V
(too low)
3rd guess: -1.25 V
(too low)
X=1110
X=111?
4th guess: -0.75 V
(too high)
Make successive guesses and
use a comparator to tell
whether your guess is too high
or too low.
Each guess determines one bit
of the answer and cuts the
number of remaining
possibilities in half.
Datacommunıcatıonin a commuinaction ASYNCHRONOUS TRANSMİTİON is used in this transmistion 7-bit chatacter will be transfered even parity will be used ,stop element is as 1,5 bits a)=select a chracter yourself and dısplay the signal transfered in this transmission , and calculate the overhead in this transmision
(i)
Find the inverse z-transform of the system H(z) =
for the following regions of
convergence. Write in the final answer for each case in the allocated rectangular box
below
(a) |z| 3
(c) 1
Chapter 3 Solutions
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 3 - The Ohms law for the magnetic circuit states that...Ch. 3 - For an ideal transformer, the efficiency is (a) 0...Ch. 3 - For an ideal 2-winding transformer, the...Ch. 3 - An ideal transformer has no real or reactive power...Ch. 3 - For an ideal 2-winding transformer, an impedance...Ch. 3 - Consider Figure 3.4. For an ideal phase-shifting...Ch. 3 - Consider Figure 3.5. Match the following, those on...Ch. 3 - The units of admittance, conductance, and...Ch. 3 - Match the following: (i) Hysteresis loss (a) Can...Ch. 3 - For large power transformers rated more than 500...
Ch. 3 - For a short-circuit test on a 2-winding...Ch. 3 - The per-unit quantity is always dimensionless. (a)...Ch. 3 - Consider the adopted per-unit system for the...Ch. 3 - The ideal transformer windings are eliminated from...Ch. 3 - To convert a per-unit impedance from old to new...Ch. 3 - In developing per-unit circuits of systems such as...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.17MCQCh. 3 - Prob. 3.18MCQCh. 3 - With the American Standard notation, in either a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.20MCQCh. 3 - In order to avoid difficulties with third-harmonic...Ch. 3 - Does an open connection permit balanced...Ch. 3 - Does an open- operation, the kVA rating compared...Ch. 3 - It is stated that (i) balanced three-phase...Ch. 3 - In developing per-unit equivalent circuits for...Ch. 3 - In per-unit equivalent circuits of practical...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.27MCQCh. 3 - Prob. 3.28MCQCh. 3 - For developing per-unit equivalent circuits of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.30MCQCh. 3 - Prob. 3.31MCQCh. 3 - Prob. 3.32MCQCh. 3 - The direct electrical connection of the windings...Ch. 3 - Consider Figure 3.25 of the text for a transformer...Ch. 3 - (a) An ideal single-phase two-winding transformer...Ch. 3 - An ideal transformer with N1=1000andN2=250 is...Ch. 3 - Consider an ideal transformer with...Ch. 3 - A single-phase 100-kVA,2400/240-volt,60-Hz...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.5PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.6PCh. 3 - Consider a source of voltage v(t)=102sin(2t)V,...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.8PCh. 3 - Prob. 3.9PCh. 3 - A single-phase step-down transformer is rated...Ch. 3 - For the transformer in Problem 3.10. The...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.12PCh. 3 - A single-phase 50-kVA,2400/240-volt,60-Hz...Ch. 3 - A single-phase 50-kVA,2400/240-volt,60-Hz...Ch. 3 - Rework Problem 3.14 if the transformer is...Ch. 3 - A single-phase, 50-kVA,2400/240-V,60-Hz...Ch. 3 - The transformer of Problem 3.16 is supplying a...Ch. 3 - Using the transformer ratings as base quantities,...Ch. 3 - Using the transformer ratings as base quantities....Ch. 3 - Using base values of 20 kVA and 115 volts in zone...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.21PCh. 3 - A balanced Y-connected voltage source with...Ch. 3 - Figure 3.32 shows the oneline diagram of a...Ch. 3 - For Problem 3.18, the motor operates at full load,...Ch. 3 - Consider a single-phase electric system shown in...Ch. 3 - A bank of three single-phase transformers, each...Ch. 3 - A three-phase transformer is rated...Ch. 3 - For the system shown in Figure 3.34. draw an...Ch. 3 - Consider three ideal single-phase transformers...Ch. 3 - Reconsider Problem 3.29. If Va,VbandVc are a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.31PCh. 3 - Determine the positive- and negative-sequence...Ch. 3 - Consider the three single-phase two-winding...Ch. 3 - Three single-phase, two-winding transformers, each...Ch. 3 - Consider a bank of this single-phase two-winding...Ch. 3 - Three single-phase two-winding transformers, each...Ch. 3 - Three single-phase two-winding transformers, each...Ch. 3 - Consider a three-phase generator rated...Ch. 3 - The leakage reactance of a three-phase,...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.40PCh. 3 - Consider the single-line diagram of the power...Ch. 3 - For the power system in Problem 3.41, the...Ch. 3 - Three single-phase transformers, each rated...Ch. 3 - A 130-MVA,13.2-kV three-phase generator, which has...Ch. 3 - Figure 3.39 shows a oneline diagram of a system in...Ch. 3 - The motors M1andM2 of Problem 3.45 have inputs of...Ch. 3 - Consider the oneline diagram shown in Figure 3.40....Ch. 3 - With the same transformer banks as in Problem...Ch. 3 - Consider the single-Line diagram of a power system...Ch. 3 - A single-phase three-winding transformer has the...Ch. 3 - The ratings of a three-phase three-winding...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.52PCh. 3 - The ratings of a three-phase, three-winding...Ch. 3 - An infinite bus, which is a constant voltage...Ch. 3 - A single-phase l0-kVA,2300/230-volt,60-Hz...Ch. 3 - Three single-phase two-winding transformers, each...Ch. 3 - A two-winding single-phase transformer rated...Ch. 3 - A single-phase two-winding transformer rated...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3.59PCh. 3 - PowerWorid Simulator case Problem 3_60 duplicates...Ch. 3 - Rework Example 3.12 for a+10 tap, providing a 10...Ch. 3 - A 23/230-kV step-up transformer feeds a...Ch. 3 - The per-unit equivalent circuit of two...Ch. 3 - Reconsider Problem 3.64 with the change that now...Ch. 3 - What are the advantages of correctly specifying a...Ch. 3 - Why is it important to reduce the moisture within...Ch. 3 - What should be the focus of transformer preventive...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q3: Material A and Material B are collected in a tank as shown where the system consists of three Push-Button, three Level Sensors, two Inlet valve, one Outlet valve, Heater, Temperature Sensor, Agitator Motor, and Alarm Light. Material A and Material B are to be mixed and heated until it reaches 90°C temperature, and it will be drain using outlet valve also high-level Alarm Light will come ON when the tank is full and stay on even if the tank level drops until the operator press Reset Push-Button. Implement automation of this system in PLC using Ladder Diagram programming language (Note: The tank is fed with Material A before B and the temperature sensor can withstand 200°C and it gives voltage from 0 to 10 volts) (25 Marks) Valve A Agitator Motor Valve B Level B Heater E Level A Low Level Sta Start Push-Button Stop Push-Button 36. ویر نکند Temperature sensor Outlet Valve Reset Push-Button Alarm Lightarrow_forward.Explain how a gated J-K latch operates differently from an edge-triggered J-K flip-flop. . For the gated T Latch circuit, answer the following: a) Draw the gate-level diagram of a gated T latch using basic logic gates and SR latch b) Write the characteristic equation. c) Draw the state diagram.arrow_forwardA Digital Filter is described by the following. difference equation: Y(n)=0.5x(n) 0.5(n-2) - Find the transfer function ..arrow_forward
- Q4) answer just two from three the following terms: A) Design ADC using the successive method if the Vmax=(3) volt, Vmin=(-2) volt, demonstrate the designing system for vin-1.2 volt.arrow_forward(a) For a voltage phasor V(jω) and a current phasor I(jω), give an expression for the complex power.(b)Give three examples of how real (average) power might be dissipated.(c)A time-domain voltage is defined by the expression v(t)= 5 cos(πt/3) V. When this is applied across an impedance Z = 4∠60° Ω, determine:(i)The instantaneous power.(ii)The average power.arrow_forwardConsider the LTI system with the input x(t) = e^28(t) and the impulse response h(t) = e−²tu(t). a) Determine the Laplace transform of x(t) and h(t). (10 marks) b) Using convolutional property, determine the Laplace transform and the ROC for the output response y(t).arrow_forward
- (A) Consider a communication system where the number of successful transsions out of 10 trials follows a binomial distribution. The success probability for each triat is 0,95, Let X be the random variable representing the number of successful transmissions. -Sketch the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the distribution. 2- Find Skewness coefficients and check if the distribution is symmetrical or skewed to the right or left. 3- Find kurtosis coefficients, Check if the distribution is mesokurtic, leptokurtic or platykurtic. 4- Find the probability of getting at most eigh. successful transmissions. 5- Find the probability P(20 with a mean 2-1 calculate the probability that the noise is greater than 3 units.arrow_forwardQ4: (A) Find the mean of a random variable X if S f(x)= 2x 0 2 for 0arrow_forward(A) Suopces the current measurements in a strip of wire are normally distributed with ca-10(mA) and a varieocom (mA)² 1- What is the probability that a current measurement lies between 7.4 and 11.6 mA? 2-Drew the probability density function of the current distribution. (8) A factory produces light bulbs with a koown probability of P(D)-0.08 that & bulo is dalective. If a bulb is defective, the probability that the quality control test detects it is defective is P(TID)-0.90. Conversely, if a bulb is not defective, the probability that the test Telesly indicaton k as defective is P(TID)-0.05. calculate the probability that a light b is notually defective given that the test result is positive, F(DIT).arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781305632134
Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:Cengage Learning
TRANSFORMERS - What They Are, How They Work, How Electricians Size Them; Author: Electrician U;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tXPy4OE7ApE;License: Standard Youtube License